Is Chemical Energy Renewable?
Is chemical energy renewable? Well, let’s dive into this fascinating topic and explore the world of energy sources. 🌍💡
When it comes to renewable energy, we often think about solar power and wind turbines. But what about chemical energy? 🤔
Chemical energy is found in various forms, such as fossil fuels like coal and oil, as well as batteries and hydrogen fuel cells. But here’s the catch: while some sources of chemical energy are renewable, not all of them are. 🔄
So, in this article, we’ll take a closer look at chemical energy, its different sources, and determine which ones are renewable and which ones are not. Are you ready? Let’s get started! 🚀🔬

Is Chemical Energy Renewable?
Chemical energy plays a significant role in our daily lives, powering various processes and technologies. However, when it comes to sustainability, the question arises: Is chemical energy renewable? In this article, we will explore the nature of chemical energy, its sources, and its impact on the environment. By understanding the characteristics and limitations of chemical energy, we can assess its renewable potential and make informed decisions about our energy consumption.
The Nature of Chemical Energy
Chemical energy is a form of potential energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules. It is released through chemical reactions, such as combustion, where the complex molecules break down into simpler compounds, liberating energy in the process. Common sources of chemical energy include fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, as well as renewable sources like biomass and biofuels.
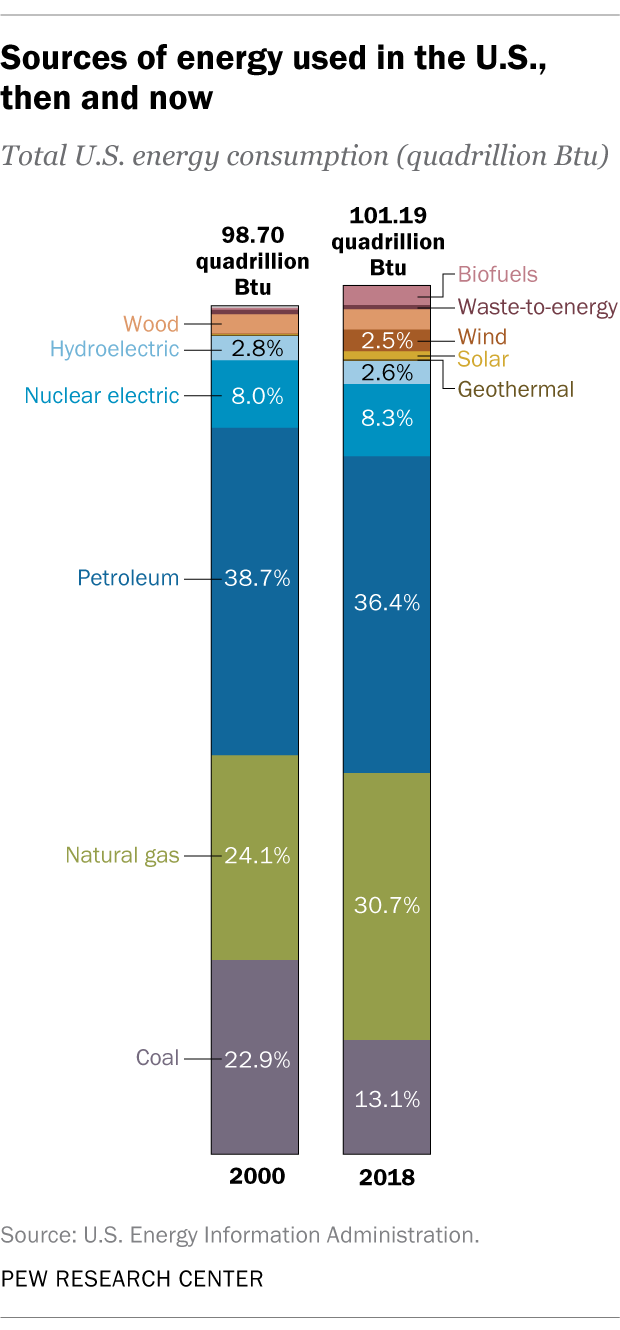
Fossil fuels, formed over millions of years from ancient organic matter, contain stored chemical energy. When burned, these fuels release carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change. In contrast, renewable sources of chemical energy, such as biomass and biofuels, are derived from organic materials, such as plants and waste, which can be replenished relatively quickly. This makes them more environmentally friendly and potentially sustainable.
