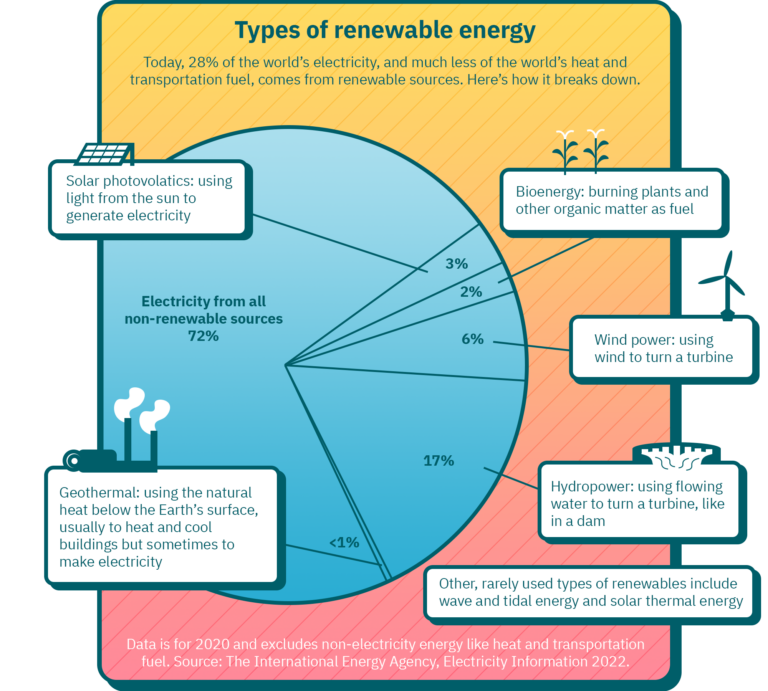
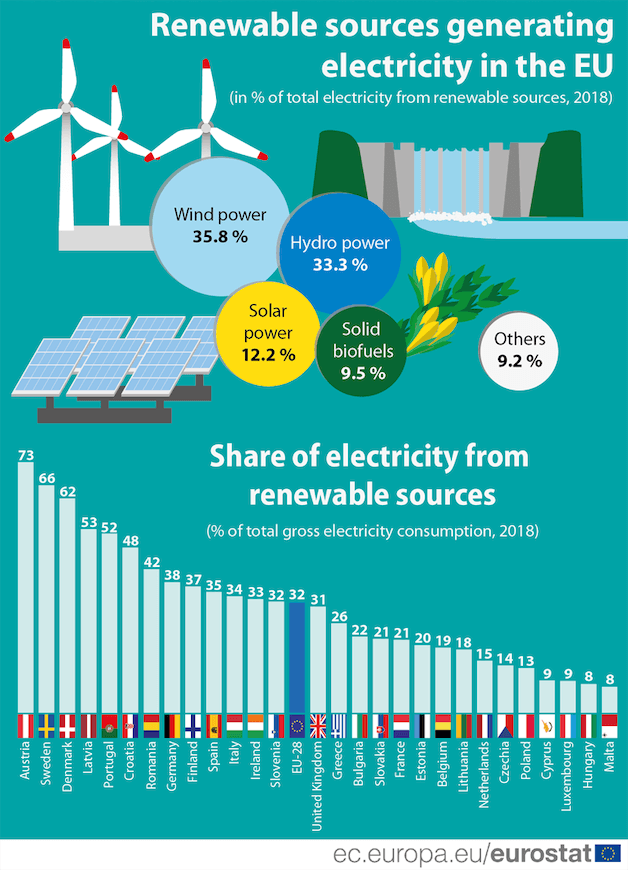
Is Hydroelectric Energy Renewable?
Wondering if hydroelectric energy is renewable? Well, you’ve come to the right place! Let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of hydroelectric power together. 💡
When it comes to renewable energy sources, hydroelectric power is definitely worth discussing. 🌊 It harnesses the power of flowing water, transforming it into electricity without depleting any natural resources. Sounds pretty cool, right?
