How Does Solar Energy Work?
Welcome to the world of solar energy! Have you ever wondered how solar power works? Well, you’re in the right place. Let’s dive in and explore the fascinating process of harnessing the sun’s energy to generate electricity.
Picture this: the sun, our very own celestial powerhouse, sends down rays of light and heat to Earth. What if we could capture and convert that sunlight into usable energy? That’s precisely what solar energy is all about! By utilizing special devices called solar panels, we can transform sunlight into electricity. It’s like having a personal, never-ending source of clean and sustainable power.
Imagine if you could generate your own electricity straight from the sun. No more relying solely on traditional power sources like fossil fuels. Solar energy is a game-changer, paving the way for a greener, more sustainable future. In this article, we’ll explore exactly how solar energy works, from the sun’s rays to powering your home. So, let’s get started on this illuminating journey!
How Does Solar Energy Work? A Comprehensive Guide
Solar energy is a renewable source of power that harnesses the energy of the sun and converts it into usable electricity. The process of generating solar energy involves the use of solar panels, which capture sunlight and convert it into electrical energy. This clean and sustainable source of power has gained significant popularity in recent years due to its numerous benefits and potential to combat climate change. In this guide, we will explore the inner workings of solar energy and delve into the technology and processes that make it possible.
The Basics of Solar Energy
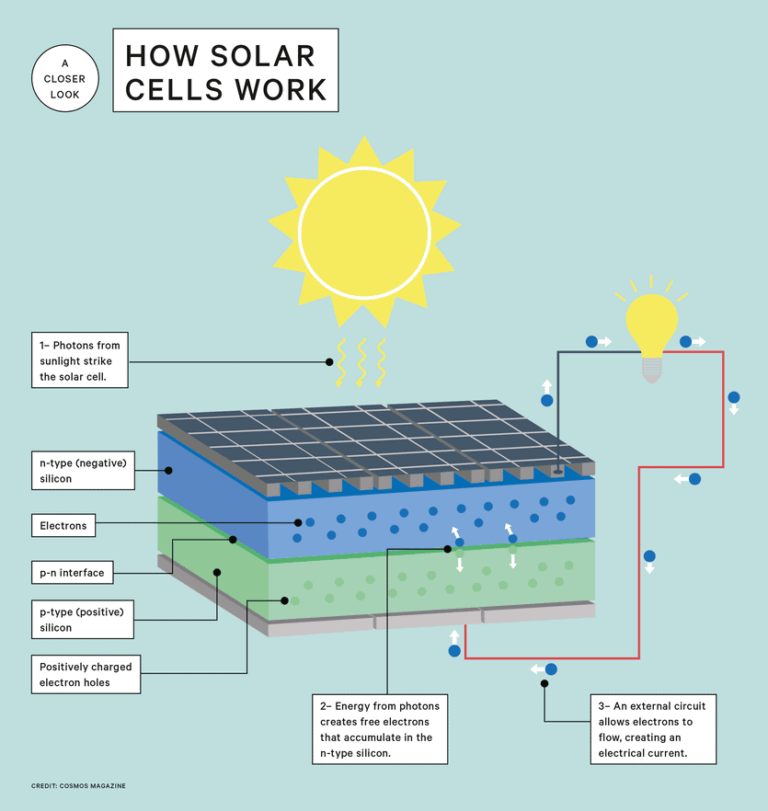
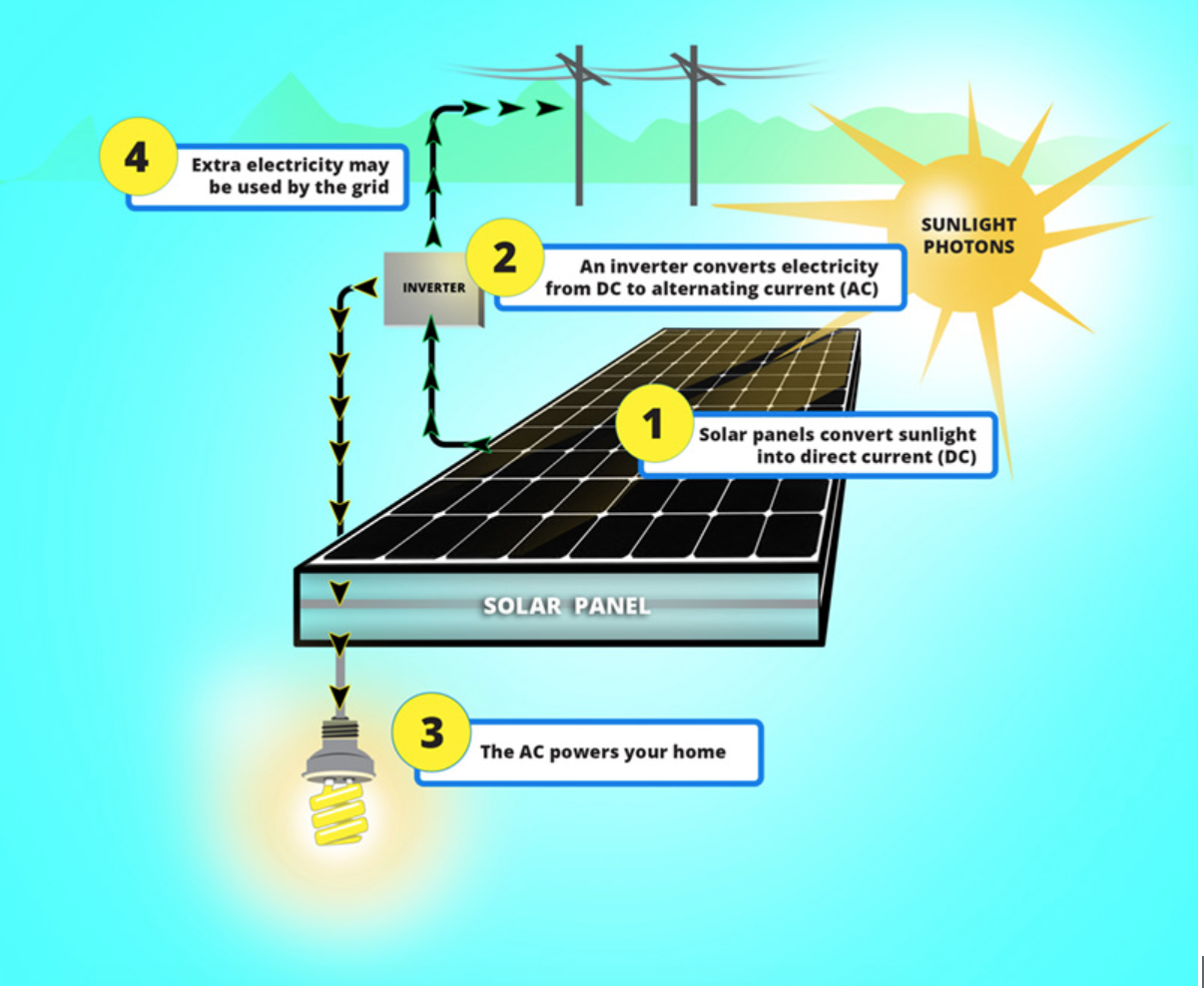
Solar energy begins with sunlight, which is abundant and freely available. When sunlight reaches the Earth’s surface, it contains energy in the form of photons. Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are made up of individual solar cells that are capable of capturing these photons. The solar cells are generally made from silicon, which is a highly efficient material for converting sunlight into electricity.
