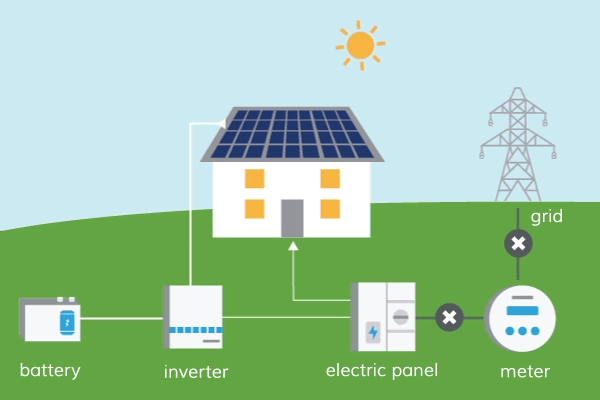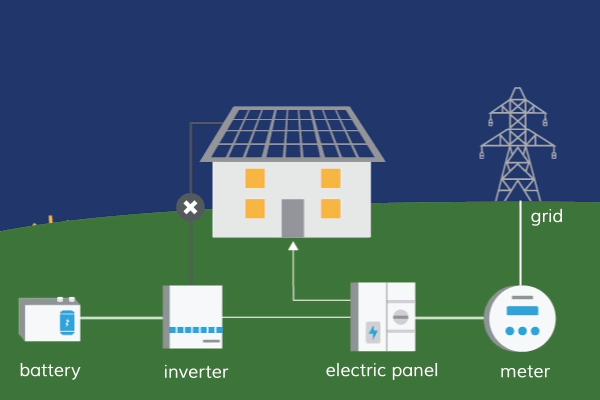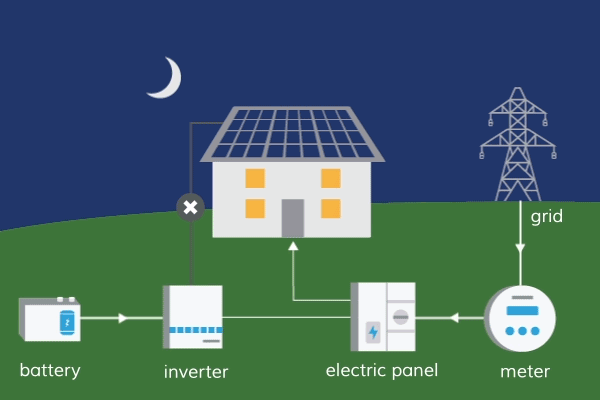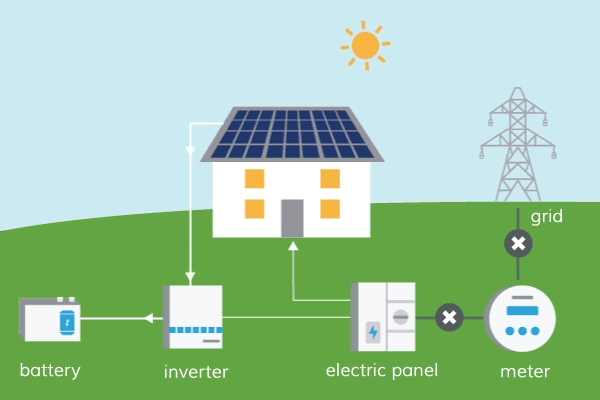
How Does Solar Energy Travel To Earth?
Welcome! Have you ever wondered how solar energy makes its way to Earth? It’s a fascinating journey that involves the sun’s incredible power and the wonders of our planet’s atmosphere. So, let’s dive in and explore the captivating process of how solar energy travels to Earth!
First, let’s consider the sun, the ultimate source of solar energy. The sun is like a massive ball of fiery gas, constantly radiating light and heat in all directions. But how does this energy reach us all the way from the sun, which is approximately 93 million miles away? Well, that’s where our atmosphere comes into play!
