How Renewable Energy Grid Integration Takes Place?
Renewable energy is a hot topic these days, and you might be wondering, “How does renewable energy grid integration take place?” Well, let me break it down for you in a way that’s easy to understand. When we talk about grid integration, we’re referring to the process of incorporating renewable energy sources, like solar and wind, into the existing power grid. It’s like adding pieces to a puzzle to create a more sustainable and efficient energy system.
Imagine this – on a sunny day, solar panels soak up the sun’s rays and convert them into electricity. Similarly, wind turbines harness the power of the wind to generate energy. But what happens to all that energy once it’s generated? That’s where grid integration comes in. The renewable energy generated is fed into the power grid, which is like a network that distributes electricity across homes, buildings, and industries.
Now, you might be wondering how this integration takes place. Well, it involves a combination of smart technologies, infrastructure upgrades, and coordination between different stakeholders. The power generated from renewable sources is first converted to a usable form, usually alternating current (AC), before being fed into the grid. This requires specialized equipment and transformers to ensure compatibility and efficient distribution.
So, there you have it – a brief introduction to how renewable energy grid integration takes place. It’s an exciting and necessary step towards a greener future, and understanding the process can give us insights into the importance of renewable energy and its role in mitigating climate change. So, let’s dig deeper and explore the fascinating world of renewable energy grid integration together!
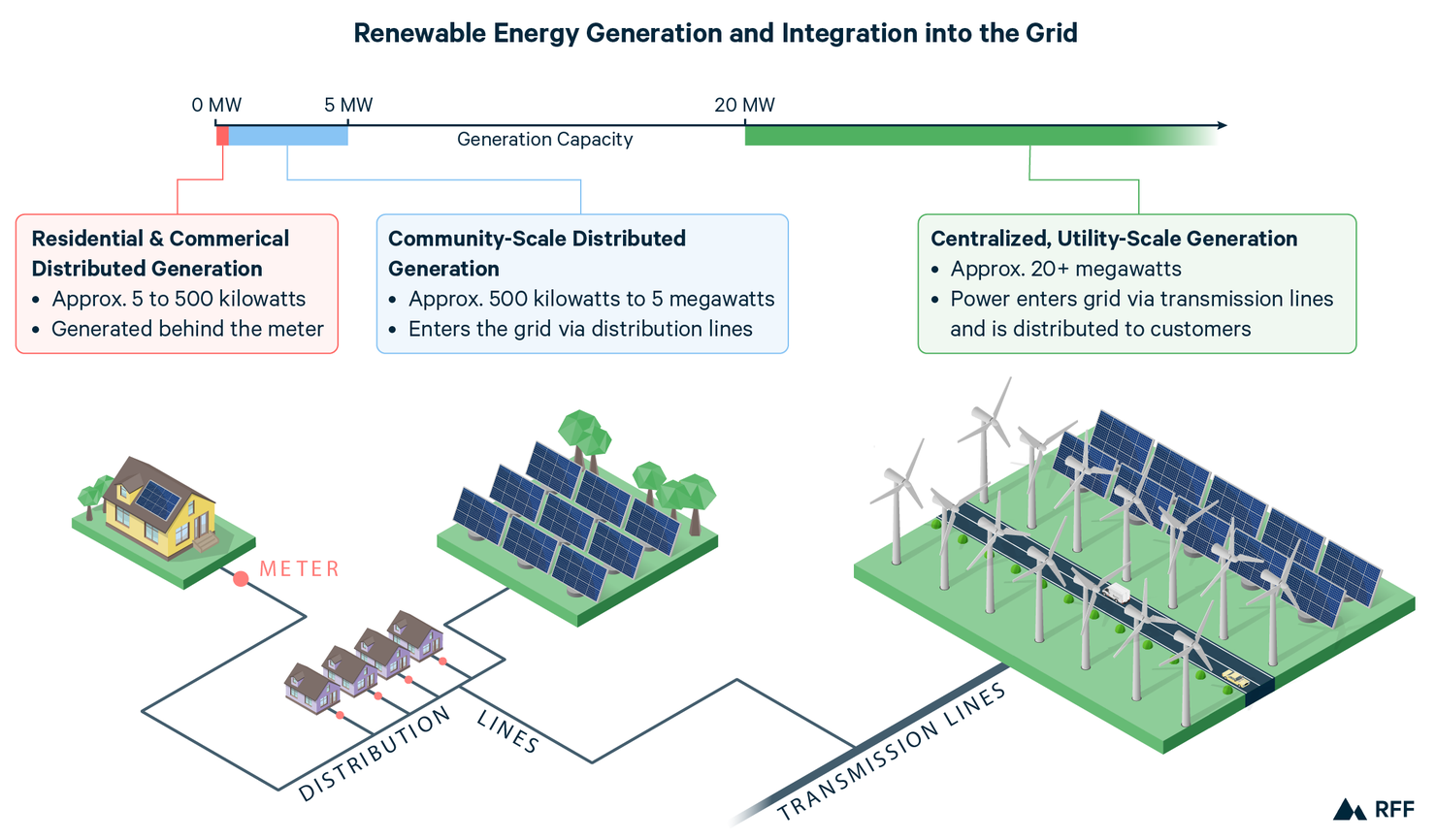
How Renewable Energy Grid Integration Takes Place?
