How Renewable Energy Grid Integration Takes Place?
Have you ever wondered how renewable energy is integrated into the power grid? Well, you’re in the right place! In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating process of how renewable energy grid integration takes place.
Imagine a world where our energy comes from clean and sustainable sources like solar and wind power. It’s not just a dream, it’s a reality that we’re actively working towards. But how does it all work? Let’s dive in and uncover the ins and outs of renewable energy grid integration.
From capturing energy from the sun and wind to transforming it into electricity and finally delivering it to our homes, there’s a lot that goes on behind the scenes. So, let’s roll up our sleeves and embark on this exciting journey to discover how renewable energy becomes an integral part of our power grid.
1. Assessment: Evaluate the potential of renewable energy in the region.
2. Planning: Develop strategies for integrating renewable energy into the grid.
3. Grid Upgrades: Enhance the grid’s capacity to handle renewable energy.
4. Connection: Establish connections between renewable energy generators and the grid.
5. Monitoring: Continuously monitor and manage the integration for optimal performance.
By following these steps, renewable energy can be seamlessly integrated into the power grid, promoting a sustainable and cleaner energy future.
How Renewable Energy Grid Integration Takes Place?
Renewable energy grid integration is the process of incorporating renewable energy sources into the existing power grid. As the world moves towards sustainable and clean energy alternatives, the integration of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power becomes crucial. This article will explore the various aspects of how renewable energy grid integration takes place and its significance in the transition to a greener future.
1. Planning and Forecasting
