What Are Some Limitations Of Solar Energy?
Are you curious about solar energy and its limitations? Well, you’ve come to the right place! In this article, we’ll explore some of the drawbacks you should be aware of when it comes to harnessing the power of the sun. 🌞
Now, you might be thinking, why even bother discussing the limitations of solar energy? After all, it’s clean, renewable, and abundant. But just like everything else, it has its pros and cons. So, let’s dive in and find out what some of those limitations are!
While solar energy has numerous benefits, it’s essential to understand its limitations too. By doing so, we can make informed decisions about how to best utilize this incredible source of power. So, grab a seat, put on your learning hat, and let’s explore the limitations of solar energy together! 🌱💡
Limitations of Solar Energy: Exploring the Challenges of Harnessing the Sun’s Power
Solar energy is touted as a clean and sustainable power source, but like any technology, it has its limitations. In this article, we will delve into the various challenges associated with harnessing solar energy and explore the potential drawbacks of relying solely on the sun for our energy needs. From intermittency and efficiency issues to high upfront costs and geographical limitations, understanding the limitations of solar energy is crucial to developing a well-rounded perspective on its viability as a widespread energy solution.
Intermittency: The Challenge of Solar Energy’s Reliability
Solar energy is dependent on the availability of sunlight, making it inherently intermittent. Cloudy days, rainy weather, and the absence of sunlight during the night pose significant challenges to the consistent generation of solar power. This intermittency can strain power grids and necessitate backup systems to ensure a continuous energy supply. While advances in energy storage technologies, such as batteries, have mitigated this issue to some extent, the need for large-scale storage solutions remains a challenge.
Moreover, the fluctuation in solar energy production throughout the day can lead to grid instability when not properly managed. Without sophisticated grid management and energy storage systems, excess solar energy generated during peak sunlight hours may go to waste, while energy shortages may arise during low sunlight periods. Balancing supply and demand in real-time is crucial to maximize the benefits of solar energy and address the challenge of intermittency.
Efficiency: Unleashing the Full Potential of Sunlight
Another limitation of solar energy lies in the efficiency of photovoltaic (PV) cells, which convert sunlight into electricity. While technological advancements have significantly increased solar panel efficiency over the years, PV cells still have room for improvement. Only a portion of the solar spectrum can be effectively converted into electricity, and factors such as temperature, dirt, and shading can further decrease the efficiency of solar panels.
Additionally, solar energy systems require a substantial amount of space to generate a significant amount of power. In densely populated areas or areas with limited land availability, harnessing sufficient solar energy to meet the energy demands of the population can be a challenge. Moreover, the efficiency of solar panels decreases over time, requiring regular maintenance and replacement to ensure optimal performance. Enhancing the efficiency of solar panels and exploring innovative designs will be crucial in maximizing the potential of solar energy.
Cost and Affordability: The Price of Going Solar
While solar energy offers long-term cost savings through reduced energy bills and potential government incentives, the initial investment required for setting up solar power systems can be a deterrent for many. The high upfront costs of purchasing solar panels, inverters, and other equipment, along with installation expenses, pose a significant barrier to widespread adoption.
Furthermore, the cost of energy storage solutions, such as batteries, can add to the overall expenses. Although the declining costs of solar equipment and technological advancements are gradually making solar energy more affordable, it remains inaccessible to many individuals and communities with limited financial resources. Addressing the cost aspect of solar energy will be essential in making it a viable option for a broader population.
Geographical Limitations: Sunlight Distribution and Solar Energy Potential
The availability of sunlight varies geographically, creating limitations on the potential of solar energy in certain regions. Areas with consistent cloud cover, frequent rain, or short daylight hours may not be as suitable for solar energy generation compared to regions with clear skies and extended periods of sunshine.
Furthermore, regions located closer to the Earth’s poles receive less sunlight intensity throughout the year, making solar energy generation less efficient. The impact of shading from tall buildings, trees, or other structures can also reduce the effectiveness of solar panels, further constraining their potential in specific locations. Understanding the geographical limitations of solar energy is crucial in determining its feasibility and optimizing its deployment on a global scale.
Environmental Considerations: The Lifecycle Impact of Solar Energy
While solar energy is generally regarded as an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels, its production, installation, and disposal can have environmental implications. The manufacturing process of solar panels involves the use of hazardous chemicals and the consumption of energy, contributing to carbon emissions and yielding potential waste management challenges.