In today’s world, renewable energy sources have become a critical component of the global energy landscape. With the increasing need for sustainable and eco-friendly solutions, the integration of renewable energy into existing power grids has gained significant momentum. This article will explore the various aspects of how renewable energy grid integration takes place, including the challenges, benefits, and techniques involved.
The Role of Renewable Energy Grid Integration
Renewable energy grid integration refers to the process of incorporating renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into the existing power grid infrastructure. This integration plays a vital role in the transition towards a more sustainable energy system by diversifying the energy mix and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. By integrating renewable energy into the grid, countries can reduce greenhouse gas emissions, enhance energy security, and promote economic growth through the development of the clean energy sector.
One of the key benefits of renewable energy grid integration is the ability to balance the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources with the demands of the grid. Unlike traditional power plants, which can generate electricity continuously, renewable energy sources are dependent on natural factors like sunlight and wind. Grid integration strategies enable efficient management of these intermittent sources, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply for consumers.
To achieve effective renewable energy grid integration, several technical, regulatory, and economic considerations need to be addressed. These include optimizing transmission infrastructure, implementing flexible grid management systems, establishing supportive policies and incentives, and conducting thorough planning and forecasting to anticipate renewable energy generation and demand fluctuations.
Challenges of Renewable Energy Grid Integration
While renewable energy grid integration offers numerous benefits, it also comes with challenges that need to be overcome to ensure the smooth functioning of the grid. One of the primary challenges is the variability and unpredictability of renewable energy sources. Unlike traditional power plants, which can be controlled to meet demand fluctuations, the availability of renewable energy depends on natural factors that are beyond human control. This poses difficulties in maintaining grid stability and balancing supply and demand.
Moreover, the existing grid infrastructure may not be well-equipped to handle the increased penetration of renewable energy sources. The intermittent nature of renewables requires the grid to be more flexible and capable of handling bidirectional power flow. Upgrading and modernizing the grid infrastructure to accommodate these changes can be a significant challenge, both technically and financially.
In addition to technical challenges, regulatory and market barriers can also hinder renewable energy grid integration. In some cases, outdated regulations and subsidy structures may discourage investment in renewable energy projects and hinder their integration into the grid. Similarly, grid operators and utilities may face challenges in adapting their business models to accommodate the evolving energy landscape.
Techniques for Renewable Energy Grid Integration
Over the years, various techniques and technologies have been developed to overcome the challenges associated with renewable energy grid integration. These techniques aim to enhance grid flexibility, improve forecasting accuracy, and optimize the utilization of renewable energy sources. Some of the common techniques include:
- Energy Storage: By incorporating energy storage systems, excess energy generated from renewable sources can be stored and used during periods of high demand or low renewable energy generation. This helps in balancing supply and demand and ensures a more stable grid.
- Smart Grids: Smart grid technologies enable real-time communication and control between power producers, grid operators, and consumers. This allows for better coordination and optimization of renewable energy integration.
- Voltage and Frequency Control: With the increased penetration of renewable energy, voltage and frequency control become crucial to maintaining grid stability. Advanced control and monitoring systems can help manage these parameters and ensure reliable power supply.
- Demand Response: Demand response programs incentivize consumers to adjust their energy consumption patterns based on grid conditions and renewable energy generation. This helps in managing the variability of renewable energy sources and reducing peak energy demand.
In addition to these techniques, comprehensive grid planning and interconnection policies are essential to ensure the seamless integration of renewable energy. By identifying suitable locations for renewable energy projects, optimizing transmission capacity, and fostering collaboration between stakeholders, the challenges of renewable energy grid integration can be effectively addressed.
Key Considerations for Renewable Energy Grid Integration
When considering renewable energy grid integration, there are several key factors that need to be taken into account. These include:
Energy Forecasting and Planning:
Accurate forecasting of renewable energy generation is crucial for effective grid integration. By leveraging advanced weather prediction models, historical data analysis, and machine learning algorithms, energy planners can optimize the utilization of renewable energy sources and ensure reliable grid operation.
Grid Infrastructure Upgrades:
Investments in grid infrastructure upgrades are essential to accommodate the higher penetration of renewable energy sources. This includes enhancing transmission capacity, integrating energy storage systems, and implementing advanced control and monitoring technologies.
Policy and Regulatory Support:
Supportive policies and regulations play a critical role in promoting renewable energy grid integration. Governments need to provide incentives, grants, and favorable market conditions to encourage renewable energy investments and facilitate their integration into the grid.
