Is Biomass Energy Renewable Or Nonrenewable?
When it comes to energy sources, there’s always the question of whether they are renewable or nonrenewable. So, is biomass energy renewable or nonrenewable? Let’s find out!
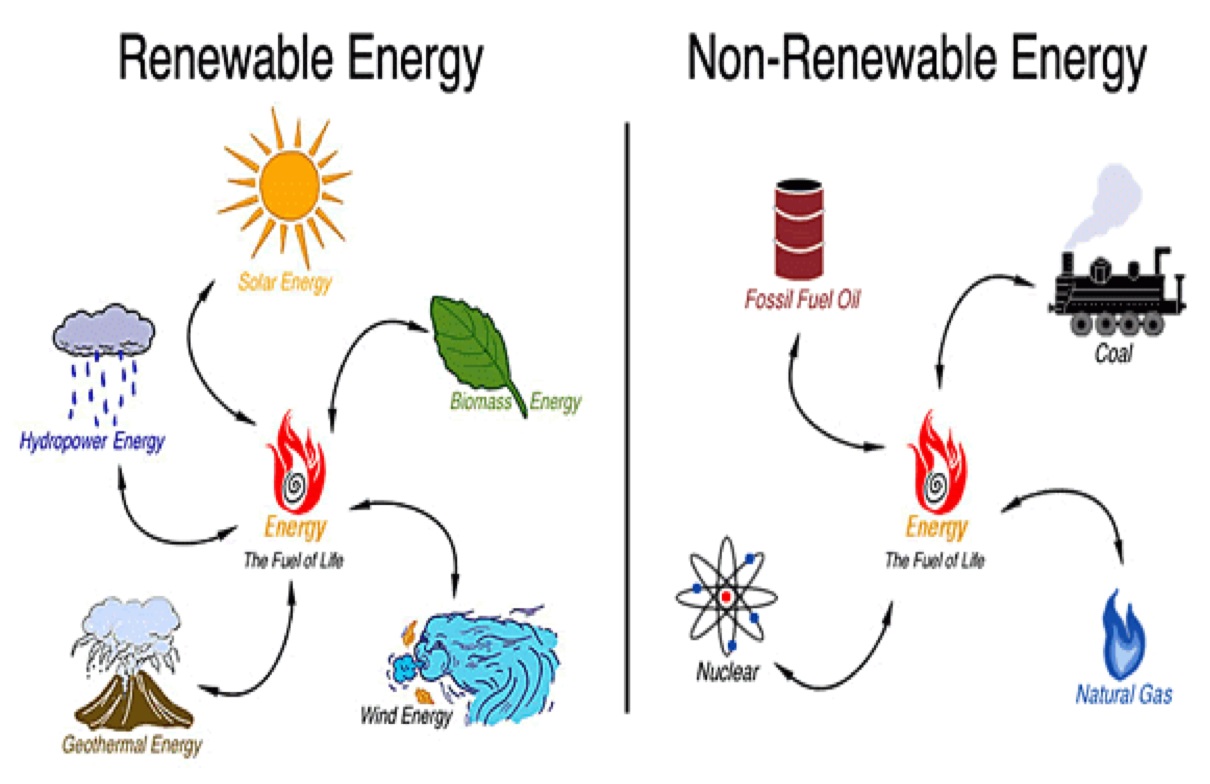
You may have heard of biomass energy before, but what exactly is it? Well, it’s energy that comes from organic matter, such as plants, crop waste, or even animal manure. Sounds pretty interesting, right?
Now, the big question is whether biomass energy is renewable or nonrenewable. Well, buckle up, because we’re about to dive into the fascinating world of renewable energy!
Is Biomass Energy Renewable or Nonrenewable?
When it comes to sustainable energy sources, one question that often arises is whether biomass energy is renewable or nonrenewable. Biomass energy refers to the energy obtained from organic matter such as plants, agricultural waste, and wood pellets. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of biomass energy and examine whether it is truly a renewable resource.
Environmental Impact of Biomass Energy
One of the key factors in determining whether biomass energy is renewable or nonrenewable is its impact on the environment. Biomass is derived from living or recently living organisms, making it a potentially renewable resource. The carbon emitted during the burning of biomass can be offset by the carbon absorbed during the growth of new plants. However, there are some nuances to consider.