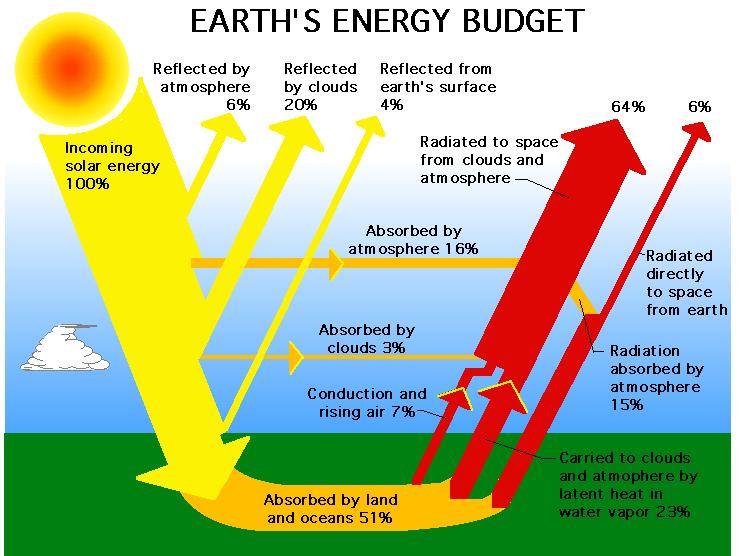
As solar energy propels through space, it encounters Earth’s atmosphere. This invisible blanket of gases extends about 600 kilometers above our planet’s surface. The atmosphere acts as a protective shield, filtering out harmful radiation and allowing beneficial solar energy to pass through. Isn’t it amazing how our atmosphere is like a giant gatekeeper, controlling what kind of energy reaches us? So, let’s continue our journey to discover how solar energy makes its way through the atmosphere down to Earth.
Now that we know the atmosphere lets solar energy through, let’s talk about how it actually travels to our planet’s surface. Solar energy, in the form of sunlight, consists of tiny particles called photons. As these photons reach Earth, they begin their descent into the atmosphere. Some photons bounce off molecules in the atmosphere and scatter in different directions, which is why we see the sky as blue during the day. But the majority of photons continue their downward path, penetrating the atmosphere to reach the ground. As they reach the Earth’s surface, they transfer their energy, bringing us warmth, light, and all the benefits of solar power. Incredible, isn’t it?
So, there you have it! The remarkable journey of solar energy as it travels from the sun to Earth. From the sun’s immense power to our atmosphere’s essential role, it’s truly a mesmerizing process. Now that we’ve scratched the surface, let’s dive deeper into the wonderful world of solar energy and explore its vast benefits and applications. Stay tuned for more exciting discoveries!
1. The sun produces energy through nuclear fusion.
2. This energy is released as electromagnetic radiation, which includes heat and light.
3. The radiation travels through space and reaches Earth.
4. As it enters Earth’s atmosphere, some of the radiation is absorbed or scattered by molecules and particles.
5. The remaining radiation reaches the Earth’s surface, where it is converted into heat and other forms of energy.
Understanding how solar energy travels to Earth helps us harness its potential for renewable power generation.
The Journey of Solar Energy: How Does It Travel to Earth?
Solar energy is an incredible resource that powers our planet and fuels all forms of life. But have you ever wondered how this energy from the sun reaches us? In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating journey of solar energy, from its creation in the core of the sun to its arrival on Earth. Join us as we uncover the secrets of this powerful and renewable energy source.
1. The Sun: A Stellar Powerhouse
Just as Superman draws strength from our yellow sun, so does our planet. The sun, our nearest star, is a massive ball of gas composed mostly of hydrogen and helium. At its core, temperatures soar to mind-boggling levels, reaching around 15 million degrees Celsius. Here, nuclear fusion occurs, converting hydrogen atoms into helium and releasing an enormous amount of energy in the process.
This energy takes the form of electromagnetic radiation, which includes both visible and non-visible light. The visible light is the portion that we perceive as sunlight. From its birth in the sun’s core, this energy begins its journey towards Earth.
