Is Coal Energy Renewable?
Coal energy has been a significant part of our energy production for many years, but have you ever wondered if it’s renewable? Well, let’s dive into the world of coal and find out the answer! 🕵️
When it comes to renewable energy sources, we often think of options like solar or wind power. But what about coal? Is coal energy renewable? 🤔
In this article, we’ll explore the characteristics of coal energy and discuss whether it can be considered a renewable source. So, grab a seat and let’s unravel the mysteries of coal power together! 💪
Coal energy is not considered renewable because it is a fossil fuel that is formed from the remains of plants and animals that lived millions of years ago. Unlike renewable energy sources like solar or wind power, coal is a finite resource that takes millions of years to form. Additionally, burning coal emits harmful greenhouse gases and contributes to climate change. Therefore, it is important to transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy alternatives.
Is Coal Energy Renewable?
Coal energy has been a long-standing source of power for industries and households alike. However, there is ongoing debate about whether or not coal can be considered a renewable energy source. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of coal energy, its origins, and its sustainability in order to answer the question: Is coal energy renewable?
Understanding Coal Energy
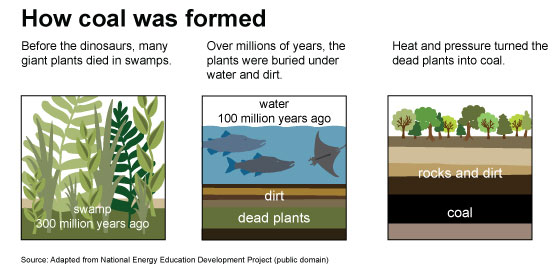
Coal is a fossil fuel that forms over millions of years from the remains of plants and trees that lived and died long ago. It is extracted through mining and is primarily composed of carbon, along with small amounts of hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen. The combustion of coal is the primary means by which it is used for energy production.
Coal energy has been a central component of the global energy mix for centuries. It has played a significant role in driving industrialization and meeting the growing demands of modern society. However, as concerns about the impact of fossil fuels on climate change mount, the sustainability of coal as an energy source has come under scrutiny.
The Non-Renewable Nature of Coal Energy
Coal is classified as a non-renewable energy source, meaning that it is finite and cannot be replenished within a human lifetime. This is in contrast to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, which are continuously replenished by natural processes and will not be depleted over time.
The formation of coal requires millions of years of geological processes under specific conditions. The rate at which coal is being consumed far exceeds the rate at which it is being formed, making it a depletable resource. Once extracted and burned for energy, it cannot be reused or replenished in any meaningful way.
The extraction and combustion of coal also have several detrimental environmental impacts. The release of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, contributes to climate change. Furthermore, coal mining can lead to land degradation, water pollution, and harm to ecosystems and wildlife.
The Role of Coal and Its Future
Despite being a non-renewable energy source, coal continues to be widely used for electricity generation and industrial processes globally. Its abundance, affordability, and reliability have made it a preferred choice, especially in countries with significant coal reserves.
However, the negative environmental and health impacts associated with coal have prompted a global shift towards cleaner and more sustainable forms of energy. Governments, businesses, and individuals are increasingly investing in renewable energy sources to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change.
While the future of coal energy remains uncertain, it is clear that transitioning to renewable energy sources is essential for a sustainable and greener future. Continued innovation, investment, and policy support are needed to accelerate the adoption of renewable energy technologies and reduce our reliance on coal and other fossil fuels.
Benefits of Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources offer several benefits over coal energy and other fossil fuels. These include:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Renewable energy sources produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions, helping to combat climate change.
- Inexhaustible supply: Unlike coal, renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power will not run out.
- Job creation: The renewable energy sector has the potential to generate numerous new job opportunities.
- Improved air quality: Fossil fuel combustion releases pollutants that can harm human health. Shifting to renewables can improve air quality and public health.
- Energy independence: Relying on renewable energy sources reduces dependence on foreign oil and increases energy security.
Transitioning to Renewable Energy
Transitioning to renewable energy sources is a complex and multifaceted process that requires the collaboration and effort of governments, businesses, and individuals. Here are a few tips for supporting and accelerating the transition to renewables:
1. Support Policy Changes
Lobby for policies that incentivize the development and adoption of renewable energy technologies. This can include tax incentives, feed-in tariffs, and renewable portfolio standards.
