What Is The Difference Between Active And Passive Solar Energy?
Are you curious about the difference between active and passive solar energy? Well, you’ve come to the right place! In this article, we’ll explore these two fascinating concepts and shed light on their distinctions. So, let’s dive in and discover what sets them apart.
When it comes to harnessing the power of the sun, active and passive solar energy are two different approaches. Active solar energy involves the use of mechanical systems, like solar panels, to capture and convert sunlight into usable energy. On the other hand, passive solar energy relies on design elements, such as windows and building orientation, to naturally heat and illuminate spaces.
So, why is this important? Understanding the difference between active and passive solar energy can help us make informed decisions about how we can best utilize renewable energy sources to reduce our carbon footprint and create a more sustainable future.
Now that we have a basic understanding, let’s delve deeper into the specifics of active and passive solar energy. Get ready to explore the fascinating world of harnessing the sun’s energy in innovative and environmentally-friendly ways!
And remember, energy is all around us, even in the rays of the sun. So, let’s start exploring the wonders of active and passive solar energy together!
The Difference Between Active and Passive Solar Energy: Harnessing the Power of the Sun
Solar energy is a renewable and abundant source of power that can be harnessed in various ways. Two popular methods of utilizing solar energy are through active and passive solar systems. While both aim to harness the power of the sun, there are distinct differences in how they operate, the technology involved, and their applications. In this article, we will explore the dissimilarities between active and passive solar energy systems, and gain a deeper understanding of their benefits and limitations.
The Basics of Active Solar Energy
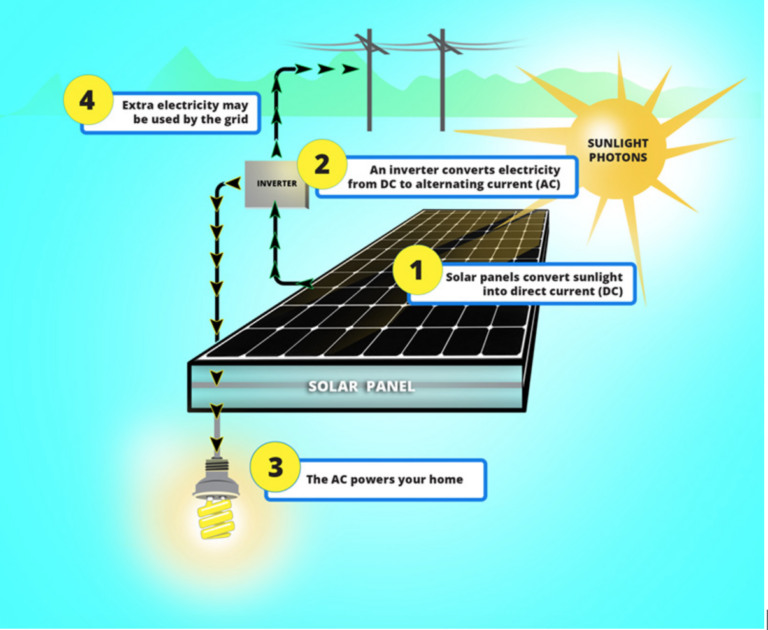
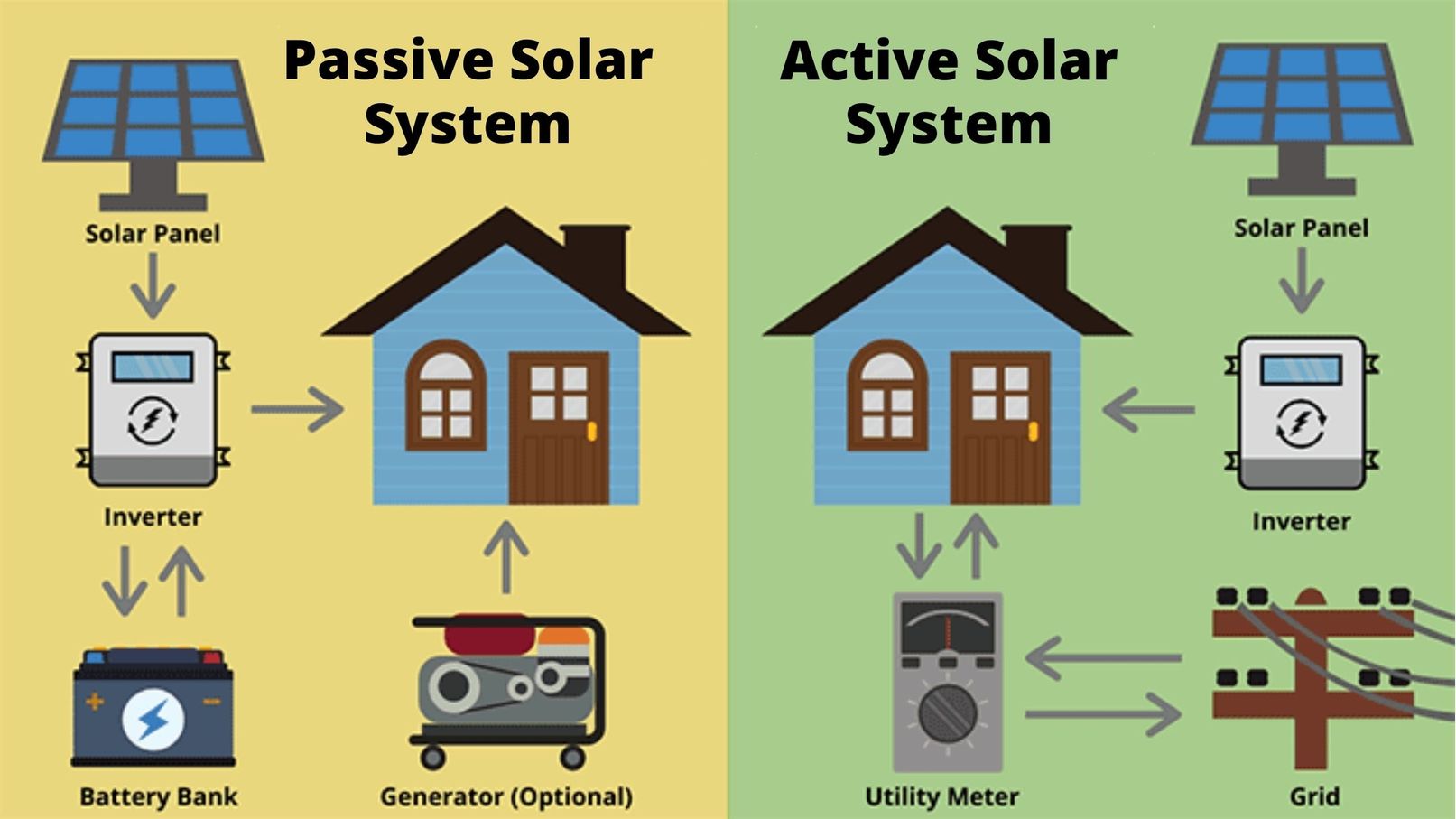
Active solar energy systems use mechanical and electrical components to capture, store, and distribute solar energy. These systems rely on external energy sources, such as solar panels, to convert sunlight into usable energy. The most common application of active solar energy is the generation of electricity through photovoltaic (PV) panels.
One of the key characteristics of active solar energy is its ability to actively track and adjust to the sun’s position to maximize energy collection. This is achieved through the use of solar trackers and automated systems that optimize the angle and orientation of the solar panels. The collected solar energy can be used to power homes, businesses, and even entire cities, reducing reliance on traditional energy sources and lowering carbon emissions.
Active solar energy systems also often employ energy storage solutions, such as batteries, to store surplus energy for use during periods of low sunlight or high demand. This allows for a consistent and sustainable energy supply even when solar irradiance fluctuates. By utilizing active solar energy systems, users can take control of their energy production and reduce their carbon footprint, leading to a greener and more sustainable future.