The Radiative Zone: A Chaotic Dance
After being generated in the core, solar energy must traverse a chaotic and densely packed region known as the radiative zone. This layer extends from the core to about 70% of the sun’s radius. The energy in this region is continually absorbed and re-emitted by the atoms in the gas. It takes an average of 170,000 years for a photon of light to make its way through this maelstrom of bouncing particles.
Despite the slow progress, the energy is gradually working its way out of the sun. It forms a dance of sorts, with photons being absorbed by atoms and then released, only to be absorbed once again. This cascading process eventually brings the energy to the outermost layer of the sun, known as the convective zone.
The Convective Zone: Rising and Falling Energy
As the name suggests, the convective zone is a region of tumultuous movement. Here, solar energy takes the form of heat and begins to rise towards the surface of the sun. The heat creates a convection current, where hot material rises and cooler material falls. These rising and falling movements churn the energy, creating a colossal boiling pot of glowing gas.
As the energy reaches the surface, it takes the form of sunlight. The surface of the sun, known as the photosphere, is what we see when we look at the sun. It appears as a bright disc with dark patches called sunspots. The energy that has successfully overcome the challenges of the solar interior now embarks on its journey through the vastness of space.
2. Traveling Through Space: The Speed of Light
Once solar energy escapes the sun’s gravitational pull, it embarks on an incredible voyage through the vacuum of space. The journey from the sun to Earth covers a distance of about 149.6 million kilometers. But how long does it take for sunlight to reach us?
The answer lies in the speed of light. Light, including the sunlight we see, travels at an astonishing speed of approximately 299,792 kilometers per second. With this unimaginable velocity, it takes sunlight just over 8 minutes and 20 seconds to travel from the sun to Earth.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: More than Meets the Eye
Sunlight consists of a wide range of electromagnetic waves, not just the visible light that our eyes can perceive. This spectrum includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays. Each of these types of radiation has its own wavelength and energy level.
As solar energy travels through space, it carries this entire spectrum of electromagnetic waves. However, it is the visible light portion that plays a crucial role in sustaining life on Earth. It is this light that warms our planet, drives photosynthesis in plants, and allows us to see the world around us.
The Earth’s Atmosphere: Protector and Filter
As solar energy nears Earth, it encounters one final obstacle – our planet’s atmosphere. The atmosphere acts as a protective shield, absorbing harmful ultraviolet radiation and filtering out some of the other types of radiation. This essential filtering process ensures that the energy reaching the Earth’s surface is at the right intensity for life to flourish.
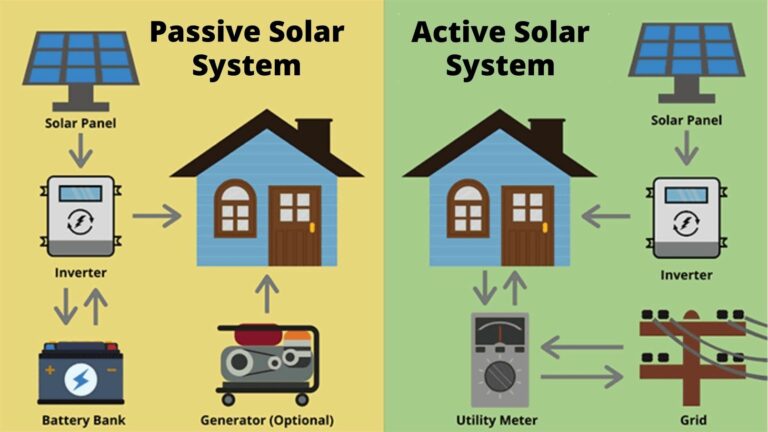
Once the sunlight reaches the surface, it can be harnessed through various technologies to generate electricity or heat for a multitude of purposes. Solar panels capture the photons of light and convert them into electrical energy, while solar thermal systems absorb the sun’s heat to create warm water or even generate electricity.
