Does Solar Energy Require Water?
Does solar energy require water? You might be surprised to learn that solar energy does not need water to generate electricity. Unlike other forms of energy production, such as fossil fuels or nuclear power, solar energy can harness the power of the sun without relying on water as a primary resource.
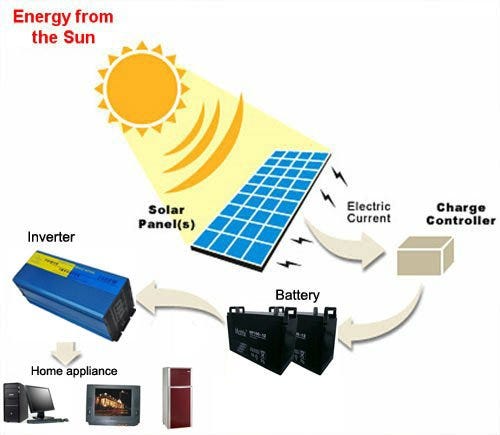
When it comes to solar panels, they work by converting sunlight into electricity through a process called photovoltaic conversion. This means that the panels directly convert sunlight into usable energy, without the need for water to generate power. Isn’t that fascinating?
By harnessing the abundant and renewable energy of the sun, solar power offers a sustainable and environmentally-friendly alternative to traditional energy sources. So, if you’ve been wondering whether solar energy requires water, the answer is a resounding no! Let’s explore more about the amazing benefits of solar energy and how it’s shaping a greener future for us all.
Does Solar Energy Require Water?
Solar energy is a rapidly growing source of renewable power, but how does it impact water resources? With concerns over water scarcity and the environmental implications of energy generation, it’s important to understand if solar energy requires water. In this in-depth article, we will explore the water requirements of solar energy systems, the impact on water resources, and alternatives to traditional solar energy that minimize water usage. So, let’s dive in and uncover the relationship between solar energy and water!
Water Requirements of Solar Energy Systems
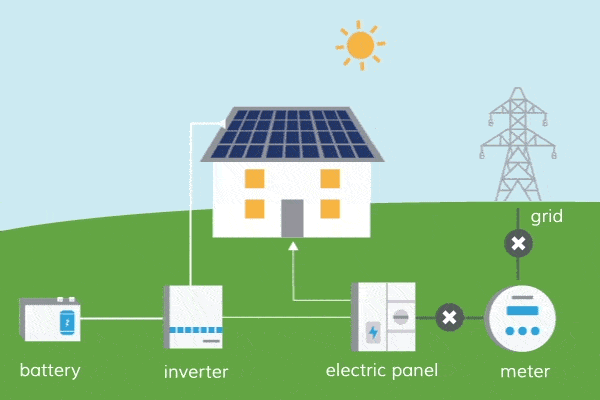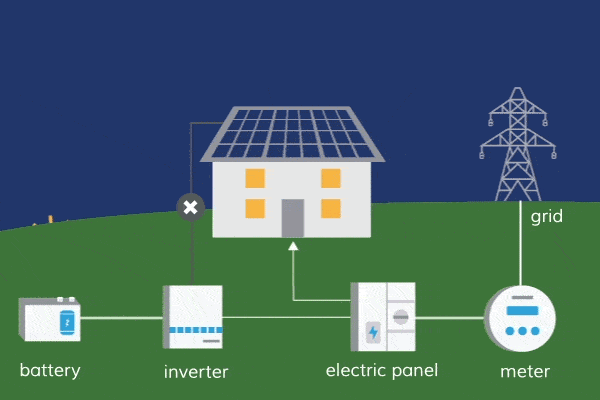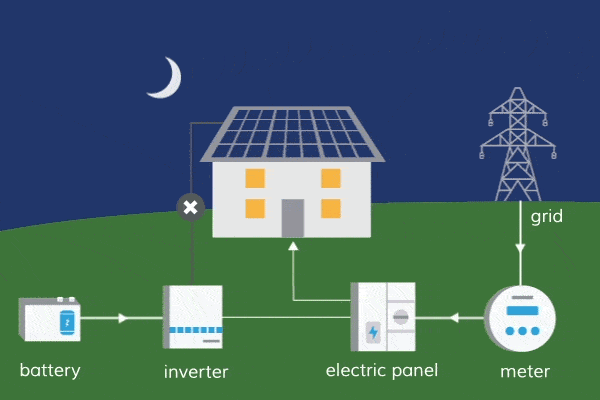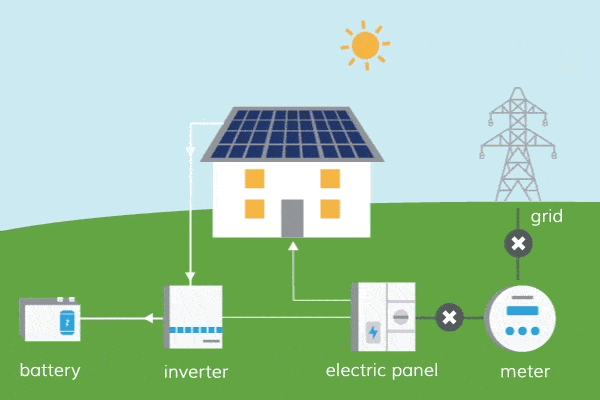
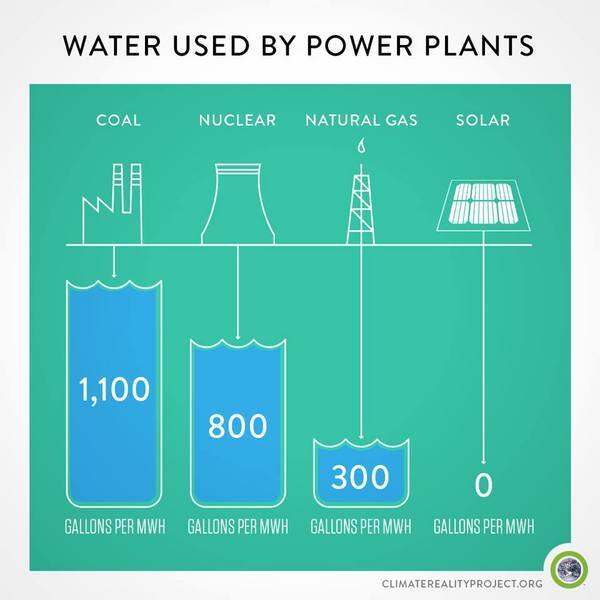
One of the key advantages of solar energy is its minimal water requirements compared to other forms of energy generation, such as fossil fuels or nuclear power. Traditional solar photovoltaic (PV) systems used for electricity generation do not require water during operation. They rely solely on sunlight, converting it into electricity through the movement of electrons in solar cells. The absence of water usage in solar PV systems is beneficial, especially in regions facing water scarcity or drought conditions.
