Is Solar Energy Inexhaustible?
If you’re wondering whether solar energy is inexhaustible, you’ve come to the right place! Solar energy has become increasingly popular as a renewable and sustainable source of power. But what exactly does it mean when we say solar energy is inexhaustible? Well, let’s dive in and find out!
Solar energy is often referred to as an inexhaustible source because it comes from the sun, which is expected to keep shining for billions of years. This means that as long as the sun continues to shine, we will have access to solar energy. It’s like having a never-ending supply of power right at our fingertips!
But what makes solar energy so special? Unlike non-renewable energy sources like coal and oil, solar energy is clean, abundant, and free. By harnessing the power of the sun’s rays through solar panels, we can generate electricity without harming the environment or depleting valuable resources. It’s a win-win situation for us and the planet!
In this article, we will explore the science behind solar energy, its advantages and disadvantages, and its potential for meeting our energy needs in the future. So get ready to embark on a solar-powered journey and discover the incredible potential of this renewable resource! Let’s dive right in!

Is Solar Energy Inexhaustible?
Solar energy is a form of renewable energy that is harnessed from the sun. It has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential to address the growing concerns of climate change and the need for sustainable energy sources. Many argue that solar energy is inexhaustible, meaning it will never run out. In this article, we will explore the concept of solar energy and whether it truly qualifies as an inexhaustible resource.
The Science Behind Solar Energy
Solar energy is derived from the nuclear fusion reactions that occur within the sun. These reactions continuously release a massive amount of energy in the form of heat and light. The Earth intercepts a tiny fraction of this energy, which can then be captured through various technologies, such as solar panels or solar thermal collectors. The captured energy can be converted into electricity or used directly for heating and cooling purposes.
One of the key reasons why solar energy is considered renewable is because it relies on a virtually infinite source: the sun. The sun is expected to continue shining for billions of years, which means we can harness solar energy without depleting the source itself. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and being consumed at an alarming rate, solar energy offers a sustainable alternative that has the potential to meet our energy needs for generations to come.
Furthermore, the process of harnessing solar energy does not produce greenhouse gas emissions, making it a clean and environmentally friendly source of power. With the right infrastructure and advancements in technology, solar energy could play a significant role in mitigating the consequences of climate change and reducing our dependence on fossil fuels.
Advancements in Solar Technology
The field of solar energy has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, leading to increased efficiency and affordability. Here are three key areas where technology has greatly improved:
Solar Panels: Harnessing the Power of Photovoltaics
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) cells, are the most widely recognized form of solar technology. They work by converting sunlight directly into electricity through a process called the photovoltaic effect. Initially, PV cells were expensive and had relatively low efficiency rates, but advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques have made solar panels more cost-effective and efficient than ever before. With ongoing research and development, the efficiency of solar panels is expected to continue improving, making solar energy an even more attractive option for widespread adoption.
Solar Concentrators: Maximizing Energy Capture
Solar concentrators are devices designed to increase the amount of sunlight that reaches solar cells, thereby boosting their energy output. They use lenses or mirrors to focus sunlight onto a smaller area, intensifying its intensity. Concentrated solar power (CSP) plants utilize this technology on a larger scale to generate electricity. By concentrating sunlight, CSP plants can achieve higher temperatures, which allows for more efficient energy conversion. Ongoing research is focused on improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of solar concentrators, making them even more viable as a large-scale energy solution.
Solar Thermal Systems: Utilizing the Heat of the Sun
Solar thermal systems harness the heat from the sun to provide direct heating or generate electricity. They work by capturing solar energy and converting it into thermal energy, which can be used for space heating, water heating, and industrial processes. Solar thermal systems have been used for centuries, with advancements in technology leading to greater efficiency and improved performance. These systems have the potential to provide cost-effective heating solutions for residential and commercial buildings, reducing the reliance on traditional heating sources and further promoting the use of solar energy.