The Fundamentals of Passive Solar Energy
Passive solar energy, on the other hand, does not rely on mechanical or electrical components to capture and distribute solar energy. Instead, it utilizes the design and structure of buildings to naturally harness and regulate the sun’s energy for heating, cooling, and lighting purposes. Passive solar systems incorporate architectural elements, such as building orientation, insulation, and thermal mass, to passively collect and distribute solar energy.
Passive solar energy systems aim to maximize solar gain during the colder months and minimize it during the warmer months. This is achieved by strategically positioning windows, utilizing thermal mass materials, and implementing shading devices. The absorbed solar energy is then stored in the building materials, such as stone or concrete, and released slowly to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
Passive solar energy systems can significantly reduce energy consumption and reliance on mechanical heating and cooling systems. They provide a more sustainable approach to building design and can result in substantial energy savings over the long term. Passive solar techniques are particularly effective in regions with ample sunlight and a moderate climate, where the building’s design can efficiently take advantage of natural heating and cooling effects.
Comparing Active and Passive Solar Energy
Now that we have an understanding of how active and passive solar energy systems differ in their operation, let’s delve deeper into the individual advantages and disadvantages of each approach.
Active Solar Energy:
Active solar energy offers the following benefits:
1. Versatility: Active solar systems can generate electricity and provide power for various applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
2. Efficiency: Active solar systems often feature advanced technology, such as solar trackers, that optimize the collection of solar energy, resulting in higher efficiency and energy production.
3. Reliability: With energy storage solutions, active solar systems can provide a consistent and reliable energy supply, even during prolonged periods of low sunlight or high demand.
Despite these advantages, active solar energy systems also have some limitations:
1. Cost: The initial investment in active solar systems can be relatively high due to the purchase and installation of solar panels, trackers, and energy storage solutions.
2. Maintenance: Active systems require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This includes inspections, cleaning of solar panels, and monitoring of battery health.
3. Complexity: Active systems involve more complex technology and wiring, which may require professional installation and troubleshooting.
Passive Solar Energy:
Passive solar energy systems offer the following benefits:
1. Cost-Effectiveness: Passive systems generally have lower upfront costs compared to active systems, as they rely on building design principles rather than expensive equipment.
2. Low Maintenance: Passive systems have fewer moving parts and electrical components, resulting in lower maintenance requirements and costs.
3. Sustainability: By utilizing natural energy sources and reducing reliance on mechanical heating and cooling, passive solar systems contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to building design.
However, passive solar energy systems also have limitations:
1. Design Constraints: Passive systems heavily rely on the building’s design and orientation, which may limit their applicability in retrofitting existing structures or in certain geographical locations.
2. Temperature Control: While passive systems excel at maintaining indoor temperatures in moderate climates, they may struggle to provide adequate heating or cooling in extreme weather conditions.
3. Lack of Control: Passive systems are dependent on the availability of sunlight and may not offer the same level of control and customization as active systems.
In conclusion, active and passive solar energy systems offer distinct approaches to harnessing the power of the sun. Active systems utilize mechanical and electrical components to actively capture and distribute solar energy, while passive systems employ building design principles to naturally regulate indoor temperature and lighting. Each approach has its own advantages and limitations, and the choice between them depends on factors such as energy needs, budget, and geographical location. By understanding the differences between active and passive solar energy, individuals and communities can make informed decisions on implementing sustainable energy solutions that align with their unique requirements and goals.
Key Takeaways: What is the Difference Between Active and Passive Solar Energy?
- Active solar energy requires the use of mechanical devices, like solar panels, to collect and convert sunlight into usable energy.
- Passive solar energy relies on natural processes, such as the design of buildings and windows, to maximize sunlight absorption and heat retention.
- Active solar systems are more complex and require maintenance, while passive solar systems are simpler and have fewer components.
- Active solar energy is suitable for generating electricity, heating water, and powering appliances, while passive solar energy is ideal for heating buildings and providing natural daylight.
