What Are The Pros And Cons Of Non Renewable Energy Resources?
Non-renewable energy resources are a hot topic these days, and you might be wondering, “What are the pros and cons of non-renewable energy resources?” Well, you’re in the right place! In this article, we’re going to explore the advantages and disadvantages of non-renewable energy sources in a fun and engaging way.
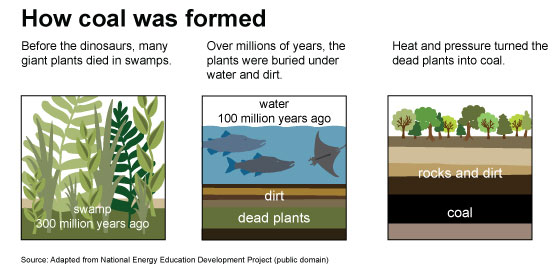
Now, before we dive into the pros and cons, let’s clarify what non-renewable energy resources are. Have you ever heard of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas? These are the primary sources of non-renewable energy. They formed over millions of years from the remains of ancient plants and animals, and once we use them up, they’re gone forever.
So, why do some people love non-renewable energy resources while others worry about their impact on the planet? Keep reading to find out the good and not-so-good sides of using non-renewable energy sources. Let’s get started!
Pros and Cons of Non Renewable Energy Resources: A Closer Look
Non-renewable energy resources play a crucial role in powering our modern world. However, they also come with their fair share of drawbacks. In this article, we will explore the pros and cons of non-renewable energy resources, shedding light on their advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these factors can help us make informed decisions about our energy consumption and explore alternative, sustainable options for the future.
The Pros of Non Renewable Energy Resources
Non-renewable energy resources, such as fossil fuels, have provided immense benefits to humanity over the years. Here are some of the advantages:
Economic Benefits
One of the major advantages of non-renewable energy resources is their contribution to the economy. Industries like oil and gas provide employment opportunities and contribute to the GDP of many countries. These resources also generate significant government revenue in the form of taxes and royalties which can be used for public services and infrastructure development.
Additionally, non-renewable energy resources offer price stability. Unlike renewable sources that fluctuate depending on weather conditions, the prices of fossil fuels are more predictable. This stability provides certainty for businesses and consumers, enabling them to plan their budgets effectively.
In terms of energy density, non-renewable resources also offer a higher energy yield compared to renewable sources. For example, fossil fuels have a higher energy density, allowing for more efficient energy production and storage.
Reliability and Availability
Non-renewable resources are available in abundance globally. This ensures a steady and reliable supply of energy that can meet the high demands of industries and societies. Unlike intermittent renewable sources, non-renewable energy can provide a constant power supply, making it suitable for baseload energy requirements and critical infrastructure.
Furthermore, non-renewable energy resources can be easily transported and stored, making them accessible even in remote areas. This accessibility contributes to energy accessibility and equity across different regions.
Technological Maturity
Non-renewable energy technologies have been developed and refined over many years, resulting in well-established infrastructures and processes. This maturity ensures that these energy sources can be efficiently converted into usable power through various means such as combustion or nuclear reactions.
Moreover, the advancements in technology have led to improved efficiency and reduced emissions in non-renewable energy production. This progress has mitigated some of the environmental concerns associated with these resources, making them increasingly environmentally friendly.
The Cons of Non Renewable Energy Resources
While non-renewable energy resources have their advantages, they also pose significant challenges and drawbacks that must be acknowledged:
Environmental Impact
One of the most significant disadvantages of non-renewable energy resources is their negative impact on the environment. Fossil fuels, for example, release greenhouse gases when burned, contributing to climate change. These emissions are responsible for global warming, leading to issues like rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and ecological imbalances.
In addition to greenhouse gases, the extraction and processing of non-renewable resources can also result in habitat destruction, water pollution, and air pollution. The negative consequences extend beyond climate change, affecting biodiversity, human health, and the overall ecological balance.
Finite Supply
Non-renewable energy resources, as the name suggests, have a finite supply. Fossil fuels, for instance, are formed over millions of years and cannot be replenished within a human timescale. This means that once these resources are depleted, they are gone forever.
Depleting non-renewable resources can lead to energy shortages and higher energy prices. As their availability decreases, the cost of extraction and exploration rises, making them less economically viable.
Dependency on Global Conflicts
Non-renewable energy resources, especially oil, often lead to international conflicts and geopolitical tensions due to their value and strategic importance. The reliance on these resources can create power imbalances and geopolitical instability, with countries vying for control over energy-rich regions. This dependency on non-renewable energy can have far-reaching political and economic consequences.