But, you might be wondering, “How exactly does hydroelectric energy work, and is it really renewable?” 🤔 Don’t worry, my friend, we’ll delve into all of that in just a moment. So, get ready to ride the waves of knowledge with me! 🌊📚

Is Hydroelectric Energy Renewable?
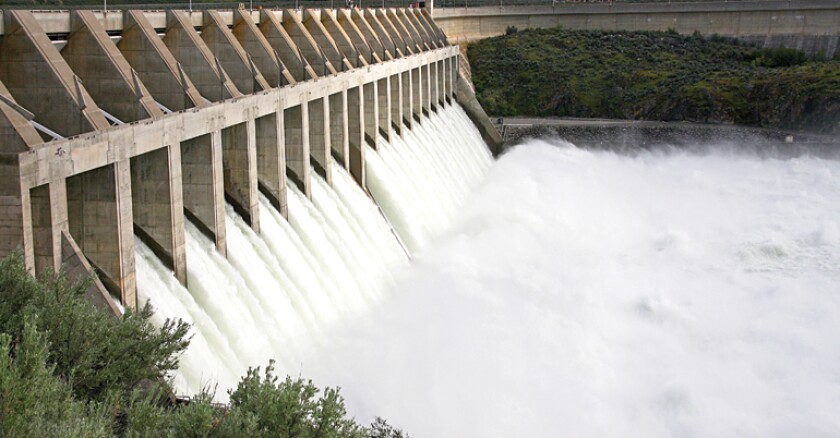
Hydroelectric energy is derived from the power of flowing or falling water. It is considered one of the oldest and most widely used forms of renewable energy. In hydroelectric power plants, water is used to generate electricity by spinning turbines connected to a generator. But is hydroelectric energy truly renewable? In this article, we will delve into the characteristics of hydroelectric energy and its sustainability to answer this question.
Understanding Renewable Energy
Renewable energy is defined as energy obtained from sources that are replenishable and virtually inexhaustible. The key characteristic of renewable energy sources is that they can be naturally replenished within a human lifetime or on a shorter timescale. Examples of renewable energy sources include solar power, wind power, geothermal energy, and, of course, hydroelectric energy. The question arises as to whether hydroelectric energy meets the criteria to be classified as truly renewable.
Hydroelectric energy is generally considered renewable because it relies on the water cycle, a naturally occurring process. The sun’s heat causes water to evaporate from lakes, rivers, and oceans, forming clouds. When the clouds condense, they release precipitation in the form of rain or snow, which then flows into rivers and streams. This water can be harnessed to generate electricity through hydroelectric power plants. As long as the water cycle continues to function, hydroelectric energy can be continuously generated, making it a sustainable and renewable energy source.
However, it is important to note that the construction of hydroelectric power plants can have environmental impacts. Altering natural waterways can disrupt ecosystems and habitats. Dams, in particular, can have significant ecological consequences, including altering water flow, affecting fish migration patterns, and damaging aquatic habitats. Therefore, while hydroelectric energy itself is renewable, it is crucial to carefully consider the environmental and social impacts of individual hydroelectric projects.
The Advantages of Hydroelectric Energy
Hydroelectric energy offers numerous advantages, which contribute to its popularity and widespread usage as a renewable energy source. Firstly, hydroelectric power plants have a long lifespan, often exceeding 50 years. This longevity makes them reliable sources of electricity. Additionally, they have a high level of efficiency, converting around 90% of the energy in falling water into electricity. Compared to other renewable sources like solar or wind power, hydroelectric plants provide a consistent and continuous flow of electricity, making them particularly useful for baseload power generation.
Moreover, hydroelectric energy can help mitigate greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike fossil fuel-based power plants that release carbon dioxide, hydroelectric power plants do not emit greenhouse gases during operation. This makes them a cleaner alternative and contributes to efforts in reducing the carbon footprint of the energy sector. Furthermore, hydroelectric power can be used for various purposes, such as irrigation, flood control, and water supply.
