How Does Global Warming Affect Solar Energy In The Atmosphere?
In today’s world, there are two major concerns on everyone’s mind: global warming and renewable energy. But have you ever wondered how these two topics intersect? Well, get ready to dive into the fascinating world of how global warming affects solar energy in the atmosphere!
But wait, what exactly is global warming? Simply put, global warming refers to the gradual increase in Earth’s temperature due to the accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Now, you may be wondering how this phenomenon impacts solar energy, which is all about harnessing the power of the sun. Hold on tight, because we’re about to find out!
When it comes to solar energy, the sun is our greatest asset. By converting sunlight into electricity, solar panels play a crucial role in reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and combatting climate change. However, with global warming on the rise, there are potential consequences for solar energy production. So, let’s explore how this environmental issue affects the very energy source we rely on.
How Does Global Warming Affect Solar Energy in the Atmosphere?
Global warming is a pressing issue that is impacting our planet in various ways. One area that is greatly affected by global warming is solar energy and its utilization in the Earth’s atmosphere. As temperatures rise and climate patterns shift, the efficiency and overall effectiveness of solar energy systems can be influenced. In this article, we will explore the impact of global warming on solar energy in the atmosphere, discussing the challenges it presents and potential solutions to mitigate these effects.
The Effect of Rising Temperatures on Solar Panel Efficiency
Rising temperatures due to global warming can have both positive and negative effects on the efficiency of solar panels. On one hand, increased temperatures can lead to a decrease in resistance within the solar cells, enhancing the flow of electrons and improving overall energy production. However, the benefits of temperature-related improvements may be negated by the decrease in the efficiency of the solar panel’s semiconductors. Excessive heat can cause these materials to degrade, reducing their ability to convert sunlight into usable energy. Additionally, higher temperatures can lead to an increase in the rate of degradation of the panel’s components, shortening their lifespan and requiring more frequent maintenance or replacement.
To combat the negative effects of increased temperatures on solar panel efficiency, researchers and manufacturers are continuously working to develop and deploy advanced cooling techniques. These include incorporating cooling systems into the panels, such as heat sinks or fans, to dissipate excess heat. Additionally, utilizing materials with enhanced thermal properties, such as advanced encapsulation materials or novel designs, can help minimize the detrimental impact of rising temperatures. It is important for the solar energy industry to adapt to these challenges to ensure continued progress and uptake of this renewable energy source.
Changes in Weather Patterns and Solar Energy Generation
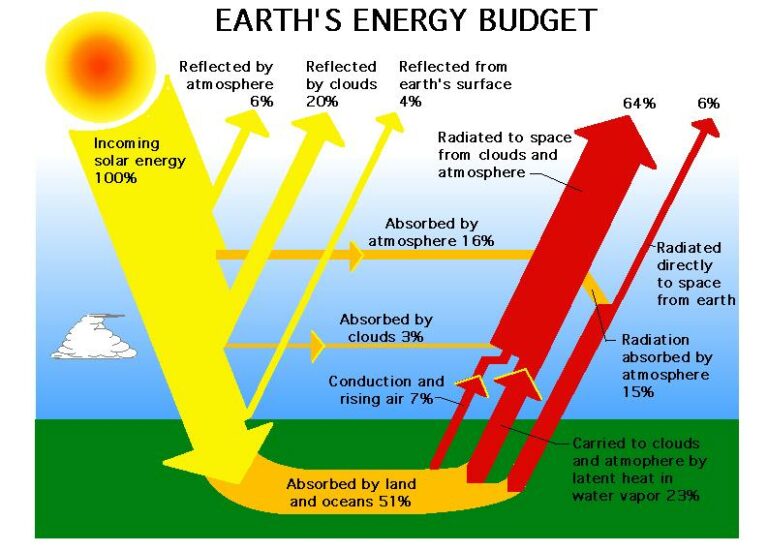
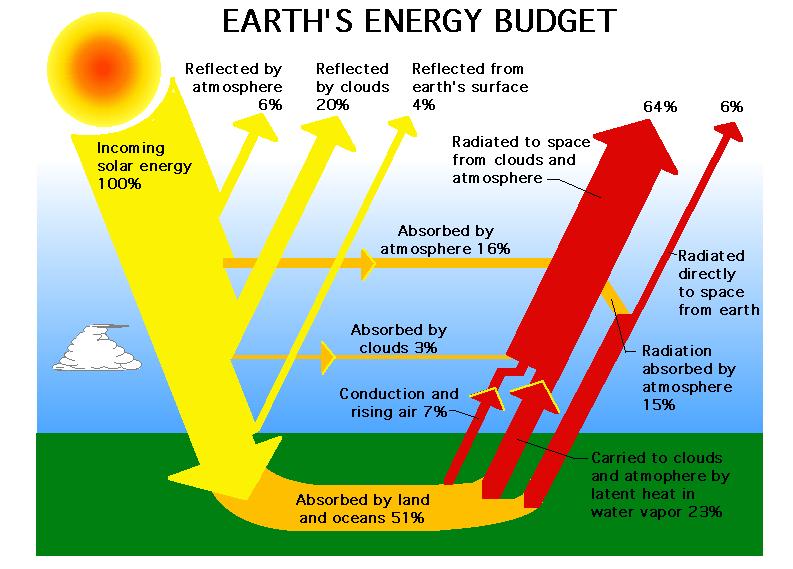
Global warming also leads to changes in weather patterns, which in turn can impact the generation of solar energy. Solar energy systems depend on sunlight, and any changes in cloud cover, precipitation, or atmospheric conditions can potentially reduce the amount of sunlight reaching the solar panels. For instance, an increase in cloud cover due to climate change can significantly reduce the amount of direct sunlight available for solar energy generation, impacting the overall output of solar power plants or individual rooftop installations.
