How Is Solar Energy Gathered?
Welcome to the fascinating world of solar energy! Have you ever wondered how we harness the power of the sun to generate electricity? In this article, we’ll explore the process of gathering solar energy and how it can be converted into a usable form.
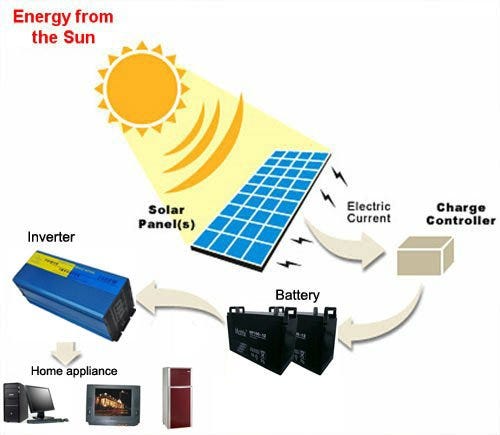
So, how is solar energy gathered, you ask? Well, it all starts with solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels. These panels are made up of small units called solar cells, which are responsible for capturing sunlight and converting it into electricity. It’s like having tiny, energy-generating machines on our rooftops!
But wait, there’s more to it! Once the sunlight hits the solar panels, the solar cells work their magic. They contain a special material that absorbs the sun’s energy and sets off a flow of electrons. This flow creates an electric current, and voila – we have electricity! It’s like having a mini power station right on our homes.
Now that we know the basics of how solar energy is gathered, let’s dive deeper into the inner workings of solar panels. Join us as we uncover the secrets behind this renewable energy revolution! Get ready to be amazed by the power of the sun and its incredible potential to shape our future. Let’s get started!
– Sunlight reaches the PV cells, exciting the electrons.
– The excited electrons create an electric current.
– The current flows through an inverter, converting it into usable AC electricity.
– The AC electricity can then be used to power homes, businesses, and more.
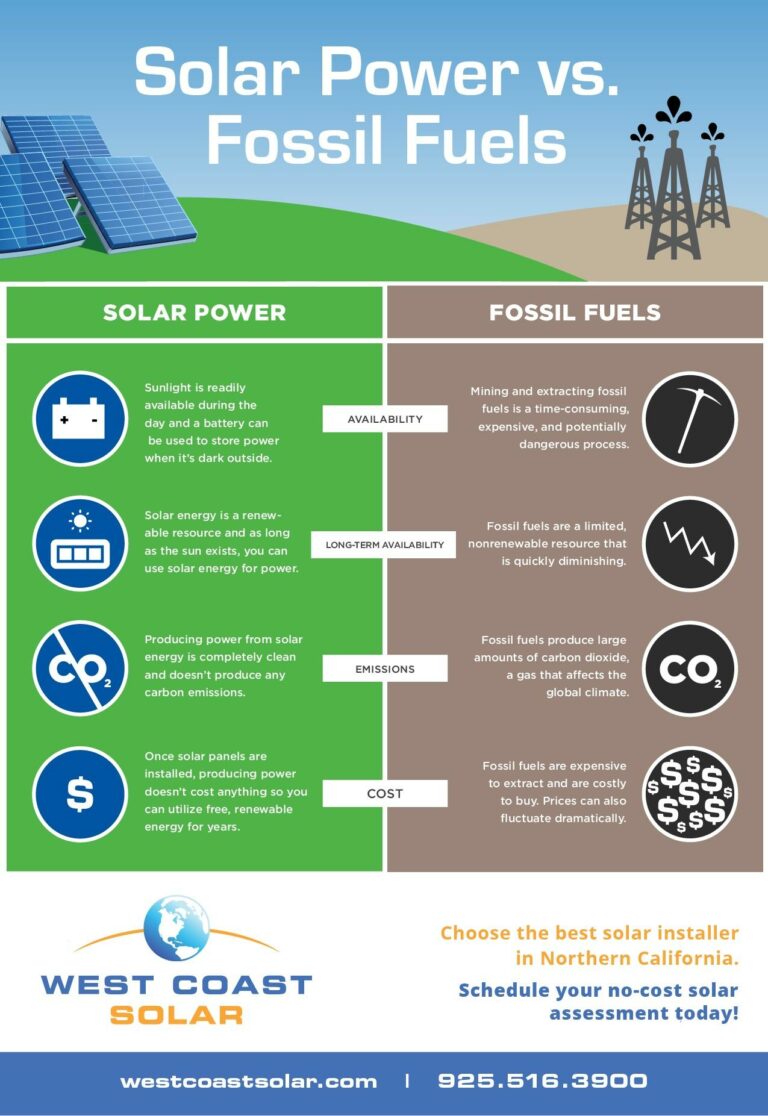
Harnessing solar energy is a clean and sustainable way to generate electricity.