Another advantage of hydroelectric energy is its ability to store and release energy. By utilizing a dam and reservoir system, excess energy can be stored during low-demand periods and released during peak demand. This flexibility enables hydroelectric power plants to respond quickly to changes in electricity demand and maintain a stable grid.
Challenges and Considerations
While hydroelectric energy has many benefits, it also faces certain challenges and considerations. The construction of large-scale hydroelectric power plants often requires the flooding of large areas of land, resulting in the displacement of communities and the loss of ecosystems and wildlife. The disruption of natural water flows can have adverse effects on ecosystems downstream, impacting water quality and resource availability.
Furthermore, hydroelectric projects can be economically demanding, requiring substantial upfront investment. The construction costs of dams and power plants, as well as the maintenance expenses, can be significant. Additionally, the location of potential hydroelectric sites is limited, as they depend on the availability of suitable rivers or bodies of water with sufficient flow and elevation change.
It is also worth noting that climate change can affect the sustainability of hydroelectric energy. Alterations in precipitation patterns and the availability of water resources can impact the amount of water flowing through rivers and affect the overall power generation capacity of hydroelectric plants. Therefore, robust planning and adaptation strategies are necessary to ensure the long-term viability of these energy systems in the face of changing climatic conditions.
Hydroelectric Energy and the Environment
Hydroelectric energy has been regarded as one of the most environmentally friendly sources of electricity generation. Its renewable nature, minimal greenhouse gas emissions, and ability to provide clean energy have garnered attention worldwide. However, it is important to consider the environmental impacts associated with hydroelectric power plants and the measures taken to mitigate these effects.
The Benefits of Hydroelectric Energy for the Environment
One of the primary advantages of hydroelectric energy is its low carbon footprint. Unlike coal or natural gas power plants, hydroelectric power plants do not burn fossil fuels to generate electricity, resulting in minimal greenhouse gas emissions. This makes hydroelectric energy a cleaner alternative and a significant contributor to climate change mitigation efforts.
Hydroelectric power plants also have a positive effect on air quality. By replacing fossil fuel-based plants, hydroelectric facilities reduce air pollution and smog. This has significant health benefits for surrounding communities, as cleaner air improves respiratory health and reduces the risk of respiratory illnesses.
In addition to air quality improvements, hydroelectric power plants offer other environmental benefits. They can help control and mitigate the impact of flooding by regulating the flow of water. Hydroelectric reservoirs can serve as a buffer during heavy rainfall or snowmelt, minimizing the risk of downstream flooding. These reservoirs can also be used for irrigation, providing water to agricultural lands in times of drought and contributing to food security.
Environmental Considerations and Mitigation Measures
Despite the advantages of hydroelectric energy, it is essential to address the potential negative environmental impacts associated with its implementation. The construction of large dams can result in the flooding of large areas, leading to the displacement of communities and the loss of habitats. The alteration of natural river flow patterns can disrupt ecosystems and impact fish migration and wildlife habitats.
Efforts have been made to mitigate these environmental concerns. Environmental impact assessments are conducted before the construction of hydroelectric power plants to identify and address potential risks. Strategies such as fish ladders or fish lifts are employed to provide a safe passage for fish and maintain their migration patterns. In some cases, reservoirs are designed with specific water release schedules to mimic natural water flows and maintain downstream ecosystems.
Additionally, proper management of sediments is crucial in maintaining the ecological balance of rivers. When dams are built, sediments can accumulate behind them, leading to erosion downstream and changes in river ecosystems. Regular sediment flushing and controlled releases can help prevent these issues and preserve river health.
Conclusion
Hydroelectric energy is regarded as a renewable energy source due to its reliance on the continuous water cycle. It offers numerous advantages, including high efficiency, long lifespan, and the ability to store and release energy. While hydroelectric power does have environmental impacts, proper planning and mitigation measures can minimize these effects. Considerations should be given to the social and ecological aspects of each project, ensuring sustainable and responsible implementation.