Firstly, the sustainability of biomass energy depends on responsible management of the biomass sources. It is crucial to ensure that the plants used for biomass are grown and harvested in a sustainable manner, avoiding deforestation and promoting reforestation practices. Additionally, the efficiency of biomass energy conversion technologies plays a significant role. Advanced technologies that optimize energy production and minimize emissions are essential for the continued sustainability of biomass energy.
Furthermore, the availability of biomass resources also affects its renewability. If biomass is extracted and utilized faster than it can be replenished, it can lead to depletion of resources and ultimately make biomass energy nonrenewable. Therefore, proper management of biomass sources and a thorough understanding of their growth rates are critical for ensuring the long-term sustainability of biomass energy.
The Benefits and Challenges of Biomass Energy
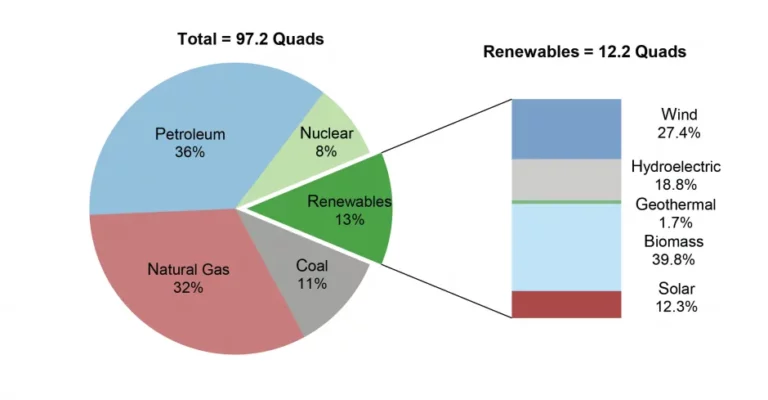
Biomass energy offers several benefits that contribute to its appeal as a renewable energy source. For starters, biomass is a widely available resource, as plant materials and agricultural waste can be found in abundance. This availability makes biomass energy a valuable alternative to fossil fuels.
In addition to being a renewable energy option, biomass energy also helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions. When organic waste decomposes naturally, it releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas. By using biomass as an energy source, this waste can be diverted and turned into a useful energy resource, reducing methane emissions and contributing to climate change mitigation.
Despite its advantages, biomass energy does face some challenges. One major concern is the emissions released during the combustion process. While biomass energy is generally considered carbon-neutral, there are still emissions of carbon dioxide and other pollutants. The efficiency of combustion technologies plays a crucial role in reducing these emissions and minimizing the environmental impact of biomass energy.
Biomass vs. Fossil Fuels: A Comparison
When comparing biomass energy with fossil fuels, the renewable nature of biomass becomes more apparent. Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, are formed over millions of years and are considered nonrenewable resources. Once they are depleted, they cannot be replenished within a human lifetime.
On the other hand, biomass energy relies on organic materials that can be grown within a relatively short timeframe. This makes biomass a sustainable energy option that has the potential to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate the environmental impacts associated with their extraction and use.
Additionally, biomass energy offers a form of decentralized energy production. Unlike fossil fuels, which often require extensive infrastructure to extract, process, and distribute, biomass energy can be generated locally, reducing the need for long-distance transportation and minimizing energy losses associated with transmission.
Tips for Promoting Sustainable Biomass Energy
To ensure the long-term sustainability of biomass energy, certain practices and considerations can be implemented:
- Invest in research and development to improve biomass conversion technologies and increase efficiency.
- Promote responsible sourcing and management of biomass resources, including reforestation efforts.
- Encourage the use of advanced pollution control technologies to minimize emissions in biomass combustion processes.
- Support policies and incentives that prioritize the development and utilization of sustainable biomass energy.
- Educate the public about the benefits of biomass energy and its role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting a cleaner energy future.
The Future of Biomass Energy
As the world seeks to transition to a more sustainable and carbon-neutral energy system, biomass energy is likely to play a vital role. However, its sustainability hinges on responsible management of biomass resources, technological advancements, and a commitment to reducing environmental impacts.