How is Solar Energy Gathered?
Solar energy is a renewable and abundant form of energy that can be harnessed using various methods. In this article, we will explore the different ways in which solar energy is gathered and converted into usable electricity. From photovoltaic panels to solar thermal systems, we will delve into the technologies and processes that make solar energy an increasingly popular choice for sustainable power generation.
1. Photovoltaic Panels: Harnessing the Power of Sunlight
Photovoltaic panels, also known as solar panels, are the most common and recognizable way of gathering solar energy. These panels are made up of multiple solar cells, which contain a material called a semiconductor. When sunlight strikes these cells, the photons in the sunlight release electrons from the semiconductor material, creating an electric current.
This generated electricity can then be used to power homes, businesses, and even entire cities. The efficiency of photovoltaic panels has improved significantly over the years, making solar power a viable and cost-effective option for many. Additionally, advancements in solar cell technology, such as thin-film solar cells and multi-junction solar cells, have made it possible to gather solar energy even in low-light conditions.
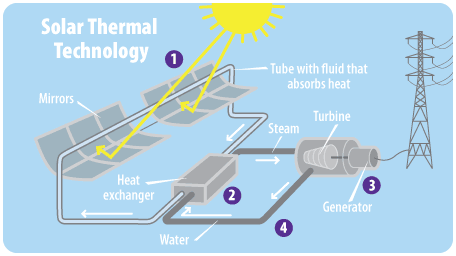
2. Solar Thermal Systems: Converting Sunlight into Heat
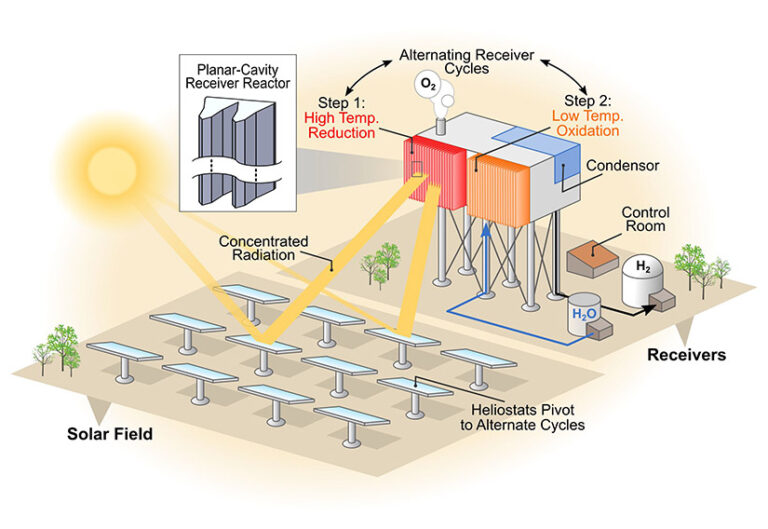
Solar thermal systems, also known as concentrating solar power systems, use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a receiver. This concentrated sunlight is then used to heat a fluid, such as water or oil, which in turn produces steam. The steam produced can power a turbine connected to a generator, generating electricity.
This method is commonly used in large-scale solar power plants, where vast arrays of mirrors or lenses are strategically positioned to capture and concentrate sunlight. Solar thermal systems are efficient in areas with high levels of direct sunlight and are particularly useful in generating electricity on a large scale.
3. Passive Solar Design: Utilizing Solar Energy in Architecture
Passive solar design is an architectural approach that maximizes the use of natural sunlight for heating and lighting purposes in buildings. This design technique incorporates features such as large windows, thermal mass materials, and proper orientation to optimize solar energy utilization.
By integrating passive solar design principles into buildings, occupants can benefit from reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills. This approach is especially popular in residential buildings, where homeowners can take advantage of natural lighting and passive heating during colder months.