Collaboration and Cooperation:
Gaining the support and cooperation of various stakeholders, including utilities, grid operators, renewable energy developers, and consumers, is essential for successful grid integration. Collaborative efforts can help address technical, economic, and regulatory challenges and pave the way for a sustainable and resilient energy future.
In conclusion, renewable energy grid integration is a complex process that involves addressing technical, regulatory, and economic challenges. However, with the right strategies, technologies, and collaboration, it offers immense benefits in terms of reducing carbon emissions, enhancing energy security, and fostering sustainable economic growth. By understanding the role, challenges, and techniques associated with renewable energy grid integration, we can pave the way for a greener and more resilient energy system.
Key Takeaways: How Renewable Energy Grid Integration Takes Place
- Renewable energy grid integration involves integrating renewable energy sources, like solar and wind, into the existing power grid.
- This integration requires the development and implementation of advanced technologies, such as smart grid systems and energy storage solutions.
- Smart grid systems help monitor and control the flow of electricity from renewable sources, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply.
- Energy storage solutions, like batteries, play a crucial role in storing excess renewable energy for use during periods of high demand.
- Renewable energy grid integration helps reduce reliance on fossil fuels, decreases carbon emissions, and promotes a sustainable energy future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Renewable energy grid integration refers to the process of incorporating and managing renewable energy sources within an existing power grid. This is crucial to transitioning to a greener and sustainable energy future. Here are some common questions and answers about how renewable energy grid integration takes place:
1. How does renewable energy integrate into the existing power grid?
Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, integrate into the existing power grid through a combination of physical infrastructure and advanced control systems. First, the electricity generated from renewable sources is converted into a suitable form and voltage level for transmission and distribution. This electricity is then injected into the grid at specific points, strategically connected to the existing network.
To ensure a smooth integration, advanced control systems are used to monitor and manage the flow of renewable energy. These systems coordinate the operation of different power sources, balance supply and demand, and stabilize the grid frequency. By integrating renewable energy into the existing power grid, we can optimize the use of renewable resources and minimize the reliance on fossil fuels.
2. What are the benefits of renewable energy grid integration?
Renewable energy grid integration offers numerous benefits for both the environment and the energy sector. Firstly, it helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. By utilizing renewable sources like solar and wind, we can significantly decrease our reliance on fossil fuels and decrease the carbon footprint associated with electricity generation.
Secondly, renewable energy grid integration enhances energy security by diversifying the sources of power generation. It reduces the dependence on imported fuels and vulnerable transmission lines. By tapping into local renewable resources, we can create a more self-sufficient and resilient energy system.
3. Does renewable energy grid integration pose any challenges?
While renewable energy grid integration is crucial for a sustainable energy future, it does come with some challenges. One challenge is the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind. Unlike traditional power plants that can run continuously, natural factors such as sunlight availability and wind patterns can affect the output of renewable energy sources. Therefore, it requires careful planning and coordination to ensure a stable and reliable energy supply.
Another challenge is the need for upgrades and modifications to the existing power grid infrastructure. Integrating large-scale renewable energy sources may require expanding transmission networks, installing new substations, and implementing advanced protection systems. These infrastructure upgrades come with costs and logistical challenges that need to be carefully managed.
4. How are energy storage systems utilized in renewable energy grid integration?
Energy storage systems play a crucial role in renewable energy grid integration. They help address the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources by storing excess energy when it’s produced and releasing it when demand is high or when renewable energy generation is low. By storing energy, we can better match supply with demand, optimize the utilization of renewable resources, and enhance grid stability.
Common energy storage technologies include batteries, pumped hydro storage, and thermal storage systems. These systems are strategically placed within the grid and can store electricity in different forms, such as chemical energy or potential energy, depending on the technology used.
5. How can smart grid technologies contribute to renewable energy grid integration?
Smart grid technologies play a crucial role in optimizing renewable energy grid integration. These technologies enable real-time monitoring and control of the power grid, allowing for efficient integration and management of renewable energy sources. Through advanced sensors, communication systems, and data analytics, smart grids can anticipate and respond to changes in renewable energy generation and consumption.
Smart grids also enable better demand response capabilities, where consumers can adjust their electricity usage based on real-time pricing or signals from the grid. This flexibility helps balance the fluctuations in renewable energy generation and ensures a more stable and reliable grid operation. Additionally, smart grids facilitate the integration of electric vehicles, energy-efficient appliances, and distributed energy resources, further enhancing the overall efficiency and sustainability of the power grid.
Summary
Renewable energy grid integration means using sources like wind and solar power to generate electricity. It’s important because it helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. There are three main ways to integrate renewables into the grid: adding more renewable energy sources, improving grid infrastructure, and using energy storage. By doing these things, we can move towards a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
In order to achieve this, we need collaboration between governments, energy companies, and individuals to invest in renewable energy projects. It’s a big task, but with everyone working together, we can create a greener world for future generations. So let’s support renewable energy and help make a positive impact on our planet!