The first step in the process of renewable energy grid integration is careful planning and forecasting. This involves assessing the potential renewable energy sources in a particular region and estimating their generation capacity. Detailed studies are conducted to determine the optimal locations for solar panels, wind turbines, or hydroelectric power plants. Additionally, sophisticated forecasting tools are utilized to predict the availability and variability of renewable energy generation.
Once the potential of renewable energy sources is assessed, grid operators and utilities strategically plan how to integrate this energy into the existing infrastructure. This includes upgrading transmission and distribution systems, designing new interconnection points, and ensuring efficient power flow management. The planning phase also considers factors such as power quality, system stability, and load balancing to ensure a reliable supply of electricity.
2. Interconnection and Smart Grid Technologies
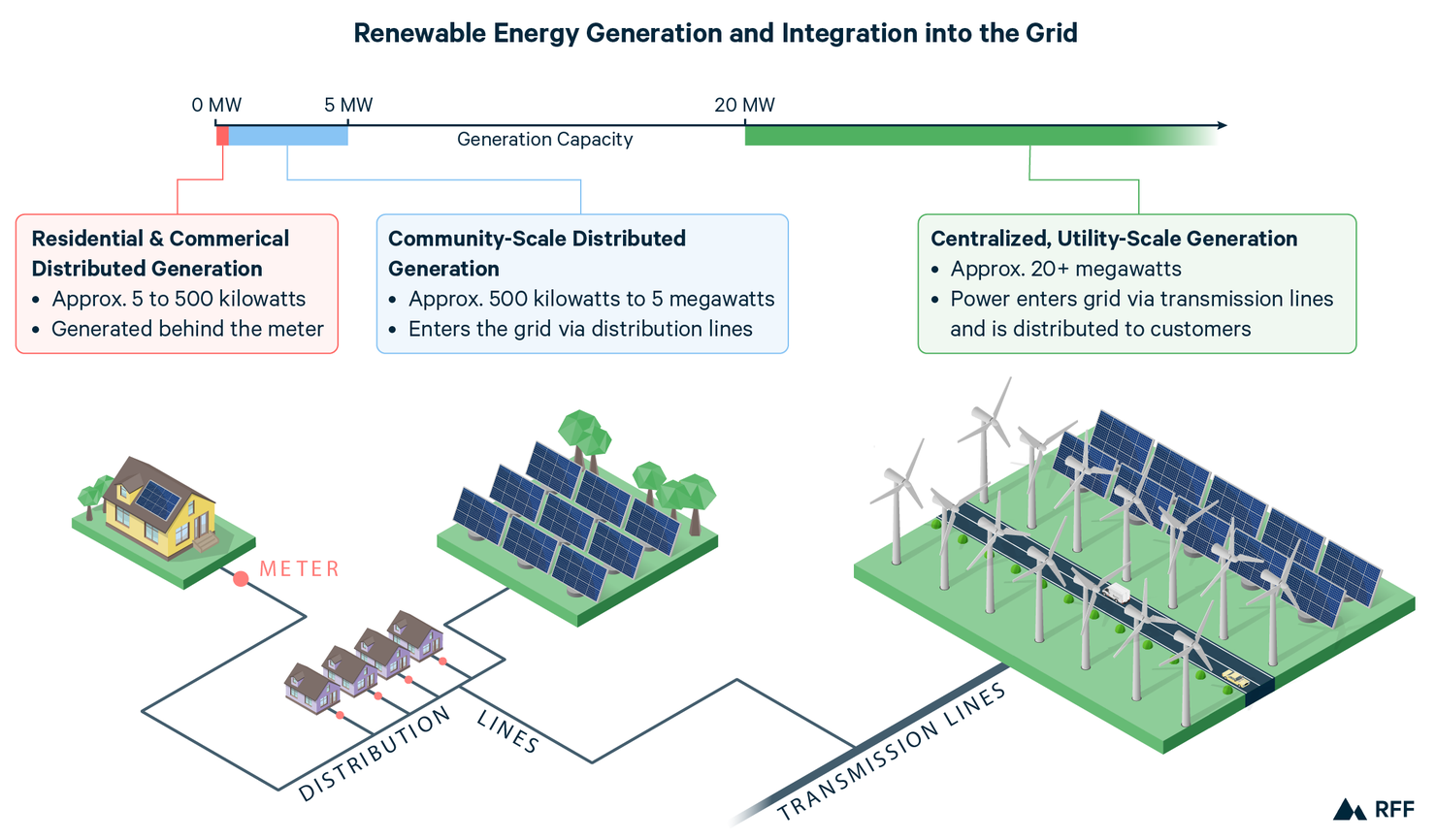
The successful integration of renewable energy into the grid relies on effective interconnection and the deployment of smart grid technologies. Interconnection refers to the physical connection of renewable energy sources to the grid. This is achieved through the installation of transformers, switches, and protection systems that enable the bidirectional flow of electricity.
Smart grid technologies play a crucial role in optimizing and managing renewable energy integration. These technologies enable real-time monitoring of energy generation and consumption, allowing grid operators to balance supply and demand effectively. Advanced communication systems, sensors, and control devices ensure smooth integration and enable the grid to dynamically respond to changes in weather conditions or fluctuations in renewable energy generation.
3. Energy Storage and Demand Response
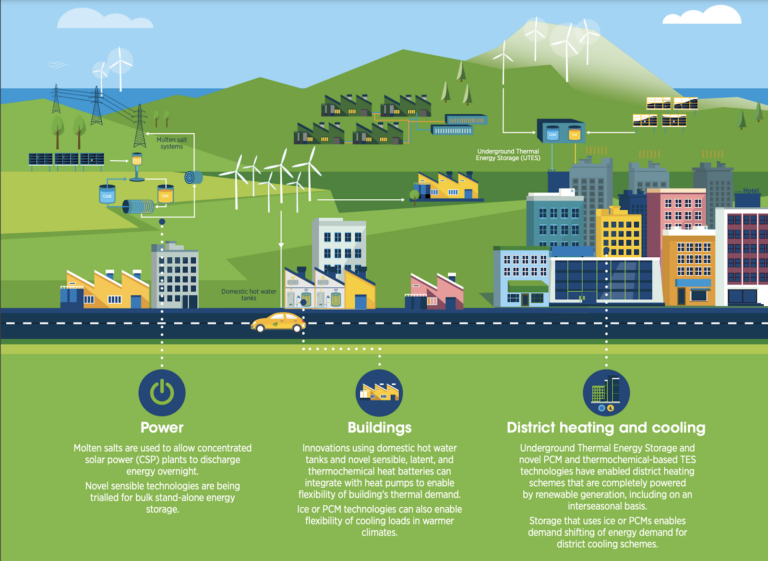
Energy storage and demand response mechanisms are key components of renewable energy grid integration. As renewable energy sources are intermittent in nature, storing excess energy during periods of high generation and utilizing it during low generation periods becomes vital. Energy storage technologies such as batteries, pumped-storage hydroelectricity, and thermal storage systems help in balancing supply and demand and provide a stable power supply.