The Limitations of Solar Energy and Future Potential
While solar energy is indeed a promising source of renewable energy, it does have some limitations that need to be addressed for widespread adoption. Here are three key challenges:
Intermittency and Storage
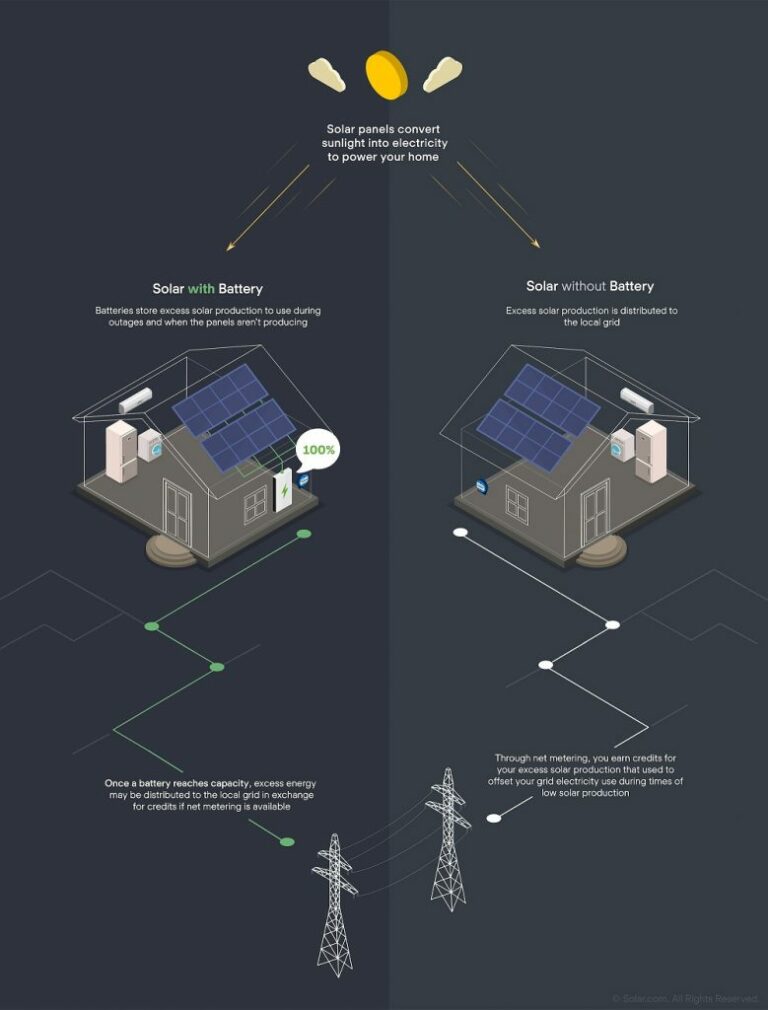
Solar energy is dependent on sunlight, making it intermittent in nature. Energy production is highest during daylight hours and significantly reduced or absent during the night or during inclement weather conditions. To overcome this challenge, the development of efficient energy storage technologies is crucial. Energy storage solutions, such as batteries, can store excess energy produced during optimal periods for use during periods of low or no sunlight. Advancements in battery technology are essential for maximizing the potential of solar energy and ensuring a consistent and reliable power supply.
Land and Space Requirements
Generating significant amounts of solar energy requires a considerable amount of space. Large-scale solar farms or installations can occupy vast areas of land, which may not always be practical or feasible, especially in densely populated regions. However, advancements in technology are enabling the development of more compact and flexible solar solutions, such as solar panels integrated into rooftops or solar windows that can harness sunlight without the need for additional land usage.
Initial Investment and Affordability
The initial cost of installing solar energy systems can be a barrier for many individuals and organizations. While the prices of solar panels have significantly decreased over the years, the overall cost of the system, including installation and maintenance, may still pose a financial challenge. However, as solar technology continues to improve and economies of scale are realized, the cost of solar energy is expected to become more competitive with traditional energy sources. Government incentives and subsidies can also play a crucial role in promoting affordability and encouraging the adoption of solar energy.
The Future of Solar Energy: A Promising Outlook
Solar Energy in Homes and Businesses
The integration of solar energy systems in residential and commercial buildings has gained significant momentum in recent years. Many homeowners and businesses are opting to install rooftop solar panels, allowing them to generate their own electricity, reduce their carbon footprint, and potentially save on energy costs in the long run. As technology advancements continue to drive down costs, solar energy is becoming a more accessible option for consumers, leading to increased adoption and widespread use.
Solar Energy in Developing Nations
In developing nations, where access to reliable electricity may be limited or nonexistent, solar energy presents an opportunity for significant positive change. With a decentralized energy system that can be easily deployed, solar energy can provide clean and sustainable power to communities, allowing them to improve their living conditions, enhance educational opportunities, and stimulate economic growth. Organizations and initiatives focused on bringing solar energy to developing regions are bridging the energy gap and bringing about meaningful change.