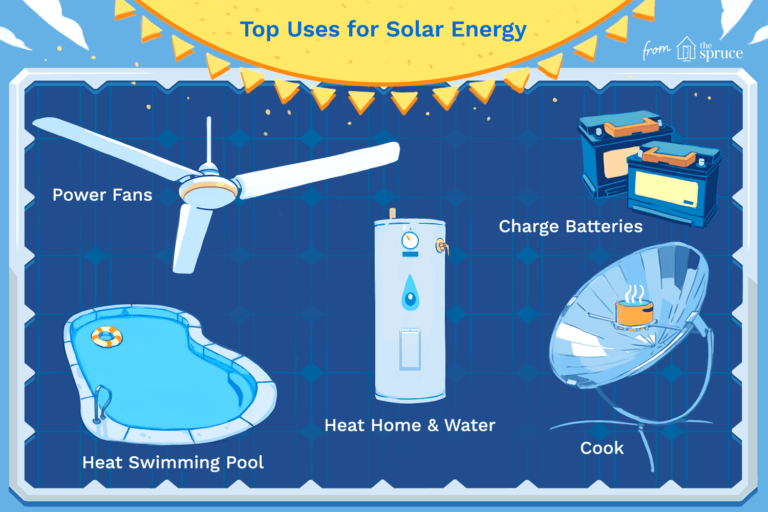
3. The Power of Solar: Benefits and Applications
Now that we understand how solar energy travels to Earth, let’s explore some of the benefits and applications of harnessing this clean and abundant source of power.
Benefits of Solar Energy
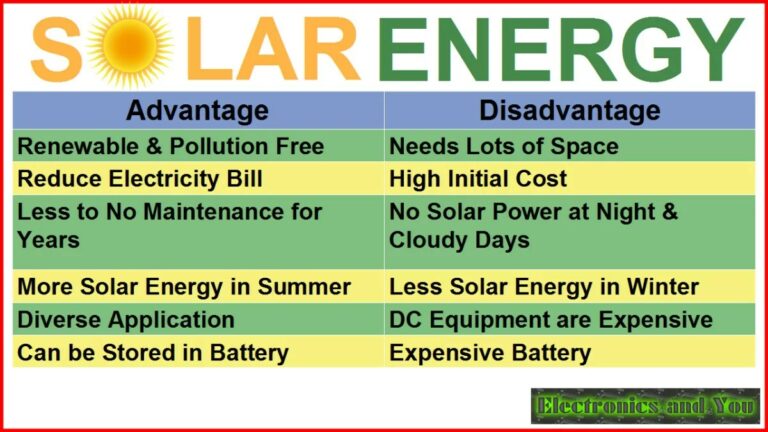
– Renewable and Sustainable: The sun is expected to continue shining for billions of years, ensuring an uninterrupted supply of solar energy.
– Environmentally Friendly: Solar energy produces no harmful emissions, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
– Energy Independence: By harnessing the power of the sun, countries and individuals can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and foreign energy sources.
– Cost Savings: Once the initial investment is made, solar energy can provide free electricity for years, resulting in significant savings on energy bills.
– Job Creation: The solar industry is growing rapidly, creating numerous job opportunities and driving economic growth.
Applications of Solar Energy
– Solar Power Plants: These large-scale installations harness solar energy to generate electricity for communities, cities, or even entire countries.
– Residential Solar Panels: Many homes now have solar panels installed on their rooftops, allowing homeowners to generate their own electricity and reduce their energy bills.
– Solar Water Heating: Solar thermal systems can heat water for domestic or commercial use, reducing the need for traditional water heaters and saving energy.
– Solar-powered Vehicles: Electric vehicles powered by solar energy are becoming increasingly popular, offering a sustainable and renewable mode of transportation.
4. Exploring Solar: Tips for a Brighter Future
As solar energy continues to gain popularity, here are a few tips to embrace this renewable resource and create a brighter future for generations to come.
1. Embrace Solar Technology
Consider installing solar panels on your home or business to generate clean and renewable electricity. Explore the various government incentives and financing options available to make the transition more affordable.
2. Educate Yourself
Learn more about solar energy and its benefits. Stay informed about new technological advancements and policies that promote the expansion of solar power.
3. Conserve Energy
By reducing your overall energy consumption, you can maximize the impact of solar energy on your household. Implement energy-efficient practices such as using LED light bulbs, properly insulating your home, and investing in energy-saving appliances.