Demand response programs also play a significant role in renewable energy grid integration. These programs incentivize consumers to adjust their energy consumption patterns based on renewable energy availability or grid conditions. By shifting energy usage to times when renewable energy generation is high, such as during the day for solar power, the overall stability and efficiency of the grid can be improved.
Challenges in Renewable Energy Grid Integration
Amidst the push for renewable energy grid integration, several challenges need to be addressed to ensure a smooth and successful transition. These challenges include:
1. Grid Infrastructure Upgrades
The existing grid infrastructure may require significant upgrades to accommodate the increased capacity of renewable energy sources. Transmission lines may need to be expanded, and substations and transformers may need to be upgraded to handle higher voltages and bidirectional power flow.
2. Grid Stability and Power Quality
Renewable energy sources are often intermittent and variable in nature, leading to grid stability and power quality issues. Grid operators need to implement advanced control systems and technologies to maintain a stable frequency and voltage level. Integration of energy storage and smart grid technologies can help mitigate these challenges.
3. Regulatory and Policy Frameworks
A supportive regulatory and policy framework is essential to encourage investment in renewable energy grid integration. Clear mandates, regulations, and incentives can facilitate the smooth integration of renewable energy sources, attract private sector investment, and promote innovation in the sector.
Grid Integration Best Practices
To ensure successful grid integration of renewable energy, the following best practices can be employed:
1. Comprehensive Planning and Analysis
Thorough planning and analysis of renewable energy resources, their potential, and grid infrastructure requirements are vital for successful integration. Collaboration among utilities, policymakers, and grid operators can lead to effective and efficient integration strategies.
2. Flexibility and Adaptability
Flexibility and adaptability are essential factors in renewable energy grid integration. As the renewable energy landscape evolves, grid operators should be prepared to adapt to changing technologies, regulations, and energy generation patterns. Embracing flexibility in grid design and operation can enhance system stability and reliability.
3. Stakeholder Engagement and Education
Engaging and educating stakeholders, including consumers, policymakers, and industry players, is crucial for the successful integration of renewable energy into the grid. By generating awareness and understanding about the benefits and challenges of renewable energy integration, stakeholders can actively contribute to the transition towards a greener energy future.
In conclusion, renewable energy grid integration is a complex process that requires careful planning, interconnection, and the deployment of smart grid technologies. Overcoming challenges and implementing best practices can ensure the successful integration of renewable energy, leading to a more sustainable and resilient power grid. By embracing renewable energy sources, we can reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and work towards a cleaner and greener future.
Key Takeaways: How Renewable Energy Grid Integration Takes Place
- Renewable energy grid integration refers to the process of connecting renewable energy sources to the existing electrical grid.
- This integration enables the efficient distribution and utilization of renewable energy.
- New technologies, such as smart grids and energy storage systems, play a crucial role in integrating renewable energy into the grid.
- Grid operators carefully manage the interconnection of renewable energy sources to maintain balance and reliability in the grid.
- Policies and regulations promote grid integration by providing incentives for renewable energy development and ensuring a smooth transition to a cleaner energy future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Renewable energy grid integration is an important process that allows the incorporation of renewable energy sources into the existing power grid. It involves multiple steps and considerations to ensure a smooth and efficient integration. Here are some common questions and answers related to renewable energy grid integration:
1. How do renewable energy sources connect to the power grid?
Renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind farms, connect to the power grid through a process called interconnection. First, the renewable energy facility must meet certain technical requirements to ensure it can safely and reliably connect to the grid. Then, the facility owner applies for interconnection to the grid operator or utility company. The application goes through a review process to determine the impact on grid stability and any necessary upgrades to accommodate the new energy source. Once approved, the renewable energy facility is connected to the grid, allowing it to supply electricity to the network.