Additionally, rare materials such as indium and gallium are required for the production of certain types of solar cells, and the extraction and processing of these resources can have significant environmental impacts. Proper recycling and waste management policies are crucial to reduce the environmental footprint associated with solar energy systems.
Social Acceptance and Integration Challenges
While the potential benefits of solar energy are vast, its implementation is not without social and integration challenges. Some communities and individuals may resist the installation of solar farms or large-scale solar projects due to aesthetic concerns, potential impact on property values, or other reasons. Balancing the need to transition to sustainable energy sources with the concerns of local communities is an ongoing challenge.
Furthermore, integrating solar energy into existing power grids requires careful planning and coordination to ensure compatibility, stability, and optimal use of resources. Upgrading aging infrastructure and implementing the necessary grid management systems can be costly and time-consuming. Overcoming these social and integration challenges is essential to pave the way for a smoother transition to solar energy.
The Way Forward: Addressing and Overcoming Limitations
While solar energy has its limitations, continued research, technological advancements, and policy support can help address and overcome these challenges. Investments in energy storage technologies, improvement of solar panel efficiency, and exploration of innovative designs are critical in maximizing the potential of solar energy.
Furthermore, policies that incentivize the adoption of solar energy and promote access to affordable financing options can enhance its affordability and accessibility. Collaborative efforts from governments, industry stakeholders, and the public will be key in overcoming barriers and fully harnessing the benefits of solar energy.
In conclusion, understanding the limitations of solar energy is crucial in developing a comprehensive perspective on its role in our future energy landscape. Intermittency, efficiency, cost, geographical limitations, environmental considerations, social acceptance, and integration challenges all play a part in shaping the potential of solar energy. By addressing these limitations and leveraging the advantages of solar energy, we can move closer to a sustainable energy future that minimizes our reliance on fossil fuels.
