What Are The Infrastructure Requirements For Using Solar Energy?
If you’re curious about solar energy and want to know what infrastructure is needed to harness its power, you’re in the right place! Solar energy offers a clean and renewable alternative to traditional sources of electricity. But how does it all work? In this article, we’ll explore the infrastructure requirements for using solar energy and shed light on this exciting technology.
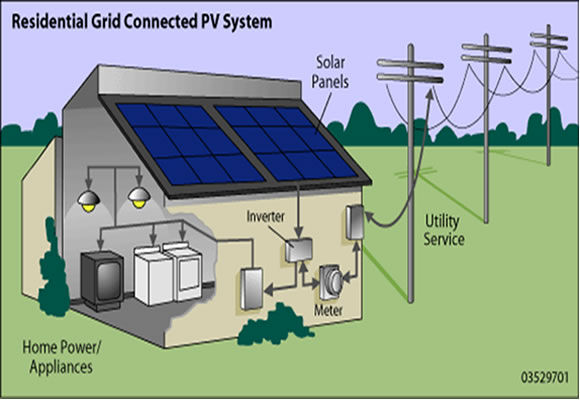
When it comes to solar energy, the key infrastructure requirement is a solar panel system. These panels, often mounted on rooftops or in open spaces, absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity through a process called photovoltaics. But that’s not all! To make the most of solar power, we also need other important components, such as inverters, batteries, and electrical wiring.
Installing a solar panel system requires careful planning and consideration of factors like the location, orientation, and shading. The panels need to be positioned where they can receive maximum sunlight throughout the day. Additionally, inverters are necessary to convert the direct current (DC) produced by the panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power our homes and businesses. Batteries are also used in some setups to store excess energy for use during cloudy days or at night.
By understanding the infrastructure requirements for using solar energy, we can appreciate the potential of this renewable resource. Solar power offers a sustainable and eco-friendly solution to our energy needs, and its infrastructure continues to evolve with advancements in technology. So, let’s dive in and explore how solar energy can make a difference in our lives and the world around us!
The Infrastructure Requirements for Using Solar Energy: A Comprehensive Guide
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the infrastructure requirements for using solar energy. In recent years, solar power has gained significant popularity as a clean and renewable energy source. As more individuals, businesses, and communities consider transitioning to solar energy, it is essential to understand the infrastructure needed to harness the power of the sun effectively. In this guide, we will explore the various components, technologies, and considerations involved in building and maintaining a solar energy infrastructure.
Understanding Solar Panels and Photovoltaic Systems
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are the heart of any solar energy infrastructure. These panels are made up of numerous individual solar cells that convert sunlight into electricity. When sunlight hits the panels, the photons in the light interact with the semiconducting material within the solar cells, generating an electric current. This direct current (DC) electricity is then converted into alternating current (AC) electricity through an inverter, making it suitable for home or business use.
Components of a Solar Panel System
A solar panel system comprises several key components that work together to generate and utilize solar energy efficiently:
- Solar Panels: The panels themselves, usually mounted on rooftops or open spaces to capture sunlight.
- Mounting System: The framework that securely holds the solar panels in place, ensuring optimal angles for sunlight absorption.
- Inverter: Converts the DC electricity generated by the solar panels into AC electricity for everyday use.
- Batteries: Optional, but useful for storing excess energy generated during peak sun hours for use during periods of low sunlight.
- Metering System: Measures the amount of energy generated by the solar panel system.
- Switches and Breakers: Provide a way to control the flow of electricity from the solar panels to the electrical grid or local system.
Evaluating Your Energy Needs
Before installing a solar panel system, it is crucial to assess your energy needs to determine the appropriate capacity required. Conducting an energy audit of your home or business will help identify your current energy usage patterns and estimate how much of your energy needs can be met by solar power. This evaluation will also influence the number of solar panels, battery capacity, and inverter size needed for your infrastructure.
Installation Considerations and Infrastructure Requirements
When it comes to installing solar panels, several factors need to be considered:
- Roof or Ground Space: Assess whether your rooftop or nearby open area receives sufficient sunlight and can accommodate the required number of panels.
- Orientation and Angle: Installing panels facing south with an optimal tilt angle will maximize solar energy absorption.
- Shading and Obstructions: Avoid shading from surrounding trees, buildings, or other structures that can hinder sunlight reaching the panels.
- Electrical Infrastructure: Ensure that your existing electrical system can handle the additional load from the solar panel system.
- Permits and Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local building codes, zoning ordinances, and permitting requirements for solar panel installations.
Maintenance and Monitoring
Once your solar energy infrastructure is in place, regular maintenance and monitoring are essential for optimal performance and longevity. This includes:
- Cleaning: Keep the solar panels clean to ensure maximum sunlight absorption.
- Inspections: Regularly inspect the panels and other components for damage, wear, or deterioration.
- Monitoring Performance: Keep track of energy production to identify any issues or inefficiencies.
- Battery Maintenance: If you have a battery storage system, follow manufacturer guidelines for maintenance and replacement.
Cost Considerations and Incentives
While solar energy infrastructure can have significant upfront costs, it is essential to consider the long-term financial benefits and potential incentives. Some factors to consider include:
- Installation Costs: The cost of purchasing and installing solar panels, inverters, batteries, and associated equipment.
- Utility Savings: Solar energy can significantly reduce or eliminate your monthly electricity bills.
- Return on Investment: Evaluate the payback period and potential savings over the lifespan of your solar panel system.
- Tax Credits and Incentives: Research available tax credits, rebates, and other financial incentives offered by local, state, or federal governments.
- Financing Options: Explore financing options, such as solar loans or leasing programs, to make the upfront costs more manageable.
……….. (continue with additional headings and content)