Renewable Chemical Energy Sources
Now let’s delve deeper into some specific sources of chemical energy and explore their renewable potential:
1. Biomass
Biomass refers to organic material, such as plants, agricultural residues, and even certain types of waste. Biomass can be converted into biofuels, such as ethanol, biodiesel, and biogas, through processes like fermentation and anaerobic digestion. These biofuels can provide an alternative to fossil fuels and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. While biomass is a renewable resource, its environmental impact and sustainability depend on responsible harvesting and management practices to ensure that it regenerates or replants itself.
2. Hydrogen
Hydrogen is often hailed as a clean and renewable source of energy. As a chemical element, hydrogen can be extracted from various sources, such as water, natural gas, and biomass. It can then be used as a fuel in fuel cells or combustion engines, producing only water vapor as a byproduct. Furthermore, hydrogen can be produced using renewable electricity through a process called electrolysis. However, hydrogen production is currently energy-intensive and relies heavily on non-renewable sources, limiting its true renewable potential.
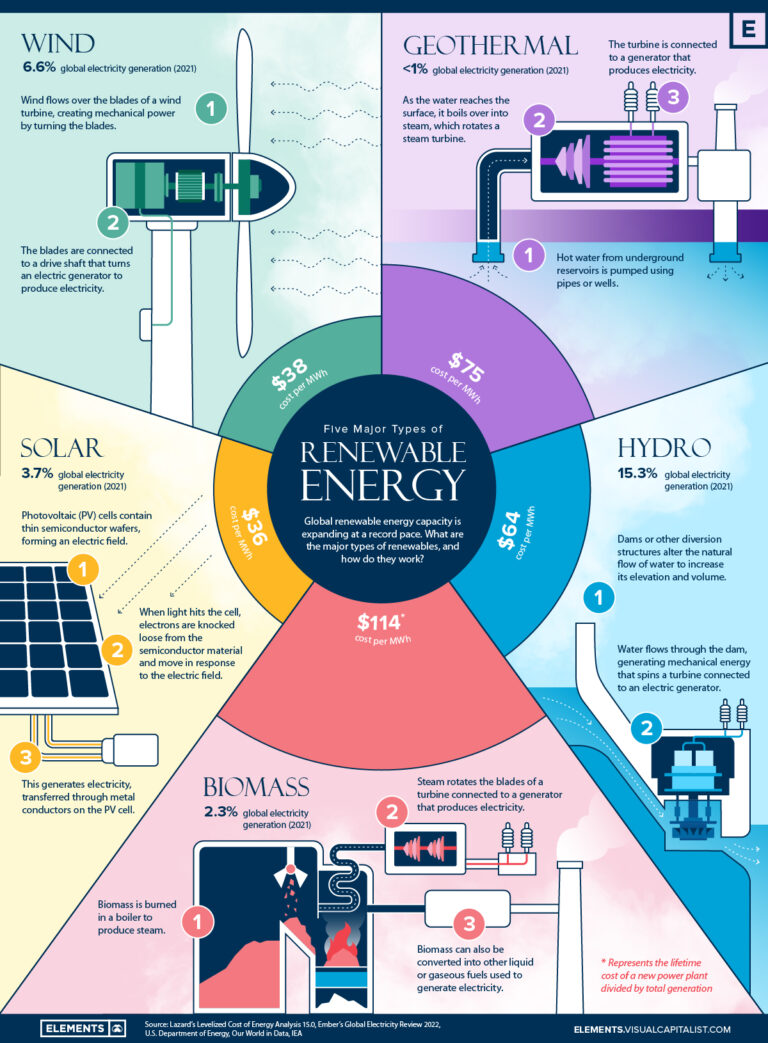
3. Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy harnesses the heat stored within the Earth’s crust, which is a form of chemical energy. By tapping into underground reservoirs of hot water or steam, geothermal power plants generate electricity. This process produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions and has a nearly inexhaustible supply, making it a promising renewable energy source. However, the accessibility of geothermal resources is limited to certain regions, which means widespread adoption may not be feasible in every location.
4. Fuel Cells
Fuel cells are devices that convert the chemical energy of a fuel directly into electricity, without combustion. They typically use hydrogen as the fuel and, similar to hydrogen production, their renewable potential depends on the source of hydrogen. If hydrogen is produced from renewable sources, such as wind or solar power, fuel cells can contribute to a more sustainable energy system. However, the current infrastructure and cost limitations pose challenges to widespread deployment of fuel cells.