Moreover, the extraction of non-renewable resources in certain areas can result in social issues, including displacement of indigenous populations, human rights abuses, and unequal distribution of wealth.
The Way Forward: Transitioning to Renewable Energy
While non-renewable energy resources have been vital in powering our modern world, it is crucial to prioritize the transition to renewable sources. Renewable energy offers numerous benefits, including environmental sustainability, long-term availability, and reduced dependence on fossil fuels.
To facilitate this transition, governments, businesses, and individuals must invest in renewable energy infrastructure, research and development, and policy initiatives. The advancements in renewable technologies, such as solar panels and wind turbines, have already made them increasingly competitive and accessible.
By embracing renewable energy sources, we can mitigate the negative impacts of non-renewable resources and pave the way for a cleaner, sustainable future for generations to come.
Key Takeaways: Pros and Cons of Non-Renewable Energy Resources
- Non-renewable energy resources like fossil fuels provide a lot of energy and are relatively cheap to produce. They have been powering our world for many years.
- However, non-renewable energy sources have drawbacks. They contribute to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, leading to climate change.
- Non-renewable energy resources are limited and will eventually run out. This can cause energy shortages and higher prices in the future.
- Extracting and processing non-renewable resources can have negative impacts on the environment, such as habitat destruction and water pollution.
- Transitioning to renewable energy sources is important for a sustainable future, as they are cleaner, more abundant, and can help mitigate climate change.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our FAQ section on the pros and cons of non-renewable energy resources! Here, we’ll address some common questions about these types of energy sources and their implications.
1. How are non-renewable energy resources different from renewable ones?
Non-renewable energy resources, such as fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas), are finite and take millions of years to form. Once depleted, they cannot be replenished within a human lifetime. In contrast, renewable energy resources, like solar and wind power, are naturally replenished and virtually inexhaustible.
While non-renewable energy resources have powered our industrial developments, their use contributes to air and water pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and climate change. On the other hand, renewable energy is cleaner, more sustainable, and helps combat the negative impacts associated with non-renewable sources.
2. What are the advantages of non-renewable energy resources?
Non-renewable energy resources do have some advantages. They are readily available and have a high energy density, meaning they can generate large amounts of power in a small space. Fossil fuels are also highly efficient, making them economically viable for producing electricity and fuel. Additionally, non-renewable energy infrastructure is well-established, making it easier to integrate into existing systems.
However, it’s important to note that these advantages come with trade-offs. The environmental consequences, such as air and water pollution, as well as the long-term impact on climate change, must be carefully considered when evaluating the benefits of non-renewable energy resources.
3. What are the disadvantages of non-renewable energy resources?
Non-renewable energy resources have several disadvantages. Their extraction, refining, and transportation processes can have significant environmental impacts, including habitat destruction and water pollution. Moreover, the combustion of fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases, contributing to global warming and climate change.
As non-renewable energy resources become scarcer, their extraction becomes more difficult and expensive. In addition, their market price can be volatile due to geopolitical factors and fluctuations in supply and demand. The reliance on non-renewable energy sources also poses a risk to national energy security, as they are often imported from other countries.
4. Can non-renewable energy resources be made more sustainable?
While non-renewable energy resources will always have their downsides, efforts can be made to mitigate their negative impacts and make them more sustainable. One approach is the development of cleaner technologies, such as advanced pollution controls and carbon capture and storage, to reduce the environmental footprint of non-renewable energy sources.
Another way to promote sustainability is through increased energy efficiency and conservation. By using non-renewable energy resources more efficiently and reducing overall energy consumption, we can minimize their environmental impact and extend their availability.
5. What is the future of non-renewable energy resources?
The future of non-renewable energy resources is uncertain. As concerns about climate change intensify, there is a growing global focus on transitioning to renewable energy sources. Efforts are being made to develop alternative energy technologies and improve energy storage capabilities.
However, it’s important to acknowledge that non-renewable energy resources will continue to play a role in the near future due to their existing infrastructure and energy demands. Thus, finding a balanced approach that gradually reduces reliance on non-renewable sources while promoting the adoption of renewable energy is crucial for a sustainable and secure energy future.
Summary
Non-renewable energy resources, like coal, oil, and natural gas, have their advantages and disadvantages. On the positive side, they provide a lot of energy and are reliable sources. However, they also create pollution, contribute to climate change, and will eventually run out.
Using non-renewable energy can help power our homes and fuel our cars, but it comes at a cost to the environment and our future. It’s important to find ways to reduce our reliance on these resources and transition to cleaner, renewable energy alternatives. By doing so, we can protect our planet and ensure a sustainable future for generations to come.