Key Takeaways: Limitations of Solar Energy
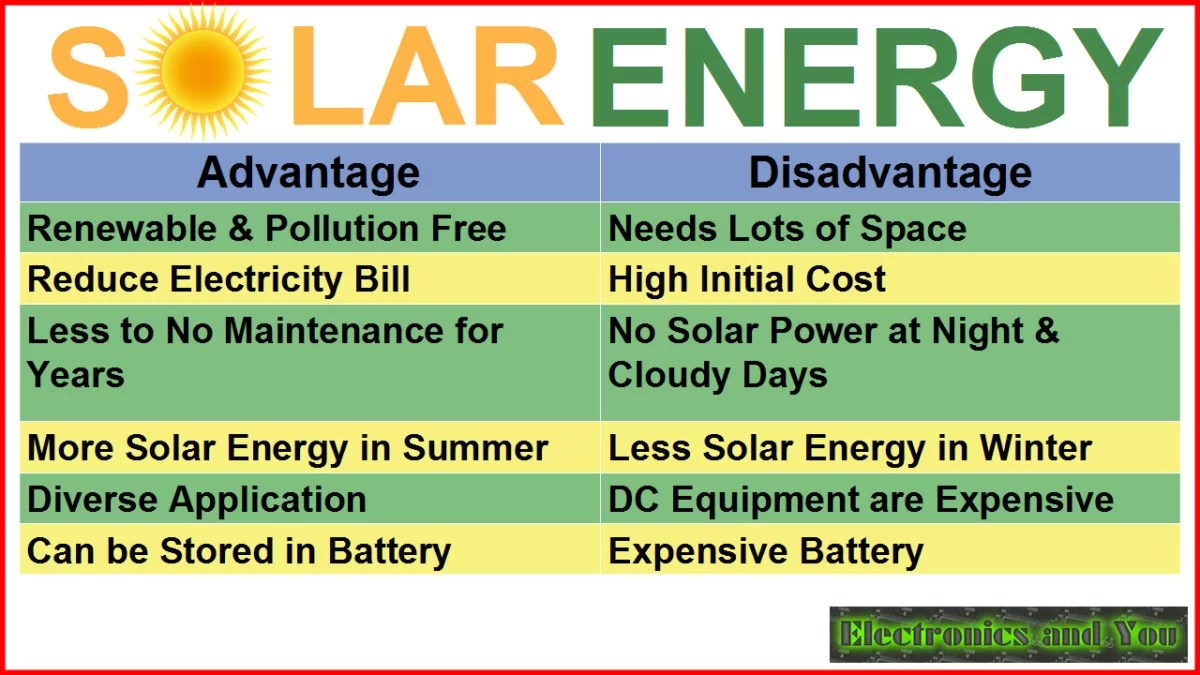
1. Solar energy is dependent on sunlight, so it may not work effectively on cloudy days.
2. Solar panels take up space and may not be suitable for small homes or apartments.
3. The initial cost of installing solar panels can be high, although it can save money in the long run.
4. Solar energy is not available at night, so it requires backup power sources for continuous electricity.
5. The efficiency of solar panels can decrease over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Solar energy is a promising source of renewable energy, but it also has its limitations. Here are some commonly asked questions about the limitations of solar energy:
1. Is solar energy reliable during cloudy or rainy days?
While solar panels do require sunlight to generate electricity, they can still produce energy even on cloudy or rainy days. However, the energy output may be significantly reduced compared to sunny days. This means that during periods of low sunlight, such as winter months or overcast days, the amount of electricity generated by solar panels may be lower than optimal.
Fortunately, there are backup systems and grid-tied connections that allow solar-powered buildings to still have access to electricity during low-sunlight periods. Additionally, advancements in solar technology, such as the development of more efficient panels and energy storage solutions, are helping to minimize the impact of cloudy or rainy days on solar energy generation.
2. Can solar energy meet all of our energy needs?
Solar energy has immense potential, but currently, it cannot fully meet all of our energy needs. The amount of electricity generated by solar panels depends on various factors, including the availability of sunlight, panel efficiency, and the size of the installation. As a result, solar energy alone may not be sufficient to power large-scale industries or heavily energy-dependent activities.
However, solar energy can serve as a significant supplementary source of electricity. By combining solar energy with other renewable sources like wind or hydroelectric power, we can create a more comprehensive and sustainable energy mix. Additionally, advancements in solar technology and increasing adoption of solar panels can bring us closer to achieving a future where solar energy can meet a larger portion of our energy needs.
3. Are there limitations to installing solar panels in all locations?
While solar panels can be installed in various locations, there are some limitations to consider. One primary constraint is the availability of adequate sunlight. Areas with frequent cloud cover or high amounts of shading from trees or buildings may not be ideal for solar panel installations, as they can significantly reduce energy production.
Another factor to consider is the available space for solar panel installation. Rooftop solar installations may require sufficient roof area or the structural capacity to support the panels. Likewise, ground-mounted solar installations require suitable land and may not be feasible in densely populated urban areas.
4. What are the environmental impacts of manufacturing solar panels?
The manufacturing process of solar panels does have some environmental impacts. The production of solar panels involves the extraction and processing of raw materials, such as silicon, which can require energy and generate waste. Additionally, the transportation of materials and the manufacturing facilities themselves can contribute to carbon emissions.
However, it is important to note that these environmental impacts are primarily associated with the production phase and are outweighed by the long-term environmental benefits of using solar energy. Once installed, solar panels produce clean and renewable electricity with minimal negative impacts on the environment.
5. Can solar energy be stored for use during nighttime or periods of low sunlight?
Traditionally, one limitation of solar energy has been its inability to be easily stored for use during nighttime or periods of low sunlight. However, advancements in energy storage technologies, such as batteries, are changing this. Energy storage systems allow excess electricity generated by solar panels during sunny periods to be stored for later use.
These energy storage solutions not only enable solar-powered buildings to have a continuous supply of electricity during nighttime or low sunlight conditions but also help in balancing the overall electricity grid. By storing excess solar energy, we can better manage the fluctuations in supply and demand, making solar energy a more reliable and versatile source of power.
Summary
Solar energy is a great source of renewable power, but it has its limitations. Firstly, solar panels need sunlight to produce electricity, so cloudy days can reduce their efficiency. Secondly, solar panels require a large area of space, which can be a challenge in urban areas or places with limited land availability. Additionally, solar energy is an intermittent source, meaning it can only generate electricity when the sun is shining, so energy storage systems are needed to provide power during nighttime or cloudy periods. Lastly, the production and disposal of solar panels can have environmental impacts, although advancements are being made to address these concerns.
In conclusion, while solar energy is a valuable resource, it is important to consider its limitations and explore other renewable energy options to meet our energy needs.