Prospects for a Renewable Future
While ongoing debates may surround the renewability of biomass energy, it is clear that with responsible management and technological innovation, biomass has the potential to be an essential component of a renewable energy future. By incorporating sustainable practices, optimizing energy conversion technologies, and promoting awareness and education, we can leverage biomass energy’s benefits while minimizing its drawbacks. It is crucial that we continue to explore and develop renewable energy solutions like biomass to address our current energy needs and secure a more sustainable and cleaner future for generations to come.
Key Takeaways: Is Biomass Energy Renewable or Nonrenewable?
- Biomass energy is considered renewable because it comes from organic materials like plants, crop residues, and wood.
- These organic materials can be regrown or replenished, making biomass energy a sustainable energy source.
- However, biomass energy can also be nonrenewable if it is obtained from unsustainable practices like deforestation.
- Efficient and responsible management of biomass resources is crucial to ensure the sustainability of biomass energy.
- Using biomass energy can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about biomass energy and whether it is considered renewable or nonrenewable.
1. How is biomass energy generated?
Biomass energy is generated by converting organic materials, such as plants or crops, into fuel. This fuel can be burned directly or transformed into other forms of energy, such as heat or electricity. The process of converting biomass into usable energy often involves combustion, gasification, or fermentation.
To put it simply, biomass energy is created by harnessing energy from the sun. Plants absorb sunlight through photosynthesis, converting it into chemical energy. When these plants or their by-products are used as fuel, their stored energy is released, generating biomass energy.
2. Is biomass energy considered renewable?
Yes, biomass energy is generally considered to be renewable. Biomass fuels come from organic matter, which can be replenished within a relatively short period of time. Trees, crops, and other plants used for biomass can be grown and harvested on a renewable basis, making biomass energy sustainable in the long run.
However, it’s important to note that the sustainability of biomass energy depends on responsible management and sourcing practices. Ensuring that biomass is harvested and used in a way that promotes regrowth and biodiversity is crucial for maintaining its renewable status.
3. What are the benefits of using biomass energy?
There are several benefits to using biomass energy. First and foremost, biomass is a renewable resource, so it can help reduce dependence on fossil fuels and contribute to a more sustainable energy mix.
Additionally, biomass energy can have positive environmental impacts. It produces lower levels of greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, helping to mitigate climate change. Biomass energy also reduces waste by utilizing organic materials that would otherwise decompose and release methane gas, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere.
4. Are there any drawbacks or challenges associated with biomass energy?
While biomass energy has its advantages, there are also some challenges and considerations to keep in mind. One key challenge is the potential impact on land use and food crops. As biomass production increases, there is a risk of diverting land away from food production, potentially impacting food security and prices.
Another consideration is the emissions from biomass combustion. While biomass energy emits lower amounts of greenhouse gases compared to fossil fuels, it still releases carbon dioxide. It is crucial to ensure that the overall emissions from the entire lifecycle of biomass energy are properly managed to minimize environmental impacts.
5. How widely is biomass energy used?
Biomass energy is used worldwide, although its prevalence varies by country and region. In some areas, biomass is a significant source of energy for heating, cooking, and electricity generation. For example, many households in rural areas depend on biomass, such as wood or agricultural residues, for their energy needs.
On a larger scale, biomass energy is also utilized by industries and power plants to produce heat and electricity. The use of biomass as an energy source is expected to grow as countries seek to reduce their carbon footprints and transition to more sustainable energy systems.
What is Biomass? A Renewable Energy Source that Puts Organic Waste to Use
Summary
So, is biomass energy renewable or nonrenewable? Well, the answer is not so simple. Biomass energy can be considered renewable when the sources used, like plants and trees, are replaced at the same rate they are consumed. However, if we cut down trees faster than we can grow them, biomass energy becomes nonrenewable.
On the plus side, biomass energy has many benefits. It can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, support local economies, and provide a reliable energy source. Yet, it also has its challenges, such as the potential for deforestation and competition for land and resources.
So, the key is to manage biomass energy sustainably, using it wisely and ensuring that the sources are replenished so future generations can continue to use this form of renewable energy.