What Renewable Energy Is The Cheapest To Produce?
When it comes to renewable energy, one question that often pops up is: “What renewable energy is the cheapest to produce?” Well, my young friend, that’s exactly what we’re going to explore together. We’ll dive into the world of green energy and uncover the most cost-effective options. So grab a seat, and let’s embark on this exciting journey to discover the affordable side of renewable power!
Now, I bet you’re wondering why this question is so important. Well, not only does renewable energy help protect our planet, but it’s also crucial for achieving a sustainable and affordable energy future. By harnessing the power of nature, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and create a cleaner, healthier world for generations to come.
But here’s the thing – not all renewable energy sources are created equal when it comes to cost. Some technologies are more affordable to produce than others. So, if you’re curious to find out which renewable energy source won’t break the bank, join me as we navigate through the realm of affordability and uncover the secrets of cheap and clean power!
So, are you ready to unlock the mystery of affordable renewable energy? Let’s dive in and discover which green power sources won’t burn a hole in our pockets!
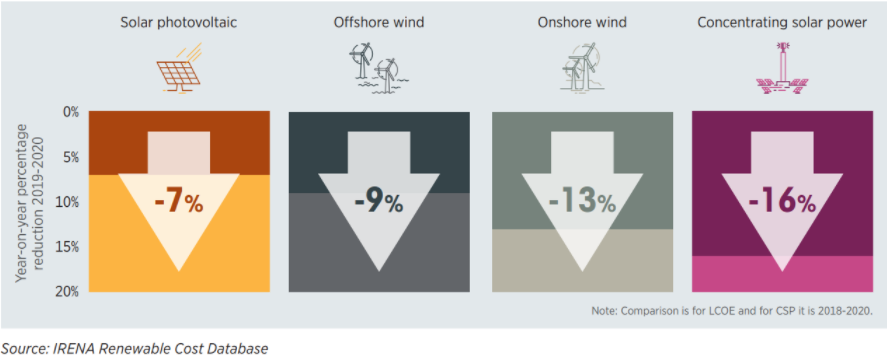
What Renewable Energy is the Cheapest to Produce?
Renewable energy sources have gained significant attention in recent years as the world moves towards a more sustainable future. As the demand for clean and affordable energy increases, it becomes crucial to explore the cheapest renewable energy sources available. In this article, we will delve into the top contenders for the cheapest renewable energy sources and explore their benefits, costs, and potential for widespread adoption.
Solar Energy: Harnessing the Power of the Sun
Solar energy is undoubtedly one of the most abundant and widely available renewable energy sources. By harnessing the power of the sun through photovoltaic (PV) cells, solar panels convert sunlight into electricity. Solar energy is not only cost-effective but also incredibly versatile. It can be utilized in various applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial contexts.
Solar energy presents several undeniable advantages. Firstly, sunlight is free and readily available, making it an incredibly cost-effective energy source. Additionally, solar panels have a long lifespan, requiring minimal maintenance. Moreover, solar energy systems often offer attractive incentives, such as net metering and tax credits, further reducing the overall cost of installation and operation.
Benefits of Solar Energy
1. Renewable and Abundant: Solar energy relies on sunlight, which is an inexhaustible resource, making it a sustainable choice for the long term.
2. Cost-Effective: While the initial installation cost may be higher, solar energy systems have significantly lower operating costs than traditional fossil fuel-based power plants.
3. Environmentally Friendly: Solar energy produces no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollutants, reducing the environmental impact of energy production.
Wind Energy: Harnessing the Power of the Wind
Wind energy is another increasingly popular and cost-effective renewable energy source. By harnessing the power of the wind through wind turbines, wind energy can be converted into electricity. Wind turbines consist of large blades that rotate when exposed to wind, generating mechanical energy that is then converted into electrical energy.
One of the main advantages of wind energy is its scalability. Wind farms can range in size from small installations for individual homes to large-scale utility projects. Additionally, wind energy can be produced both onshore and offshore, providing flexibility in terms of location and accessibility.
The Benefits of Wind Energy
1. Abundant and Widely Available: Wind is a resource that is abundantly available in many regions, making wind energy a globally accessible solution.
2. Competitive Costs: Wind energy has become increasingly cost-competitive, with significant price reductions driven by innovations in turbine technology and economies of scale.
3. Clean and Sustainable: Wind energy is a clean and sustainable energy source that produces no air or water pollution, contributing to a healthier environment.
Hydropower: Harnessing the Power of Water
Hydropower, also known as hydroelectric power, is one of the oldest and most widely used renewable energy sources. It involves harnessing the energy from moving water, such as rivers or dams, to generate electricity. Hydropower systems can vary in size, from small-scale installations to large dams used for massive energy production.
Hydropower offers several advantages that contribute to its cost-effectiveness. Firstly, water is a free and abundant resource, making it a reliable and sustainable energy option. Additionally, hydropower facilities have a long lifespan and require minimal maintenance once installed. Moreover, hydropower systems provide flexibility in operation, allowing for efficient load balancing and storage of excess energy.
The Benefits of Hydropower
1. Renewable and Reliable: Water, the source of hydropower, is a sustainable resource that is continuously replenished by the natural water cycle.
2. Cost-Effective: Once the initial construction costs are covered, hydropower facilities have low operational and maintenance expenses, resulting in long-term cost savings.
3. Emission-Free Energy Generation: Hydropower does not produce greenhouse gas emissions or air pollutants during energy production, contributing to a cleaner environment.
Biomass Energy: Utilizing Organic Matter
Biomass energy is generated by burning organic matter, such as wood, crop residues, and agricultural waste, to produce heat or electricity. It is considered a renewable energy source as the organic materials used for biomass production can be replenished through sustainable forestry practices and agricultural activities.