4. Solar Water Heating: Heating Water with the Sun
Solar water heating systems utilize the sun’s energy to heat water for various purposes, such as domestic use or swimming pools. These systems typically consist of solar collectors, storage tanks, and a circulation pump.
The solar collectors, often mounted on rooftops, absorb heat from the sun and transfer it to the water in the storage tank. The heated water can then be used as needed. Solar water heating systems are a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional water heating methods.
5. Solar Pumps: Pumping Water using Solar Power
Solar pumps are another application of solar energy that is widely used in agricultural and rural areas. These pumps use solar energy to power a motor that draws water from a well or other water sources.
Solar pumps offer advantages such as lower operational costs, reduced dependence on fuel, and ease of maintenance. They provide a reliable and sustainable solution for water supply in remote locations where traditional electricity supply may be limited.
6. Solar Chimneys: Harnessing Natural Ventilation
Solar chimneys, also known as thermal chimneys or solar updraft towers, utilize the sun’s heat to create natural ventilation and generate electricity. These structures consist of a tall chimney-like tower with a large glass roof or collector at the base.
As sunlight passes through the glass roof, it heats the air inside the tower, causing it to rise. This upward movement of hot air creates a pressure difference, which draws in cooler air from outside. The airflow drives turbines at the base of the tower, generating electricity. Solar chimneys are a unique and innovative way of gathering solar energy while promoting natural ventilation.
7. Solar Cars: Driving on Sunshine
Solar cars harness solar energy to power their electric motors, making them incredibly eco-friendly and sustainable modes of transportation. These cars are equipped with solar panels on their roofs or hoods, which capture sunlight and convert it into electricity.
Though solar cars are not yet widely available for commercial use, they showcase the potential of solar energy in the automotive industry. With advancements in solar panel technology and battery storage, solar cars could become a more feasible and practical option for everyday transportation in the future.
The Future of Solar Energy Gathering
As technology continues to advance, the ways in which we gather and harness solar energy will evolve. Researchers are exploring new materials and technologies that can improve the efficiency of solar panels, increase the storage capacity of solar power, and expand its applications. From solar-powered wearables to solar-integrated building materials, the possibilities for solar energy gathering are expanding.
Advancements in Solar Energy Gathering
1. Solar-Powered Wearables: A Portable Energy Source
The miniaturization of solar panels and advancements in flexible and transparent solar cells have paved the way for solar-powered wearables. These devices, such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and even clothing, integrate solar panels to capture and convert sunlight into electricity to power their functionalities.
Solar-powered wearables offer the convenience of not having to rely on external power sources or frequent battery charging. They also promote sustainability by reducing the need for disposable batteries and minimizing environmental impact.
2. Solar-Integrated Building Materials: The Power of Aesthetics
Innovations in solar technology have led to the development of solar-integrated building materials, such as solar roof tiles and solar windows. These materials blend seamlessly with the aesthetics of buildings, allowing for the integration of solar energy gathering into architectural designs.
Solar roof tiles, for example, replace traditional roofing materials while generating electricity from the sun. Solar windows incorporate transparent solar cells into the glass, allowing natural light to pass through while harnessing solar energy. These advancements enable buildings to become self-sufficient in their energy needs while maintaining their visual appeal.
3. Solar-Powered Desalination: Addressing Water Scarcity
Solar-powered desalination is a promising solution to address water scarcity in regions where freshwater resources are limited. This process combines solar energy with desalination technologies to convert seawater or brackish water into freshwater.
By harnessing solar energy to power the desalination process, solar-powered desalination plants can provide clean and sustainable freshwater sources. This technology holds great potential in coastal areas and arid regions that face water scarcity issues.
In conclusion, solar energy can be gathered using various methods such as photovoltaic panels, solar thermal systems, passive solar design, solar water heating, solar pumps, solar chimneys, and solar cars. Each method has its advantages and applications, contributing to the growing utilization of solar energy across different sectors. Furthermore, advancements in solar energy gathering continue to expand its potential, leading to innovations such as solar-powered wearables, solar-integrated building materials, and solar-powered desalination. As we strive towards a more sustainable future, solar energy will play a crucial role in meeting our energy needs while reducing our impact on the environment.
Key Takeaways: How is Solar Energy Gathered?
– Solar energy is gathered through the use of solar panels, which consist of photovoltaic cells that convert sunlight into electricity.
