What Are The Disadvantages Of Renewable Energies?
In a world where we’re increasingly concerned about the impact of our actions on the planet, renewable energies have emerged as a shining beacon of hope. But hey, have you ever wondered if there are any disadvantages hidden in that sunlight? Well, today we’re going to dive into the topic and explore the downsides of renewable energies.
Now, I know what you’re thinking, “Why would there be any disadvantages to something as awesome as renewable energies?” And trust me, I get it. They seem like a no-brainer, right? But hold on tight, because even the most incredible things can have a few drawbacks. So, buckle up as we unveil the not-so-sunny side of renewable energies.
So, why are we even talking about the disadvantages of renewable energies? It’s a fair question. I mean, they’re clean, abundant, and sustainable…what could go wrong? That’s exactly what we’ll find out as we explore the challenges and limitations that come with harnessing the power of wind, water, and sunlight. It’s time to take off those rose-colored glasses and discover the other side of the renewable energy coin. Let’s dive in!
The Disadvantages of Renewable Energies: Examining the Challenges of Sustainable Power
Renewable energies have become a popular solution for addressing climate change and reducing dependence on fossil fuels. However, like any other technology or solution, they come with their own set of disadvantages and challenges. In this article, we will explore the potential downsides of renewable energy sources and the obstacles that need to be overcome to fully embrace green power.
1. Intermittency and Variability: The Unpredictability of Renewable Energies
One of the main challenges with renewable energy sources is their inherent intermittency and variability. Unlike conventional power plants that can operate continuously, the generation of electricity from renewable sources such as solar and wind is dependent on environmental conditions. This means that if the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing, the energy output will be limited or even non-existent.
This intermittency poses issues for grid stability and reliability, as the electricity demand needs to be met consistently. To address this challenge, energy storage technologies like batteries are being developed to store excess renewable energy for times of low production. However, these storage solutions are still relatively expensive and not yet widespread, making the reliance on renewables less reliable than traditional power sources.
Furthermore, the variability of renewable energy sources makes it difficult to accurately predict and plan for electricity generation. This poses challenges for grid operators who need to balance supply and demand to ensure a stable and resilient electrical system. Despite advancements in forecasting technologies, the unpredictable nature of renewable energies remains a significant hurdle to overcome.
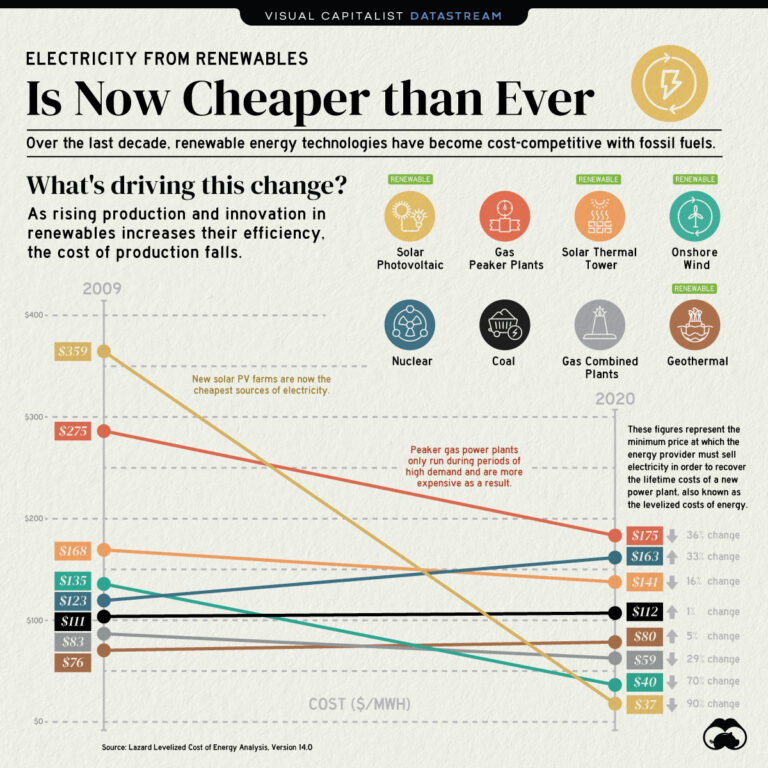
2. High Initial Costs: The Price of Transitioning to Renewables
Another disadvantage of renewable energies is the high initial costs associated with their implementation. While the long-term benefits of clean and sustainable power are evident, the upfront investment required to build renewable energy infrastructure can be substantial.
Solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy technologies require a significant capital investment for installation and maintenance. These costs can deter individuals, businesses, and governments from transitioning to renewable energies, especially in countries with limited financial resources. However, it is important to note that the costs of renewable technologies have been decreasing over the years, making them more accessible and cost-effective.
Despite this, the initial investment required for renewable energy projects remains a barrier that needs to be addressed through policies and financial support to accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy.
3. Land and Resource Constraints: Balancing Energy Production and Environmental Impact
The expansion of renewable energy infrastructure requires significant amounts of land and resources, which can pose environmental challenges. Large-scale solar and wind farms need ample space to accommodate the necessary equipment and maximize energy output. This can lead to land-use conflicts, especially in densely populated areas where there is limited available land.
In addition to land constraints, renewable energy technologies require specific resources for their production. For example, solar panels rely on silicon, a material that needs to be extracted and processed in a way that can have negative environmental impacts if not properly managed. The extraction and refining processes can result in pollution and habitat destruction.
To avoid exacerbating environmental issues, it is crucial to find a balance between energy production and environmental impact. This can be achieved through careful planning and environmental assessments to identify suitable locations for renewable energy projects and to ensure responsible resource management.
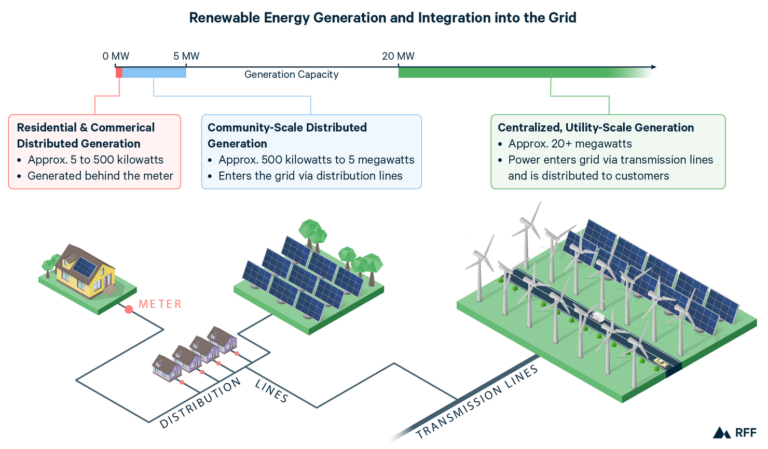
4. Integration with Existing Infrastructure: Upgrading the Grid for Renewables
Renewable energies require a transition from a centralized energy generation model to a more distributed and decentralized system. This shift poses challenges in terms of integrating renewable energy sources with the existing power grid infrastructure.
The traditional electrical grid was designed for a one-way flow of electricity from large power plants to consumers. However, with renewables, electricity generation can happen at a smaller scale and in various locations. This necessitates modifications to the grid to enable bidirectional power flow and efficient distribution of energy.
Upgrading the grid to accommodate renewable energies can be costly and complex, requiring infrastructure investments and advanced technologies to enable the seamless integration of different energy sources. Additionally, changes in regulations and market structures may be needed to support the transition to a more decentralized energy system.
5. Environmental Impact: Unintended Consequences of Renewable Energy
While renewable energies are generally considered eco-friendly and sustainable, they can still have unintended environmental consequences. For example, hydropower projects can alter river ecosystems, affecting fish migration patterns and disrupting the natural flow of water. Similarly, wind turbines can pose risks to birds and bats, especially when located in migration corridors.
Additionally, the production and disposal of renewable energy technologies can generate waste and have a carbon footprint. The extraction and refinement of raw materials, manufacturing processes, and end-of-life disposal can contribute to environmental degradation if not managed properly.