Biomass energy offers several advantages, making it an attractive option for renewable energy production. Firstly, biomass is a widely available and abundant resource. It can be sourced from various agricultural and forestry residues, reducing dependence on non-renewable energy sources. Additionally, biomass plants can provide a stable and consistent energy supply, as the fuel can be stored and used as needed.
Advantages of Biomass Energy
1. Renewable and Localized: Biomass is derived from organic matter, making it a locally available and sustainable source of energy.
2. Waste Management Solution: Utilizing agricultural and forestry residues for biomass energy production helps manage waste and reduces environmental pollution.
3. Carbon Neutral: Biomass energy is considered carbon neutral, as the CO2 released during combustion is equal to the CO2 absorbed during plant growth.
Geothermal Energy: Tapping into the Earth’s Heat
Geothermal energy harnesses the natural heat from the Earth’s interior to generate electricity or provide heating and cooling for buildings. This renewable energy source relies on the Earth’s heat that is continuously being generated by the decay of radioactive substances and the residual heat from the planet’s formation.
Geothermal energy holds several advantages that contribute to its cost-effectiveness. Firstly, geothermal resources are available year-round, making it a reliable and consistent energy option. Additionally, geothermal power plants have a long lifespan and require minimal maintenance once established. Moreover, geothermal energy production produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a cleaner environment.
The Advantages of Geothermal Energy
1. Renewable and Reliable: Geothermal energy relies on the Earth’s heat, which is continually regenerated, making it an inexhaustible and reliable energy source.
2. Cost-Effective: While the initial development costs can be significant, geothermal power plants have relatively low operational and maintenance expenses in the long term.
3. Low Environmental Impact: Geothermal energy production emits only a small fraction of the greenhouse gases and air pollutants associated with conventional power plants, minimizing its environmental footprint.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a variety of renewable energy sources offer cost-effective solutions for energy production. Solar energy, wind energy, hydropower, biomass energy, and geothermal energy are all viable options that harness the power of natural resources in a sustainable and economically feasible manner. Each of these renewable energy sources has unique advantages and considerations, making them suitable for different applications and locations. By embracing these cheap and clean alternatives, we can pave the way for a greener and more sustainable future.
Key Takeaways: What renewable energy is the cheapest to produce?
- Wind energy is one of the cheapest forms of renewable energy.
- Solar energy has become increasingly cost-effective in recent years.
- Geothermal energy is affordable and provides a steady source of power.
- Hydroelectric power is cost-effective and relies on natural water resources.
- Biomass energy is relatively inexpensive and uses organic waste materials.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we’ll answer some common questions related to the cheapest forms of renewable energy.
1. What factors determine the cost of producing renewable energy?
Several factors influence the cost of producing renewable energy. The type of technology used, the availability of resources, and the scale of the project are key considerations. Additionally, the cost of materials, labor, and any necessary infrastructure also play a role.
For example, solar energy costs vary depending on the type of solar panels used (e.g., monocrystalline, polycrystalline, thin-film) and the efficiency of the panels. Meanwhile, wind energy costs are influenced by factors such as turbine size and location. It’s crucial to analyze these variables when determining the cost of renewable energy production.
2. Which renewable energy source is currently the cheapest to produce?
As of now, solar energy is generally the cheapest form of renewable energy to produce. The cost of solar panels has significantly declined over the years, making it more accessible and cost-effective. Additionally, advancements in technology have increased the efficiency of solar panels, further reducing production costs.
On the other hand, wind energy has also become increasingly competitive in terms of cost. The construction of wind turbines has become more efficient, leading to lower production costs. The availability of reliable wind resources in certain areas also contributes to its affordability. Although solar energy often takes the lead in terms of cost, the competition between solar and wind energy continues to drive down prices in both sectors.
3. Are there any other renewable energy sources that are becoming more affordable?
Yes, hydroelectric power is another renewable energy source that has seen significant cost reductions in recent years. Hydroelectric power relies on the flow of water to generate electricity and is generally considered a reliable and cost-effective energy source. The cost of constructing hydroelectric projects has decreased due to improved construction techniques and a better understanding of environmental impacts.
In addition, advancements in energy storage technologies, such as batteries, have made it easier to integrate intermittent energy sources like solar and wind into the power grid. This has led to improved efficiency and reduced costs in renewable energy generation.
4. What are the potential cost-saving benefits of investing in renewable energy?
Investing in renewable energy can have several cost-saving benefits. First and foremost, as technology improves and economies of scale are realized, the cost of producing renewable energy decreases. This means that over time, investments in renewable energy become more financially attractive.
Furthermore, by reducing dependence on fossil fuels, which frequently experience price fluctuations, economies can become more resilient to energy cost volatility. Moreover, renewable energy sources such as solar and wind receive significant environmental subsidies, making them increasingly financially viable options.
5. How can governments and policymakers contribute to reducing the costs of renewable energy?
Governments and policymakers play a crucial role in reducing the costs of renewable energy. They can implement supportive policies and incentives, such as tax credits, grants, or feed-in tariffs, to stimulate investment and innovation in the renewable energy sector. These measures help reduce the financial burden on renewable energy developers and accelerate the adoption of these technologies.
Additionally, governments can invest in research and development to further advance renewable energy technologies, making them more efficient and cost-effective. By fostering collaborations between industries, academic institutions, and research centers, governments can create an environment conducive to innovation and technological advancements in renewable energy production.
Summary
Renewable energy sources like wind and solar power are the cheapest to produce. These sources don’t rely on fossil fuels and don’t produce harmful emissions. While there are upfront costs, the long-term savings and environmental benefits make them a smart choice for the future.
It’s important to invest in renewable energy and continue to research and develop new technologies. By transitioning to clean and affordable energy, we can decrease our reliance on fossil fuels and work towards a more sustainable and greener future.