2. Invest in Renewable Energy
Consider investing in renewable energy companies or projects through stocks, funds, or crowdfunding platforms. This can help drive the growth of renewable energy and generate financial returns.
3. Conserve Energy
Reducing your overall energy consumption can help decrease the demand for fossil fuels, including coal. Implement energy-efficient measures in your home, such as using LED bulbs, insulating walls, and upgrading to energy-efficient appliances.
The Way Forward
While coal energy has played a significant role in powering our society, its non-renewable nature and environmental impact cannot be ignored. As we move towards a cleaner and more sustainable energy future, the transition to renewable energy sources becomes vital. By investing in renewables, supporting policy changes, and conserving energy, we can create a greener and healthier world for generations to come.
Key Takeaways: Is Coal Energy Renewable?
- Coal energy is not renewable because it is a fossil fuel formed from the remains of ancient plants and animals.
- Coal takes millions of years to form, so it cannot be replenished within a human lifetime.
- Using coal for energy releases greenhouse gases and contributes to climate change.
- Relying on coal energy can lead to environmental pollution and negative health effects.
- Investing in renewable energy sources like solar and wind power is a more sustainable choice for the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our Frequently Asked Questions section about coal energy and its renewability. Below, you’ll find answers to common queries regarding this topic. Take a look!
Q: How is coal formed and why is it considered an energy source?
Coal is formed over millions of years as ancient plants and organisms decompose and undergo a process called carbonization. This organic material transforms into solid rock-like substances known as coal. It is considered an energy source because it contains combustible carbon and produces heat when burned. This heat is harnessed to generate electricity in power plants and other industries.
Coal’s energy content and availability make it an attractive option for powering electricity grids, especially due to its abundance in many regions worldwide. However, there are concerns about its environmental impact due to carbon emissions and other pollutants released during combustion.
Q: Is coal energy renewable or non-renewable?
Coal energy is classified as non-renewable. This means that it is not naturally replenished at a rate that matches its consumption. Coal formation takes millions of years, so once we deplete the coal reserves, they cannot be replaced within a human lifetime. Non-renewable energy sources, like coal, also contribute to environmental issues such as air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
The limited nature of coal reserves highlights the need for more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternatives, such as renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower.
Q: Are there any sustainable practices associated with coal energy?
While coal energy itself is non-renewable, there are some practices aimed at making its extraction and consumption more sustainable. One such practice is known as “clean coal technology.” This involves implementing technologies that reduce carbon emissions and other pollutants released during the burning of coal.
Examples of clean coal technologies include carbon capture and storage, where carbon dioxide is captured before or after combustion and stored underground. Additionally, coal plants can use advanced filters and scrubbers to remove other harmful emissions, helping to minimize their environmental impact.
Q: What are the main environmental concerns associated with coal energy?
Coal energy poses several environmental concerns. The primary issue is the release of carbon dioxide (CO2) when coal is burned, which contributes to climate change and global warming. Burning coal also emits other pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter, which can have detrimental effects on human health and ecosystems. Coal mining can also result in habitat destruction, water pollution, and land subsidence.
To mitigate these environmental concerns, there have been efforts to transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, reduce coal consumption, and improve the efficiency of coal-fired power plants through the use of cleaner technologies.
Q: What are the advantages and disadvantages of using coal energy?
The advantages of using coal energy include its abundance and availability in many regions, its energy density, and its historical contribution to economic development. Coal has also played a significant role in electricity generation, providing a reliable base load of power.
On the other hand, the disadvantages of coal energy include its non-renewable nature, environmental impacts such as air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, the extraction and mining issues associated with it, and the finite supply of coal reserves. Additionally, the economics of coal are influenced by factors such as market demand, transportation costs, and competing cleaner energy sources.
Renewable Energy Beats Coal
Summary
So, is coal energy renewable? The answer is no. Coal is a fossil fuel, meaning it takes millions of years to form. Once we use it up, it’s gone. Plus, burning coal releases harmful greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change.
But wait, there’s good news! There are other renewable energy sources like solar and wind power that are cleaner and won’t run out. So, let’s focus on using these sustainable options and leave coal behind for a healthier planet.