Why Do Green Plants Require Solar Energy?
Why do green plants require solar energy? Well, let’s dive into the fascinating world of photosynthesis and uncover the secret behind this essential process. You see, green plants are like tiny solar panels, soaking up the sun’s radiant energy to survive and thrive. But why do they need this solar power in the first place? Let’s find out!
Picture this: green plants basking in the sun’s warm rays, converting sunlight into something magical called “food.” Just like we need food to fuel our bodies, plants need a special kind of food to grow and stay healthy. This unique food is called glucose, and solar energy is the key ingredient that plants use to produce it.
But why can’t plants just order glucose delivery like we order pizza? Well, that’s because plants are incredible, living organisms with their own plants-tastic superpowers! And one of their superpowers is the epic ability to make their own food through photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is like a power plant inside every green plant. It’s a process that converts sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen. The most important ingredient here is sunlight or solar energy. Without it, plants just wouldn’t have the energy they need to produce their own food and grow big and strong.
So, the next time you see a green plant soaking up the sun, remember that it’s not just enjoying a sunny day. It’s actually harnessing the power of solar energy for a gourmet meal of glucose. Now you know why green plants require solar energy—it’s the secret ingredient that keeps them healthy, vibrant, and full of life!
Why Do Green Plants Require Solar Energy?
Green plants, as we know, play a crucial role in our ecosystems. They serve as the primary producers, converting sunlight into energy through the process of photosynthesis. But have you ever wondered why green plants specifically rely on solar energy? In this article, we will explore the fascinating reasons behind this phenomenon and understand the importance of solar energy for the survival and growth of green plants.
1. Harnessing the Power of the Sun
Green plants are the ultimate solar-powered machines. Through the process of photosynthesis, they convert sunlight into chemical energy, which is stored in the form of carbohydrates such as glucose. This energy-rich molecule becomes the fuel for all cellular activities in the plant. The process of photosynthesis occurs in specialized structures called chloroplasts, which contain a pigment called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll absorbs light energy, particularly in the blue and red wavelengths, and uses it to power the chemical reactions necessary for photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis can be divided into two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions. In the light-dependent reactions, photons from sunlight excite electrons in chlorophyll molecules, initiating a cascade of chemical reactions that generate energy-rich molecules such as ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). These energy carriers are then used in the subsequent light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin Cycle, where CO2 is fixed and transformed into carbohydrates.
2. The Source of Elements for Growth
In addition to providing energy, solar radiation is also responsible for the availability of key elements required for plant growth. Plants are autotrophs, meaning they can synthesize organic compounds from inorganic sources. Carbon is obtained from carbon dioxide in the atmosphere through photosynthesis. Oxygen, another crucial element, is released as a byproduct of photosynthesis and is vital for all aerobic organisms.
Furthermore, solar energy drives the water cycle, evaporating water from oceans, lakes, and rivers and causing precipitation. Rainwater supplies plants with the essential element of hydrogen, which is a constituent of all organic compounds. Solar energy also fuels the nutrient cycle by driving weathering processes that release minerals and nutrients from rocks and soils into the environment, making them available for plant uptake.
3. Adapting to Different Light Conditions
Green plants have evolved diverse strategies to adapt to different light conditions, ensuring their survival and optimizing their energy capture. Some plants are adapted to low-light conditions, such as those found in the understory of forests, by having larger and thinner leaves to maximize light absorption. They may also contain more chlorophyll and accessory pigments to capture light more efficiently.
On the other hand, plants in bright and sunny environments often have smaller and thicker leaves to minimize water loss through evaporation. They may have adaptations such as waxy coatings or fine hairs on their leaves to reflect excess sunlight. These adaptations allow plants to maintain an optimal balance between capturing enough energy for photosynthesis while minimizing the risk of damage from excessive light or heat.
By utilizing solar energy, green plants have shaped the Earth’s ecosystems and provided the foundation for all life forms. From capturing sunlight to producing essential elements and adapting to different light conditions, their dependence on solar energy is a testament to the wonders of nature’s design.
The Significance of Solar Energy in Plant Ecology
Green plants have an intimate relationship with solar energy that extends beyond mere energy production. Here, we delve deeper into the significance of solar energy in plant ecology and explore how this energy source influences various aspects of plant life.
1. Driving Growth and Development
One of the significant roles of solar energy in plant ecology is its influence on growth and development. Solar radiation is a crucial environmental factor that affects processes like seed germination, leaf expansion, flowering, and fruit ripening. A sufficient supply of solar energy enables plants to undergo these developmental stages effectively.
Seed germination is particularly dependent on solar energy. Light-dependent germination, also known as photoblastic germination, occurs when seeds require specific wavelengths of light to initiate the germination process. This phenomenon is observed in many plant species and is an example of how solar energy directly influences a fundamental aspect of plant life.
2. Regulation of Plant Responses
Solar energy also plays a pivotal role in regulating various plant responses. One such example is phototropism, the bending or growth of a plant in response to light. By sensing the direction and intensity of sunlight, plants can orient their growth towards the most optimal light source.
Additionally, plants use solar cues to regulate various physiological processes. The daily light-dark cycle, or the photoperiod, serves as a critical environmental signal that influences processes like flowering time, dormancy, and leaf senescence. Solar energy acts as a timer for these events, ensuring that plants undergo the appropriate developmental shifts in response to changing seasons.