When sunlight strikes the solar cells, it excites the electrons in the silicon atoms, causing them to break free from their atomic bonds. This creates a flow of electric charge, resulting in direct current (DC) electricity. However, most appliances and electrical grids use alternating current (AC) electricity, which means the DC electricity generated by the solar panels must be converted.
To convert the DC electricity into AC electricity, an inverter is used. The inverter changes the direction of the current, ensuring that the electricity generated by the solar panels is suitable for use in homes, businesses, and the power grid. Once the electricity is converted, it can be immediately used to power appliances or fed into the grid for others to utilize.
The Components of a Solar Energy System
A solar energy system consists of several key components that work together to harness and convert sunlight into usable electricity. These components include:
1. Solar panels: These are the primary component of a solar energy system. Typically mounted on rooftops or in open spaces, solar panels consist of solar cells that capture sunlight and convert it into electricity.
2. Inverter: The inverter is responsible for converting the DC electricity produced by the solar panels into AC electricity, which is used by most appliances and the power grid.
3. Mounting system: Solar panels need to be securely mounted, whether on rooftops or on the ground. Mounting systems ensure that the panels are oriented properly and able to capture the maximum amount of sunlight.
4. Battery storage (optional): Some solar energy systems incorporate battery storage, which allows excess electricity generated during the day to be stored for use during the night or during periods of low sunlight.