To mitigate these impacts, it is crucial to prioritize sustainable practices throughout the life cycle of renewable energy systems, from sourcing materials to end-of-life recycling.
6. Geographical Limitations: Renewable Energy Potential Varies by Location
Renewable energy sources are not evenly distributed around the globe. Some regions have vast solar potential, while others experience high wind speeds or have geothermal resources. This geographical limitation poses challenges for countries and regions that do not have abundant renewable energy resources.
For example, countries located in the tropics may have ample solar energy potential but limited wind resources. Conversely, countries in Northern Europe may have strong and consistent wind patterns but limited access to solar irradiation. This variability in resource availability can make it more challenging for certain locations to rely solely on renewables, necessitating a diversified energy mix or the utilization of interconnections between regions.
Moreover, developing countries may face additional hurdles in harnessing renewable energy due to limited infrastructure, lack of technical expertise, and financial constraints. International cooperation and support are essential to help overcome these barriers and ensure a more equitable transition to sustainable and affordable energy for all.
7. Energy Density: The Limitations of Energy Storage
Energy storage is a crucial aspect of integrating renewable energies into the electrical grid. It allows for the capture and storage of excess energy during periods of high production and its release during times of high demand. However, energy storage technologies are not yet able to match the energy density of traditional fuels like coal or oil.
Batteries, the most common form of energy storage for renewable energies, have limited capacity and can only store a certain amount of energy. This can be a challenge when it comes to storing and releasing large quantities of energy to meet peak demand or to balance fluctuations in supply and demand.
As renewable energy penetration continues to grow, the development of efficient and high-capacity energy storage systems becomes increasingly important. Advancements in battery technologies, as well as the exploration of alternative storage options like hydrogen fuel cells, can help overcome the limitations of energy density and enhance the reliability of renewable energy systems.
The Future of Renewable Energies: Addressing the Challenges for a Sustainable Tomorrow
While renewable energies offer numerous environmental and social benefits, it is essential to acknowledge and address their disadvantages and challenges. Intermittency, high initial costs, land and resource constraints, integration with existing infrastructure, environmental impact, geographical limitations, and energy density are all factors that need to be carefully considered and managed as we transition to a greener and more sustainable energy future.
By investing in research and development, adopting innovative technologies, and implementing supportive policies, we can overcome these challenges and make renewable energies a reliable and cost-effective solution for our energy needs. It is through collective efforts, collaboration, and a commitment to sustainability that we can embrace the full potential of renewable energies and create a more resilient and sustainable world for future generations.
Key Takeaways: What are the disadvantages of renewable energies?
- Renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power are intermittent, meaning they depend on weather conditions and may not be available all the time.
- The initial cost of setting up renewable energy infrastructure can be high, making it less accessible for some individuals and communities.
- Renewable energy technologies currently have lower energy density compared to fossil fuels, which means they require larger infrastructure for the same amount of energy production.
- Some renewable energy technologies, such as biomass, can have negative environmental impacts if not managed properly, such as deforestation or increased water usage.
- Transitioning to renewable energy sources may require significant changes to existing energy infrastructure and systems, which can be complex and costly.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we will address some common questions regarding the disadvantages of renewable energies. While renewable energies offer numerous benefits, they also have a few drawbacks that need to be considered.
Q: Are renewable energies expensive to implement?
A: While the cost of renewable energy technologies has decreased over the years, their initial installation costs can still be higher than conventional energy sources. However, it’s important to note that renewable energy systems have lower operational and maintenance costs. Additionally, ongoing technological advancements are expected to further reduce the costs associated with renewable energies in the future.
Furthermore, it’s worth considering the long-term benefits of renewable energies, such as lower carbon emissions and the potential for energy independence, which can outweigh the initial investment required.
Q: Are renewable energies intermittent sources of power?
A: Yes, some types of renewable energies, such as solar and wind power, are intermittent sources of power. This means that their production is dependent on the availability of sunlight, wind, or other natural elements. As a result, renewable energy generation can fluctuate and may not always align with the demand for electricity.