– These panels are typically installed on rooftops or in large-scale solar farms to maximize exposure to sunlight.
– When sunlight hits the solar panels, the photons in the light excite electrons in the photovoltaic cells, creating an electrical current.
– This electrical current is then captured and stored in batteries or sent to the electrical grid for immediate use.
– Solar energy can be gathered during the day, even on cloudy days, as long as there is enough sunlight to generate electricity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Solar energy is a popular and renewable source of energy that can be harnessed from the sun and converted into usable electricity. Here are some common questions about how solar energy is gathered:
1. How does solar energy get converted into electricity?
The process of converting solar energy into electricity starts with solar panels or photovoltaic (PV) cells. These panels consist of many tiny silicon cells that absorb sunlight. When sunlight hits the PV cells, it creates an electric field across the layers, causing electricity to flow. This electricity is typically in the form of direct current (DC), and it needs to be converted into alternating current (AC) for household use through an inverter.
Once the electricity is in AC form, it can be used to power homes, businesses, or even feed it back into the electric grid. The entire process of converting solar energy into electricity happens silently and without emitting any harmful pollutants, making it a clean and sustainable energy source.
2. Are solar panels the only way to gather solar energy?
Solar panels are one of the most common and efficient ways to gather solar energy, but they are not the only option. Solar thermal systems use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a fluid-filled pipe, heating the fluid, which can then be used to generate electricity or heat water. Concentrated solar power (CSP) plants work similarly but on a larger scale, using mirrors to concentrate sunlight toward a tower to create steam and drive a turbine, producing electricity.
There are also other emerging technologies to harness solar energy, such as solar paint and solar shingles, which can be integrated into the architecture of buildings. These innovative ways of gathering solar energy are continuously being developed to provide more options and flexibility for utilizing the sun’s power.
3. How much sunlight is needed to generate electricity from solar energy?
The amount of sunlight required to generate electricity from solar energy depends on several factors, including the location, time of year, and efficiency of the solar panels. On average, a sunny day with about five hours of direct sunlight can produce enough energy to power a home for 24 hours.
It’s important to note that solar panels can still generate electricity on cloudy days or when there is indirect sunlight. While the energy production may be reduced, modern solar panels are designed to capture a wide spectrum of light, allowing them to generate electricity even in less-than-perfect conditions.
4. Can solar energy be stored for use at night or during cloudy periods?
Yes, solar energy can be stored for use during times when the sun is not shining or when there is insufficient sunlight. One common method of storing solar energy is by using batteries. Excess electricity generated during the day can be stored in batteries, which can then be used to power homes or businesses during the night or when there is limited sunlight.
Another way to store solar energy is through grid-tied systems. In this setup, any surplus electricity is fed back into the electric grid, and the energy provider credits the system owner for the contribution. When solar energy production is low, the system can draw electricity from the grid. This process is known as net-metering, ensuring a continuous power supply even when solar energy production varies.
5. Is solar energy gathering technology improving?
Yes, solar energy gathering technology is constantly improving. Researchers and engineers are continuously finding ways to increase the efficiency of solar panels, making them more cost-effective and capable of generating more electricity from the same amount of sunlight. This ongoing innovation is crucial in making solar energy a competitive alternative to traditional energy sources.
Advancements in materials, such as perovskite solar cells, hold promise for more efficient and affordable solar panels. Additionally, smart solar technologies are being developed to optimize solar energy generation, including tracking systems that follow the sun’s movement and automatically adjust the angle of the solar panels for maximum sunlight exposure. These advancements contribute to the growth and viability of solar energy as a sustainable and reliable power source.
Summary
Solar energy is gathered by using special devices called solar panels. These panels contain cells that convert sunlight into electricity. The electricity can then be used to power homes and buildings, or stored in batteries for later use. Solar energy is a clean and renewable source of energy, meaning it doesn’t produce pollution or run out. By harnessing the power of the sun, we can reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and help protect the environment.
To gather solar energy, the panels need to be placed in an area where they can receive direct sunlight. This is typically on rooftops or in open fields. The panels are made up of many small solar cells that work together to capture sunlight and convert it into usable energy. When the sunlight hits the cells, it creates an electric current that can be used to power various devices. Solar energy is a sustainable and environmentally friendly way to meet our energy needs and should be encouraged for a brighter future.