In conclusion, the journey of solar energy is a remarkable tale of creation, perseverance, and sustainability. From the core of the sun to the surface of Earth, solar energy travels through space as light, providing us with warmth, illumination, and the power to transform our world. By embracing solar energy and its infinite possibilities, we can build a brighter and greener future for ourselves and future generations. So let’s harness the power of the sun and make every ray count.
Key Takeaways: How Does Solar Energy Travel to Earth?
- Solar energy travels to Earth in the form of sunlight.
- When the sun shines, it releases energy in the form of electromagnetic waves known as photons.
- These photons travel through space and reach Earth in about 8 minutes.
- Once the photons reach Earth, they are absorbed by various objects, such as plants, buildings, and our skin.
- When solar energy is absorbed, it is converted into heat or other forms of energy that we can use.
Frequently Asked Questions
Solar energy is a fascinating topic, and understanding how it travels from the sun to Earth is essential. Read on to explore some common questions related to this process.
What is solar energy?
Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the sun that is harnessed and converted into usable energy. This energy is abundant and renewable, making it a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. It provides a clean source of power without harmful greenhouse gas emissions.
Through a process called nuclear fusion, the sun’s core releases vast amounts of energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation. This radiation, composed of photons, travels through space and reaches the Earth as solar energy.
How does solar energy travel to Earth?
Solar energy travels to Earth in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Specifically, it travels through space in the form of photons, which are tiny particles of light. These photons travel at a speed of about 186,000 miles per second from the Sun’s core to its surface.
Once the photons reach the Sun’s surface, they begin a journey across space toward Earth. This travel takes approximately 8 minutes and 20 seconds, covering a distance of about 93 million miles. This incredible speed allows solar energy to reach our planet and provide us with the light and heat we need.
Can solar energy be blocked or absorbed?
While solar energy can travel through space, it can be blocked or absorbed by certain materials or atmospheric conditions. One example is the Earth’s atmosphere, which filters out some of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation. This filtering process helps protect life on Earth from excessive UV exposure.
On Earth’s surface, various objects and materials can also absorb or reflect solar energy. For example, buildings with dark roofs can absorb a significant amount of solar energy as heat. Solar panels, on the other hand, are designed to absorb photons and convert them into electricity. These panels utilize materials like silicon to harness solar energy efficiently.
How does solar energy power our planet?
Solar energy plays a vital role in powering our planet. Through a process called photovoltaic conversion, solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. The semiconducting materials within the solar panels, usually made of silicon, absorb photons and release electrons.
When these freed electrons flow through an electrical circuit, they generate an electric current that can power various devices and systems. This clean and renewable energy source is used to operate homes, businesses, and even entire cities. When excess solar power is generated, it can be stored in batteries for later use, making solar energy a truly versatile and sustainable solution.
What are the benefits of solar energy?
Solar energy offers numerous benefits for individuals and the environment. Firstly, it is a renewable and sustainable energy source, meaning it will never run out. Additionally, solar energy produces no harmful greenhouse gas emissions, unlike the burning of fossil fuels.
By harnessing solar power, individuals can reduce their energy costs and rely less on traditional electricity grids. Solar energy also helps create jobs in the renewable energy sector while reducing dependence on imported energy sources. Furthermore, using solar energy can contribute to a cleaner and healthier environment, helping mitigate climate change and air pollution.
Summary
Solar energy travels to Earth in the form of sunlight, which is a type of electromagnetic radiation. This radiation is generated by nuclear reactions happening in the sun’s core. The energy from the sun travels through the vacuum of space as electromagnetic waves, specifically in the form of photons. These photons then reach the Earth’s atmosphere and continue their journey towards the surface.
Once the sunlight reaches the Earth’s atmosphere, it encounters various particles and molecules. Some of these particles absorb or scatter the light, causing changes in its direction and intensity. However, the majority of the sunlight penetrates through the atmosphere and reaches the surface. This is how solar energy ultimately arrives on Earth and can be harnessed for various purposes such as electricity generation or heating water.