5. Electrical meter: To measure the amount of electricity generated by the solar panels and the amount of electricity used or fed back into the grid, an electrical meter is installed as part of the system.
6. Connection to the electrical grid: A solar energy system can be connected to the main electrical grid, allowing excess electricity to be supplied to the grid when the system is producing more electricity than is being used. This process is commonly known as net metering.
7. Electrical panels and wiring: These components connect the solar panels, the inverter, and the electrical meter, ensuring that the generated electricity is properly distributed within the building or fed back into the grid.
By combining these components, a solar energy system can generate clean, renewable electricity that can power homes, businesses, and entire communities. The technology behind solar energy continues to advance, making it increasingly efficient and affordable for both residential and commercial use.
The Environmental Benefits of Solar Energy
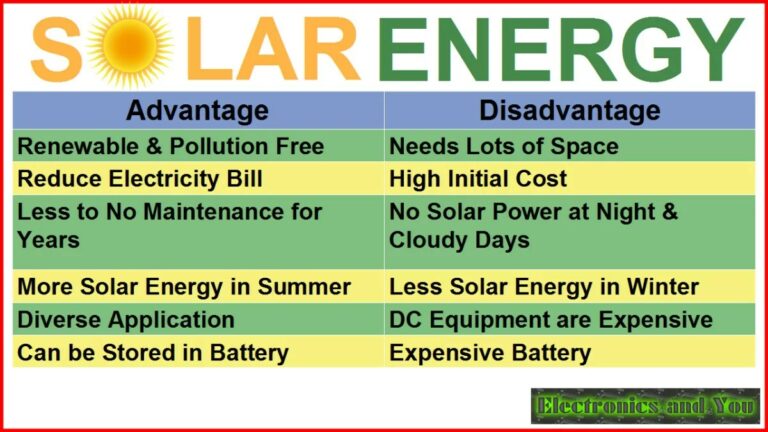
Solar energy offers several environmental benefits that contribute to its growing popularity as a sustainable power source. Some of the key benefits include:
1. Reduced carbon footprint: Solar energy produces electricity without emitting greenhouse gases or other pollutants. By using solar power, individuals and businesses can significantly reduce their carbon emissions, helping combat climate change.
2. Conservation of natural resources: Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and will eventually run out, sunlight is an abundant resource that will continue to be available for billions of years. By harnessing solar energy, we can reduce our reliance on depletable resources like coal, oil, and natural gas.
3. Improved air and water quality: Traditional sources of electricity generation, such as coal-fired power plants, produce harmful pollutants that contribute to air and water pollution. Solar energy, on the other hand, produces clean electricity without any emissions or pollutants, leading to improved air and water quality.
4. Reduced dependence on foreign energy sources: Solar energy reduces dependence on imported fossil fuels, increasing energy independence and security. By generating electricity from a domestic source, countries can protect themselves from fluctuations in fuel prices and geopolitical tensions.
In conclusion, solar energy is a clean, renewable source of power that is harnessed through the use of solar panels. By capturing sunlight and converting it into electricity, solar energy offers numerous environmental benefits, such as reduced carbon emissions, conservation of resources, and improved air and water quality. As technology continues to advance, solar energy is becoming increasingly affordable and accessible, paving the way for a more sustainable and eco-friendly future.
Key Takeaways for “How Does Solar Energy Work?”
- Solar energy is converted from sunlight into electricity.
- Solar panels, made of cells called photovoltaic cells, absorb sunlight and generate electrical energy.
- When sunlight hits the solar panels, the cells release electrons, creating a flow of electric current.
- This electric current can be used to power homes, businesses, or even charge electric cars.
- Solar energy is a renewable and sustainable source of power that helps reduce carbon emissions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Solar energy is becoming an increasingly popular renewable energy source. Here are some commonly asked questions about how it works.
1. How does solar energy generate electricity?
Solar energy generates electricity through photovoltaic (PV) cells, which are made of semiconductors like silicon. When sunlight hits these cells, it excites the electrons in the atoms of the semiconductor material. This creates an electric current that can be captured and used to power homes and businesses.
The PV cells are arranged in panels or modules, and when exposed to sunlight, they convert solar energy into direct current (DC) electricity. An inverter is then used to convert the DC electricity into alternating current (AC), which is the type of electricity used in most homes and buildings.