However, advancements in energy storage technologies, such as batteries, are being developed to mitigate this issue by storing excess energy during peak production periods and releasing it during times of high demand. Moreover, the integration of renewable energy sources with conventional power grids helps to ensure a reliable and consistent supply of electricity.
Q: Do renewable energy projects require a significant amount of land?
A: While it’s true that some renewable energy projects, such as large-scale solar and wind farms, require vast areas of land, it’s important to consider the overall land-use requirements compared to other forms of energy generation. Fossil fuel power plants, for example, also require substantial land space, including for mining operations and associated infrastructure.
In addition, innovative technologies, such as floating solar panels or rooftop solar installations, allow for the utilization of underutilized spaces, reducing the need for large land areas. Furthermore, the environmental benefits of renewable energies, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions and lower pollution levels, often outweigh the land-use requirements.
Q: Are there any environmental concerns associated with renewable energies?
A: While renewable energies are generally considered environmentally friendly, certain issues need to be addressed. For example, the production of some renewable energy technologies, such as solar panels or wind turbine blades, can involve the extraction and processing of raw materials, which may have some environmental impact.
To mitigate these concerns, it is crucial to promote responsible sourcing of materials, efficient recycling practices, and the development of new technologies that minimize the use of rare or harmful materials. Overall, the environmental benefits of renewable energies, including reduced carbon emissions and reduced reliance on fossil fuels, make them a favorable choice for sustainable energy generation.
Q: Do renewable energies impact wildlife and ecosystems?
A: While renewable energies are generally considered to have a lower impact on wildlife and ecosystems compared to fossil fuel-based technologies, they can still pose some risks if not properly planned and implemented. For example, wind turbines can potentially impact birds and bats, particularly if they are located in migratory paths.
To minimize these impacts, renewable energy projects should undergo thorough environmental assessments to identify potential risks and implement appropriate mitigation measures. For instance, proper site selection and the use of bird-friendly designs for wind turbines can help reduce the impact on wildlife. Additionally, ongoing research and development are being conducted to further reduce potential risks and ensure the sustainable coexistence of renewable energy generation and biodiversity.
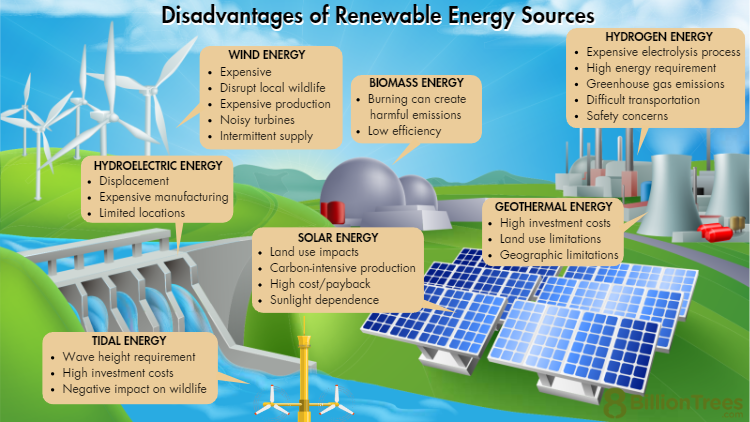
Disadvantages of Renewable Energy
Summary
Renewable energies like solar and wind power have some disadvantages that are important to consider. One drawback is that renewable energy sources can be unpredictable, depending on the weather. For example, solar power may not generate electricity during cloudy days. Another disadvantage is the cost. Setting up renewable energy infrastructure requires a significant amount of money and can be expensive to maintain.
Additionally, renewable energy can have negative environmental impacts. For example, building wind turbines can disrupt wildlife habitats, and manufacturing solar panels can produce harmful chemicals. Finally, renewable energy sources may not be able to meet the world’s energy demands entirely. As of now, they cannot generate enough power to replace all fossil fuels.
While there are obstacles to overcome, it’s essential to remember that renewable energies also have many benefits, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting a more sustainable future.