To mitigate the effect of changing weather patterns on solar energy generation, researchers and engineers are exploring innovative solutions, such as the implementation of smart grid technologies and energy storage systems. These technologies allow for better integration of solar energy into the existing power grid, ensuring a stable supply of electricity even during periods of reduced solar irradiance. Additionally, advances in forecasting models can provide more accurate predictions of weather patterns, helping solar energy operators optimize their power generation strategies and minimize the impact of variations in sunlight availability.
Impact on Environmental Benefits and Future of Solar Energy
Solar energy is often hailed as a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, offering numerous environmental benefits such as reduced greenhouse gas emissions and improved air quality. However, global warming poses challenges to the continued growth and adoption of solar energy systems. The increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes or heatwaves, can damage or destroy solar infrastructure, disrupting electricity generation and impacting the reliability of solar power as a renewable energy source.
To ensure the future viability and resilience of solar energy in the face of global warming, it is crucial to implement effective mitigation and adaptation measures. This includes bolstering the resilience of solar infrastructure by designing systems that can withstand extreme weather events, investing in backup power storage, and diversifying the locations of solar installations to reduce the risk of widespread disruptions. Additionally, continued research and development efforts focused on improving the efficiency and durability of solar panels will play a vital role in making solar energy a more reliable and sustainable option in the face of changing climate conditions.
The Role of Government Policies in Shaping the Future of Solar Energy
Government policies and regulations play a significant role in shaping the growth and development of solar energy systems, particularly in the context of global warming. Here, we explore the various ways in which government policies can influence the future of solar energy and its ability to mitigate climate change.
Incentives and Subsidies for Solar Energy Adoption
To encourage the adoption of solar energy systems and reduce reliance on fossil fuels, governments around the world have implemented various incentives and subsidies. These measures can include tax credits, grants, and low-interest financing options for individuals and businesses looking to invest in solar installations. By making solar energy more economically feasible, these incentives help accelerate the transition to a clean energy future, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainability.
Net Metering and Feed-in Tariffs
Net metering and feed-in tariff programs are mechanisms that allow solar energy system owners to sell excess electricity back to the grid. Net metering enables consumers to offset their electricity bills by receiving credits for the surplus energy they generate, while feed-in tariffs provide a fixed payment rate for every kilowatt-hour of electricity generated. These policies incentivize solar energy system owners to maximize their energy production and contribute to the overall energy supply, promoting the growth of renewable energy generation and reducing the reliance on traditional power sources.
Renewable Portfolio Standards and Power Purchase Agreements
Renewable portfolio standards (RPS) are policies that require utilities to obtain a certain percentage of their electricity generation from renewable sources, including solar energy. RPS policies provide long-term stability and commitment to renewable energy investments, spurring the development of solar power plants and encouraging the transition to cleaner energy sources. Power purchase agreements (PPAs) are contractual arrangements between renewable energy producers and utilities or corporations, guaranteeing the sale of solar energy at predetermined rates. PPAs provide financial security for solar energy developers and increase the accessibility of solar power for consumers.
Research and Development Funding
Government funding for research and development (R&D) in the field of solar energy plays a critical role in driving technological advancements and improving the efficiency of solar panels. R&D initiatives focused on materials development, manufacturing processes, and storage technologies can contribute to reducing the cost of solar energy systems and increasing their overall efficiency. By investing in R&D, governments can support the growth of the solar energy industry, foster innovation, and accelerate the deployment of clean energy solutions.
Conclusion
Global warming presents significant challenges to the utilization of solar energy in the Earth’s atmosphere. Rising temperatures can impact the efficiency of solar panels, while changes in weather patterns can affect the generation of solar energy. However, through ongoing research, technological advancements, and the implementation of effective government policies, it is possible to mitigate the negative effects of global warming and ensure the continued growth and adoption of solar energy as a vital component of our clean energy future. By recognizing the importance of solar energy in combating climate change and investing in its development, we can pave the way for a sustainable and resilient future.