Challenges and Considerations
While some sources of chemical energy are considered renewable, several challenges and considerations should be addressed to ensure their sustainable and responsible use:
1. Environmental Impact
The extraction, production, and use of chemicals for energy can have environmental consequences. It is crucial to minimize the negative impacts, such as deforestation for biomass production or the release of harmful byproducts during chemical reactions. Implementing stringent regulations and adopting technologies that reduce pollution and resource consumption are essential in maximizing the renewable potential of chemical energy sources.
2. Efficiency
The efficiency of energy conversion and utilization is another crucial aspect to consider. Renewable chemical energy sources should be able to provide consistent and reliable energy while minimizing waste. Research and development efforts aim to improve the efficiency of energy conversion technologies, making them economically viable and competitive with traditional fossil fuel-based systems.
3. Scalability
For chemical energy sources to truly have a significant impact on global energy consumption, they need to be scalable to meet the growing demand. While certain sources, like biomass, may offer potential scalability, others, such as geothermal energy, are limited by their geographic distribution. Promoting technological advancements and investing in infrastructure are necessary steps to ensure widespread adoption and utilization of renewable chemical energy sources.
Key Takeaways: Is Chemical Energy Renewable?
- Chemical energy is not considered renewable because it relies on the extraction and consumption of finite resources.
- Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are considered sustainable alternatives to chemical energy.
- Chemical energy is derived from the combustion of fossil fuels, which release greenhouse gases and contribute to climate change.
- By transitioning to renewable energy sources, we can reduce our dependence on non-renewable chemical energy and mitigate environmental impact.
- Understanding the difference between renewable and non-renewable energy is important for making informed choices about energy consumption.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our FAQ page on chemical energy. Here, we will answer some common questions related to the topic. Whether you’re curious about the renewability of chemical energy or just want to learn more, we’ve got you covered!
1. How is chemical energy different from other forms of energy?
Chemical energy is a type of potential energy stored within the bonds of atoms and molecules. It is released through chemical reactions. Unlike other forms of energy such as solar or wind energy, chemical energy is not directly derived from natural resources like the sun or wind. Instead, it is obtained through the conversion of other forms of energy into chemical compounds.
Chemical energy is incredibly versatile and is present in various everyday objects, from food to batteries. It plays a crucial role in powering our lives and enabling countless reactions and processes in both nature and technology.
2. Is chemical energy considered a renewable source of energy?
In general, chemical energy is not considered a renewable source of energy. This is because most chemical energy comes from finite resources, such as fossil fuels, which are formed over millions of years and cannot be replenished in a short period of time.
However, it’s important to note that there are some exceptions. For example, certain chemical processes can utilize renewable resources like biomass to produce energy. Additionally, advancements in technology may create new ways of harnessing chemical energy from renewable sources in the future.
3. What are the advantages of chemical energy?
Chemical energy offers several advantages. Firstly, it is a highly concentrated source of energy, allowing for compact storage and transportation. It is also easily convertible into other forms of energy, making it versatile for various applications. Additionally, chemical reactions can release large amounts of energy quickly, making it suitable for tasks that require a rapid energy release.
Another advantage of chemical energy is that it can be stored relatively easily and for long periods of time. This means it can serve as a backup source of energy or be used in situations where a continuous energy supply is not available, such as in remote locations or during power outages.
4. What are the environmental implications of using chemical energy?
The use of chemical energy, particularly from non-renewable sources like fossil fuels, can have significant environmental implications. The combustion of fossil fuels releases harmful pollutants such as carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change and air pollution.
However, utilizing chemical energy from renewable sources or adopting cleaner technologies can help mitigate these environmental impacts. Transitioning to cleaner forms of chemical energy, as well as embracing energy efficiency and conservation practices, can contribute to a more sustainable future.
5. How can we reduce our reliance on non-renewable forms of chemical energy?
Reducing our reliance on non-renewable sources of chemical energy involves various strategies. One approach is to embrace energy conservation and efficiency measures, optimizing the use of energy in our daily lives and reducing waste.
Additionally, transitioning to renewable sources of energy, such as solar or wind power, can help decrease the demand for non-renewable chemical energy. Supporting and investing in research and development of cleaner technologies, such as hydrogen fuel cells or advanced battery systems, is also crucial to reduce our dependence on non-renewable chemical energy sources.
Summary
Chemical energy is not renewable because it comes from fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gas. These resources take millions of years to form and will eventually run out. Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power are better for the environment because they can be replenished naturally and won’t run out as quickly as fossil fuels. It’s important to transition to more renewable energy sources to reduce our impact on the planet and ensure a sustainable future.