- Active solar systems can be more expensive to install and operate compared to passive solar systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
In today’s world, solar energy is becoming increasingly popular as a renewable energy source. When it comes to harnessing the power of the sun, there are two main approaches: active solar energy and passive solar energy. Understanding the difference between these two can help you make informed decisions about which method is best for your needs. Let’s explore some common questions regarding active and passive solar energy.
1. How do active and passive solar energy systems differ?
Active solar energy systems rely on mechanical devices, such as pumps and fans, to convert solar energy into usable power. These systems actively collect and distribute the sun’s energy to meet specific heating, cooling, or electrical needs. On the other hand, passive solar energy systems do not require mechanical devices. Instead, they rely on the design and construction of a building to capture and distribute solar energy naturally. Passive systems use techniques like building orientation, window placement, and materials with high thermal mass to passively heat, cool, and provide lighting within a space.
Simply put, active systems use technology to actively convert and distribute solar energy, while passive systems utilize design principles to naturally capture and utilize solar energy.
2. Which system is more cost-effective: active or passive solar energy?
The cost-effectiveness of active and passive solar energy systems depends on various factors, including the size of the system, location, and energy needs. Active solar energy systems often require more upfront investment due to the installation of mechanical components and technology. However, they can be more efficient in converting and utilizing solar energy, potentially resulting in long-term energy savings. Passive solar energy systems, on the other hand, generally require less upfront investment as they rely on the design and construction of the building itself. However, the energy savings may vary depending on the efficiency of the building design and other factors. It’s essential to consider your specific circumstances, energy requirements, and long-term financial goals when deciding which system is more cost-effective for you.
3. Can active and passive solar energy systems be used together?
Absolutely! In fact, combining active and passive solar energy systems can often result in the most efficient and effective use of solar energy. For example, you can have an active solar water heating system that uses mechanical components to circulate heated water throughout your home. At the same time, you can incorporate passive solar design principles, such as large south-facing windows and thermal mass materials, to naturally heat your living spaces. By using both approaches, you can optimize the benefits and energy efficiency of your solar energy system.
The integration of active and passive solar energy systems allows for a comprehensive and customized approach to harnessing the power of the sun.
4. Which system is more suitable for residential use: active or passive solar energy?
Both active and passive solar energy systems have their advantages and considerations when it comes to residential use. Active systems are commonly employed for specific needs such as heating water or generating electricity. If you’re looking to power your entire home or need precise control over temperature and energy distribution, an active system may be more suitable. On the other hand, passive solar systems can be an excellent choice for residential buildings seeking to reduce energy consumption and reliance on non-renewable resources. Passive systems can provide natural heating, cooling, and lighting while promoting energy efficiency and sustainability. The choice between active and passive solar energy systems for residential use depends on your energy goals, budget, and the design of your home.
5. Are there any limitations or challenges associated with active and passive solar energy systems?
Active solar energy systems may come with some limitations and challenges. The mechanical components of active systems can require maintenance and occasional replacement, adding to the system’s overall cost. Additionally, factors such as weather conditions and system inefficiencies can affect their performance. As for passive solar energy systems, they heavily rely on proper building design, orientation, and location. If these elements are not adequately considered during construction, the system’s effectiveness may be compromised. It’s crucial to consult with professionals and experts in solar energy systems to overcome potential limitations and ensure optimal performance.
When evaluating and implementing active or passive solar energy systems, it’s important to understand these limitations and address them effectively to maximize the benefits of solar energy.
Summary
Active and passive solar energy are two different ways to harness the power of the sun.
Active solar energy uses technology like solar panels and pumps to collect and distribute the sun’s energy. Passive solar energy, on the other hand, relies on building design and materials to naturally heat and cool a space using the sun’s energy.
Active solar energy is more expensive to install and maintain, but it can generate electricity and heat water. Passive solar energy is cheaper and relies on design features like large windows and thermal mass to maximize the sun’s energy.
In conclusion, active solar energy requires technology, and passive solar energy relies on smart building design. Both have advantages and can be used to create a more sustainable future.