Key Takeaways: How Does Global Warming Affect Solar Energy in the Atmosphere?
- 1. Global warming increases greenhouse gas emissions, which trap more heat in the atmosphere.
- 2. The trapped heat leads to higher temperatures, causing more intense sunlight and increasing solar energy production.
- 3. However, global warming also causes changes in weather patterns, such as increased cloud cover, which can reduce the amount of solar energy reaching the Earth’s surface.
- 4. Rising sea levels due to global warming can pose a threat to solar energy infrastructure located in coastal areas.
- 5. Efforts to mitigate global warming, such as reducing carbon emissions, can help ensure a stable and reliable future for solar energy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Solar energy has become an increasingly popular source of renewable energy in recent years. However, global warming has the potential to impact its effectiveness. Here are some common questions about how global warming affects solar energy in the atmosphere:
1. How does global warming impact solar panel efficiency?
Global warming can lead to increased temperatures, which can negatively affect the efficiency of solar panels. Solar panels work best under cool and moderate temperatures. When exposed to high temperatures, the performance of solar panels can decline, resulting in a decrease in energy production. To combat this, solar panel manufacturers are developing new technologies that can handle higher temperatures and maintain efficiency.
Another way global warming affects solar panel efficiency is through changes in weather patterns. Increased extreme weather events like storms or hurricanes can damage solar panel installations, reducing their overall output. This highlights the need for proper maintenance and insurance coverage to protect solar energy systems from potential climate-related risks.
2. Does global warming affect the availability of sunlight for solar energy?
While global warming does not directly impact the availability of sunlight, it can indirectly affect solar energy production. Changes in climate patterns due to global warming, such as increased cloud cover or changes in precipitation, can result in less sunlight reaching the Earth’s surface. This decrease in sunlight can lead to a reduced solar energy potential in affected areas.
Additionally, global warming can contribute to air pollution, which can further diminish the amount of sunlight reaching solar panels. Airborne particles, such as soot or smog, can block sunlight and reduce solar energy generation. Adopting measures to mitigate climate change, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, can help preserve sunlight availability for solar energy generation.
3. Can global warming impact the lifespan of solar panels?
Global warming can potentially impact the lifespan of solar panels. Exposure to extreme weather conditions caused by global warming, such as intense heatwaves or severe storms, can result in physical damage to solar panels. Hailstorms, for example, can cause significant harm to the surface of solar panels, reducing their efficiency and longevity.
Furthermore, increased exposure to UV radiation due to thinning of the ozone layer can also degrade the materials used in solar panels over time. This can lead to a decrease in the overall lifespan of the panels. However, advancements in solar panel technology and improved durability can help mitigate these potential effects and prolong the lifespan of solar panels in the face of global warming.
4. Does global warming affect the cost of solar energy?
Global warming can indirectly impact the cost of solar energy. For instance, extreme weather events caused by global warming, such as hurricanes or storms, can lead to disruptions in the supply chain for solar energy components. This can result in increased costs for manufacturing and installing solar panels.
Additionally, the need to incorporate resilient design features to withstand the effects of global warming can add extra expenses to solar energy projects. These features may include measures to protect installations from extreme temperatures or modifying structures to withstand severe weather events. However, as the demand for renewable energy technologies continues to rise, advancements in manufacturing and economies of scale may help offset these potential cost increases in the long run.
5. How can solar energy help mitigate global warming?
Solar energy plays a crucial role in mitigating global warming by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Solar power plants produce electricity without generating carbon dioxide, one of the main contributors to global warming. By transitioning from fossil fuel-based electricity generation to solar energy, we can significantly decrease the emission of greenhouse gases, helping to slow down the rate of global warming.
Furthermore, solar energy is a renewable resource, meaning it can be harnessed continuously without depleting natural resources or contributing to environmental degradation. By relying more on solar energy and less on fossil fuels, we can reduce our carbon footprint, supporting the fight against climate change. The widespread adoption of solar energy systems at both residential and industrial levels can contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable future for our planet.
Causes and Effects of Climate Change | National Geographic
Summary
Global warming affects solar energy in the atmosphere in a few important ways. First, the increase in greenhouse gases caused by global warming traps more heat in the atmosphere, leading to higher temperatures. This means that solar panels may become less efficient because they work best in cooler temperatures. Second, global warming can cause changes in weather patterns, leading to less predictable and reliable sunlight for solar energy generation. Finally, the impact of global warming on ecosystems can also indirectly affect solar energy production, as changes in vegetation and animal habitats can disrupt the accessibility and availability of sunlight.
It is important to address global warming and its impact on solar energy because it can help us understand the challenges and opportunities we face in transitioning to renewable energy sources. By mitigating global warming and promoting sustainable energy solutions, we can ensure a brighter and cleaner future for ourselves and future generations. So let’s work together to combat climate change and harness the power of the sun for a greener planet.