During the interconnection process, factors like voltage compatibility, power quality, and grid capacity are carefully assessed to ensure the integration of renewable energy sources does not disrupt the stability and reliability of the grid.
2. What are the benefits of integrating renewable energy into the grid?
Integrating renewable energy into the grid brings numerous benefits. Firstly, renewable energy sources reduce greenhouse gas emissions and pollution compared to conventional energy sources, helping combat climate change and improve air quality. Additionally, renewables provide a diversified energy mix, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and increasing energy security. Moreover, integrating renewables can stimulate local economies by creating jobs in the renewable energy sector. Furthermore, renewable energy projects often lead to the development of new technologies and innovations, driving progress in the energy industry.
Renewable energy grid integration also allows for improved grid flexibility and resilience, as it incorporates distributed energy resources that can contribute to load balancing and grid stability. It enables a transition to a more sustainable and sustainable energy future.
3. How is the variable nature of renewable energy managed in grid integration?
The variable nature of renewable energy, such as solar and wind, is managed through various techniques. One approach is diversifying the renewable energy portfolio, combining different sources with complementary generation patterns. For example, while solar energy production peaks during the day, wind energy output is typically higher at night. By integrating multiple renewable sources, the overall variability of the energy supply is reduced.
Storage solutions, like batteries or pumped hydro storage, also play a crucial role in managing renewable energy fluctuations. Excess energy produced during high generation periods can be stored and used during low generation periods, ensuring a more consistent energy supply. Additionally, advanced forecasting technologies help grid operators anticipate renewable energy production and adjust grid operations accordingly.
4. What challenges are involved in integrating renewable energy into the grid?
Integrating renewable energy into the grid comes with certain challenges. One challenge is the need for grid upgrades and reinforcements to accommodate the increased capacity and variable nature of renewable energy sources. Upgrading transmission and distribution infrastructure can be costly and time-consuming. Proper planning and investment are essential to ensure a resilient and reliable grid.
Another challenge is the complexity of managing the integration process, as it involves coordination between various stakeholders, such as renewable energy developers, grid operators, and regulatory authorities. Balancing grid stability, power quality, and energy demand requires effective communication and collaboration among these parties.
5. How does grid integration affect the overall electricity system?
Grid integration of renewable energy sources has a significant impact on the overall electricity system. It encourages a transition towards a cleaner and more sustainable energy mix, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating the environmental impact of power generation. By diversifying the energy sources, the grid becomes more resilient and less vulnerable to disruptions caused by fuel supply constraints or price fluctuations.
Moreover, grid integration allows for better utilization of renewable energy resources, maximizing their benefits. It facilitates the integration of decentralized generation units, like rooftop solar panels or community wind farms, empowering individuals and communities to generate their own electricity and participate in the energy market. Overall, grid integration is a critical step towards a greener and more sustainable energy future.
Summary
Renewable energy is when we use the Earth’s natural resources, like the sun and wind, to make power. But how does this energy get to our homes and businesses? That’s where grid integration comes in. The grid is like a big power network, and it helps to transfer electricity from where it’s made to where it’s needed. Grid integration is all about finding ways to connect renewable energy sources to the grid so that we can use clean energy instead of polluting fossil fuels. It involves things like building new power lines, using advanced technology to manage the flow of electricity, and even storing excess energy for when the sun is not shining or the wind is not blowing. By integrating renewable energy into the grid, we can make our electricity system greener and more sustainable for the future.
To make sure that renewable energy is integrated smoothly into the grid, we need to consider a few things. One is the location. It’s important to build renewable energy sources, like solar panels and wind farms, in places where they can get good access to the grid. Another thing to consider is the timing. Renewable energy is not always available at the same time that we need it. So, we need to find ways to store extra energy for when there is less sun or wind. Finally, we need to invest in new technologies and infrastructure to make grid integration easier. This includes things like smart grids that can monitor and control the flow of electricity in real-time. By addressing these challenges and working together, we can create a future where clean and renewable energy powers our homes and protects our planet.