As the world moves towards a more sustainable future, hydroelectric energy plays a significant role in the renewable energy mix. By harnessing the power of flowing water, we can reduce our dependence on fossil fuels, mitigate climate change, and contribute to a cleaner and greener planet.
Key Takeaways: Is Hydroelectric Energy Renewable?
- Hydroelectric energy is considered a renewable energy source.
- It is generated by harnessing the power of flowing water, such as rivers or dams.
- This energy can be constantly replenished by rainfall and melting snow.
- Hydroelectric power plants produce electricity without emitting greenhouse gases.
- However, the construction of dams can have environmental impacts on ecosystems and wildlife.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we will answer some common questions related to hydroelectric energy and its renewability.
How does hydroelectric energy work?
Hydroelectric energy is generated by the flow of water which spins turbines connected to generators, converting kinetic energy into electricity. This is achieved by building dams to create large reservoirs, which store water. When the dam gates are opened, the force of the water flowing through the turbines generates electricity. This process is clean and does not produce greenhouse gas emissions.
Furthermore, hydroelectric power plants can be constructed in different sizes, from small-scale facilities to large dams, making it a versatile energy source that can adapt to different needs.
Is hydroelectric energy renewable?
Yes, hydroelectric energy is considered a renewable energy source. This is because it relies on the power of water, a naturally replenished resource. As long as there is rainfall or snowmelt, rivers and reservoirs will continue to provide water for hydroelectric power plants, making this energy source sustainable in the long run.
While the construction of dams and reservoirs has an impact on the environment, the actual generation of electricity from water does not deplete or consume the resource, making it a renewable and sustainable energy option.
What are the benefits of hydroelectric energy?
Hydroelectric energy provides numerous benefits. First and foremost, it is a clean and renewable source. It does not emit harmful greenhouse gases, contributing to a reduction in air pollution and combatting climate change. Additionally, hydroelectric power plants have a long lifespan and can operate for several decades, providing a stable and reliable source of electricity.
Hydroelectric plants also offer other advantages such as flood control and water management, as dams can store water during periods of heavy rainfall and release it when needed. They also create reservoirs that can be used for recreational activities such as boating and fishing, benefiting communities and tourism.
Are there any drawbacks to hydroelectric energy?
While hydroelectric energy has many benefits, it also has some drawbacks. One of the main concerns is the environmental impact of building large dams and reservoirs. This can lead to the displacement of communities and the loss of natural habitats. Additionally, the construction process can disrupt local ecosystems and alter the flow of rivers.
Another drawback is the high initial investment required to build hydroelectric power plants. Constructing dams, turbines, and transmission lines can be costly. However, once the infrastructure is in place, the operating costs are relatively low, making it a cost-effective long-term solution.
Is hydroelectric energy widely used?
Yes, hydroelectric energy is one of the most widely used renewable energy sources. It accounts for a significant portion of global electricity production. Many countries have invested in hydroelectric power plants, leveraging the power of water to generate clean and renewable energy. In fact, some countries heavily rely on hydroelectric energy for their electricity needs.
In addition to large-scale hydroelectric power plants, there are also smaller, decentralized hydroelectric systems that generate electricity for remote or off-grid areas. These systems can provide sustainable energy solutions for communities located in areas with abundant water resources.
Summary
So, is hydroelectric energy renewable? The answer is yes! Hydroelectric power is generated by water, which is a renewable resource. It doesn’t get used up or run out. As long as we have flowing water, we can continue to generate electricity from it. Plus, hydroelectric power doesn’t produce harmful emissions, making it a clean source of energy.
However, there are some environmental impacts to consider. Building dams for hydroelectric power plants can disrupt ecosystems and displace wildlife. It’s important to strike a balance between harnessing the power of water and preserving the natural environment. So while hydroelectric energy is renewable, we must be mindful of its potential effects on the planet.