Solar Energy and Environmental Impact
The environmental benefits of solar energy cannot be overstated. As more countries and industries transition to renewable energy sources, the reduction in greenhouse gas emissions will aid in combating climate change. Solar energy has the potential to play a crucial role in achieving global sustainability goals, leading to cleaner air, reduced reliance on fossil fuels, and a healthier planet for future generations.
In conclusion, while solar energy may not be truly inexhaustible, it offers an incredibly abundant and sustainable energy source. Advancements in solar technology are making it more efficient and affordable than ever before. As we continue to tackle the challenges associated with solar energy, it’s clear that it has the potential to transform our energy systems and pave the way for a cleaner and greener future.
Key Takeaways
- Solar energy is a renewable source of energy.
- The sun’s energy is inexhaustible, meaning it will never run out.
- Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity.
- Solar energy is clean and does not produce harmful emissions.
- Using solar energy helps reduce our dependence on fossil fuels.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are some common questions about the sustainability of solar energy.
How does solar energy work?
Solar energy is captured by photovoltaic (PV) panels or solar thermal systems. PV panels convert sunlight directly into electricity. Solar thermal systems use sunlight to heat water or air. In both cases, the energy from the sun is harnessed and used for various purposes.
The process of converting sunlight into electricity involves the movement of electrons within silicon cells. When sunlight hits the cells, it generates an electrical charge and creates a direct current (DC). An inverter then converts the DC into alternating current (AC), which is suitable for powering homes and businesses.
Are solar panels made from renewable materials?
Yes, most solar panels are made from renewable materials. The most common type of panel uses silicon, which is derived from sand. Sand is an abundant and naturally occurring resource. The manufacturing process involves extracting silicon from sand and then shaping it into PV cells.
Solar panels also include other materials such as metals and glass, which can be recycled. Additionally, certain manufacturers are exploring the use of more sustainable materials, such as perovskite, which can further enhance the renewable aspect of solar panels.
How long do solar panels last?
Solar panels typically have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years. Most manufacturers offer performance warranties to ensure that the panels maintain a certain level of efficiency during this period. However, it’s important to note that the actual lifespan can vary depending on factors such as maintenance, environmental conditions, and panel quality.
Even after the warranty period, solar panels can continue to generate energy, although their efficiency may gradually decline. Regular maintenance and cleaning can help to optimize their performance and extend their lifespan.
Is solar energy inexhaustible?
Solar energy is considered virtually inexhaustible. The sun is estimated to have a lifespan of about 5 billion years, and it radiates an enormous amount of energy into space every second. The energy we receive from the sun in just one hour could power the entire world for a year.
While the supply of solar energy is indeed finite on a cosmic timescale, it is effectively limitless for practical purposes. As long as the sun continues to shine, we will have access to its energy, making solar power a sustainable and renewable resource.
What are the environmental benefits of solar energy?
Solar energy offers several environmental benefits. Firstly, it does not produce harmful greenhouse gas emissions when generating electricity, unlike fossil fuels. This helps to combat climate change and reduce air pollution.
Additionally, solar energy reduces our reliance on non-renewable energy sources, which are finite and contribute to environmental degradation. By utilizing solar power, we can conserve natural resources and preserve ecosystems. Solar installations also have minimal water requirements, unlike certain conventional power plants, further mitigating strain on water resources.
Summary
Solar energy is a great source of power because it comes from the sun, which will never run out. It is renewable, meaning it can be replenished over and over again. Unlike fossil fuels, solar energy does not produce harmful emissions that harm our planet. Solar panels can be used to capture the sun’s energy and convert it into electricity. Solar power is clean, abundant, and can help reduce our dependence on non-renewable energy sources like coal and oil.
It’s important to note that while solar energy is inexhaustible, it has its limitations. Solar panels are dependent on sunlight, so they may not be as effective in cloudy or shaded areas. Additionally, the cost of installing solar panels can be expensive upfront, although it will eventually save money on electricity bills in the long run. Despite these limitations, solar energy is a promising and sustainable solution for our energy needs, and its potential for growth and innovation makes it an exciting part of our future. So let’s harness the power of the sun and embrace solar energy as an eco-friendly and renewable energy source!