2. Can solar energy be used at night or on cloudy days?
While solar panels produce the most electricity when exposed to direct sunlight, they can still generate power on cloudy days or during the early morning and late afternoon hours. However, the output may be reduced compared to sunny days.
To ensure a constant supply of electricity, solar energy systems are often connected to the grid. This allows excess electricity generated during sunny periods to be fed back into the grid, and at times when there is less sunlight, electricity can be drawn from the grid. Alternatively, energy storage systems like batteries can be used to store excess electricity for use during periods of low solar generation.
3. Do solar panels work in cold climates?
Solar panels can still work effectively in cold climates, despite the lower temperatures. In fact, solar panels operate more efficiently at cooler temperatures. However, it’s important to note that solar panel performance is affected by factors other than just temperature, such as sunlight intensity and the angle at which the panels are installed.
In regions with cold climates, it is also important to consider snow accumulation on the panels. If snow covers the panels, it can block sunlight and reduce their efficiency. However, many modern solar panel designs are made with materials that discourage snow from sticking, and some systems are equipped with mechanisms that allow the panels to be tilted to help shed snow.
4. Are there any environmental benefits of using solar energy?
Yes, there are several environmental benefits of using solar energy. Solar power is a clean source of energy that produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation. By switching to solar energy, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, which contribute to air pollution and climate change.
Additionally, solar energy systems have a long lifespan and require minimal maintenance, reducing the environmental impact associated with the production and disposal of other forms of energy generation. The use of renewable energy sources like solar power also helps conserve natural resources and decrease dependence on finite resources like coal, oil, and gas.
5. Can I save money by using solar energy?
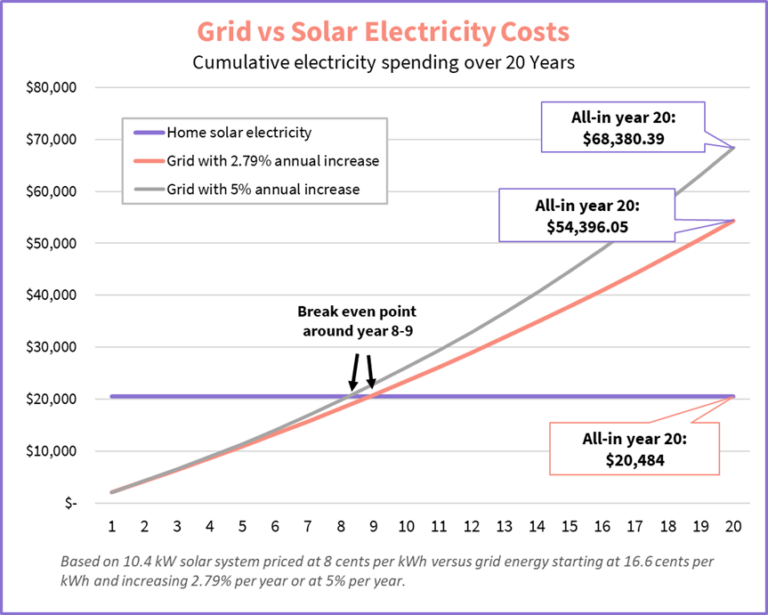
Yes, using solar energy can help save money in the long run. While the initial installation cost of solar panels may be higher compared to traditional energy sources, the ongoing cost of generating electricity from solar energy is significantly lower. This allows homeowners and businesses to reduce their electricity bills over time.
Furthermore, some countries and regions offer financial incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and net metering programs, which can further reduce the cost of installing and using solar energy systems. Additionally, if you generate more electricity than you consume, you may be able to sell the excess back to the grid, providing a potential source of income.
How do solar panels work? – Richard Komp
Summary
Solar energy is a renewable source of power that comes from the sun. When sunlight hits solar panels, it creates an electric current. This electricity can be used to power homes and cities. Solar energy is clean, meaning it doesn’t produce harmful pollutants like fossil fuels. It also saves money in the long run because the sun’s energy is free once the solar panels are installed. Solar power is a great way to help the environment and reduce our dependence on non-renewable energy sources.
Solar panels work by using special cells made of silicon, which absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity. These panels can be placed on rooftops or in large fields, where they are exposed to the most sunlight. The electricity produced by solar panels can then be used to power everything from light bulbs to electric cars. Solar energy is becoming more popular because it helps fight climate change and reduces our reliance on fossil fuels. By harnessing the power of the sun, we can create a more sustainable future for ourselves and future generations.