3. Interactions with Other Organisms
Solar energy also plays a significant role in shaping the interactions between plants and other organisms in their environment. Bees, for example, rely on solar energy to navigate and locate flowering plants for nectar collection. The availability of sunlight also determines the distribution and diversity of plants in various habitats, creating niches for other organisms within these ecosystems.
Furthermore, solar energy is indirectly responsible for driving food webs and energy transfer between trophic levels. Green plants, as primary producers, convert solar energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis. This energy is then transferred to herbivores, carnivores, and decomposers, forming the foundation of all ecological food chains.
In conclusion, solar energy serves as a cornerstone for the survival and functioning of green plants. From driving growth and development to regulating plant responses and influencing interactions with other organisms, the reliance on solar energy is ingrained in the very fabric of plant ecology. Understanding the significance of solar energy in plant life can provide us with profound insights into the intricate web of relationships that sustain our planet’s ecosystems.
Key Takeaways: Why Do Green Plants Require Solar Energy?
- Plants need solar energy for photosynthesis, a process that helps them make food.
- Solar energy is converted into chemical energy in plants through a process called photosynthesis.
- This chemical energy is used by plants to grow, reproduce, and perform various functions.
- Without solar energy, plants would not be able to produce oxygen, which is essential for all living organisms.
- Solar energy also helps plants maintain their green color and healthy growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Green plants rely on solar energy for their survival and growth. This energy is necessary for carrying out photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into food. Here are some common questions related to why green plants require solar energy:
1. How do green plants obtain solar energy?
Green plants use specialized structures called chloroplasts to capture sunlight. Chloroplasts contain a pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy. This energy is then used to power the process of photosynthesis, where plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Without access to solar energy, plants would not be able to produce food and would ultimately die. Through the process of photosynthesis, plants not only create their own energy source but also release oxygen, which is essential for supporting life on earth.
2. Why do green plants specifically require solar energy?
Green plants specifically require solar energy because of their unique ability to carry out photosynthesis. The green pigment chlorophyll in plants is responsible for capturing sunlight and converting it into chemical energy, which is then used to sustain the plant’s growth and development.
Unlike animals, plants cannot directly consume food for energy. Solar energy is the primary source that allows plants to synthesize organic compounds, providing them with the necessary nutrients to survive and thrive.
3. Can green plants survive without sunlight?
No, green plants cannot survive without sunlight. Sunlight provides the necessary energy for photosynthesis, which is essential for the plant’s growth, metabolism, and survival. Without sunlight, plants will not be able to produce food and energy, leading to their eventual demise.
Some plants that grow in low-light conditions may have adaptations to maximize their exposure to available sunlight, but ultimately, all green plants rely on solar energy to survive.
4. Do all parts of a green plant require solar energy?
Yes, all parts of a green plant require solar energy. While the leaves are the primary sites for photosynthesis due to their abundance of chloroplasts, other plant parts, such as stems and roots, also need solar energy. Solar energy enables plants to produce food, which is then transported and used by different parts of the plant for growth, repair, and reproduction.
Even though some parts of a plant may be partially shaded or receive less direct sunlight, they still receive energy indirectly through the interconnectedness of plant systems.
5. What happens if a green plant does not receive enough solar energy?
If a green plant does not receive enough solar energy, it will not be able to perform photosynthesis effectively. This hinders the plant’s ability to produce food, resulting in stunted growth, weakened immune responses, and ultimately, the plant’s death.
Insufficient solar energy can also impact the plant’s ability to carry out essential functions such as nutrient uptake and root development. In extreme cases, plants may exhibit yellowing or browning of leaves, indicating a lack of chlorophyll and compromised health.
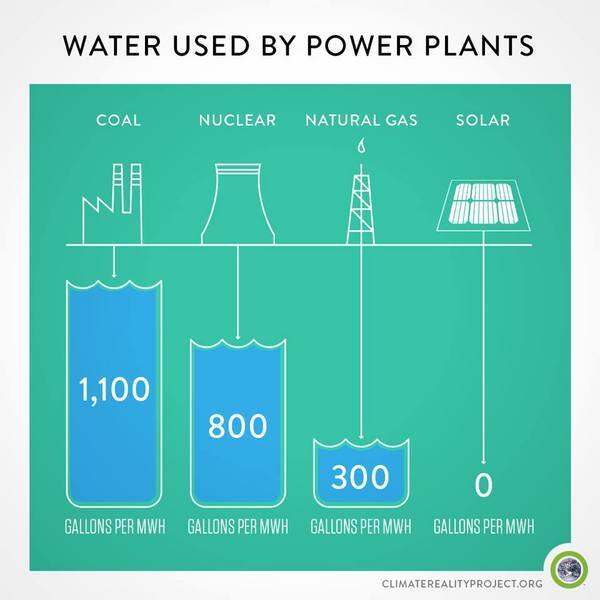
How green is solar energy really?
Summary
Plants need solar energy because they use it to make food in a process called photosynthesis. When plants get sunlight, they use it to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This glucose gives them energy to grow and survive. Sunlight is like a meal for plants!
Without solar energy, plants wouldn’t be able to make food, and they would die. Green plants are special because they have a pigment called chlorophyll that helps them absorb sunlight. So, the next time you see a plant soaking up the sun, remember that it’s not just getting a tan, it’s getting the energy it needs to live!