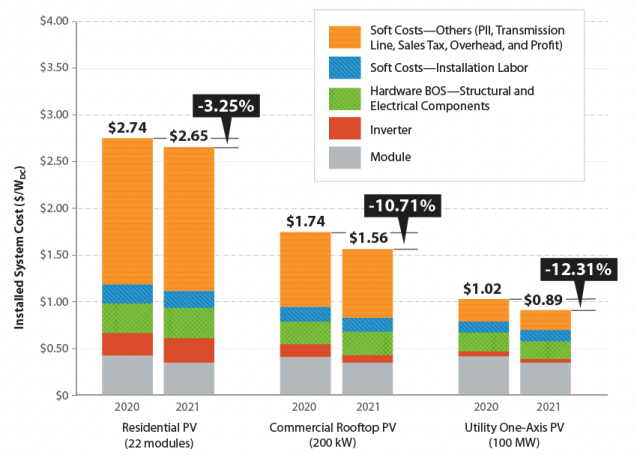
However, it’s important to note that water is still used in certain stages of the solar energy production process. The manufacturing of solar panels and related components, such as silicon wafers and metals, requires water. Additionally, some concentrated solar power (CSP) systems, which use mirrors to concentrate sunlight and generate heat for electricity production, may require water for cooling purposes. The water usage in these stages is relatively minimal compared to other energy sources, but it’s crucial to consider the entire life cycle of solar energy systems.
Despite the water usage in manufacturing and cooling, solar energy remains a much more water-efficient option compared to conventional energy sources. The minimal water requirements contribute to the overall sustainability and environmental benefits of solar energy.
Impact on Water Resources
The water impact of solar energy primarily lies in its potential competition for water resources with other sectors. As mentioned earlier, the water usage in solar energy manufacturing and cooling is relatively minimal. However, the production of solar panels and components may require high-quality or purified water, which can affect local water availability in certain regions.
Furthermore, the deployment of large-scale solar farms or CSP systems that utilize water for cooling can have localized impacts on water resources. These systems may draw water from nearby sources, such as rivers or aquifers, for cooling purposes. If not managed properly, this can lead to water depletion or alter the natural flow of water bodies, impacting ecosystems and local communities that rely on those water sources for their water supply.
However, it is essential to highlight that these potential impacts can be mitigated through various measures. For instance, the use of dry cooling technologies instead of water-based cooling systems can significantly reduce the water requirements of CSP plants. Additionally, proper water management practices and regulations can ensure that the water used in solar energy production does not cause significant harm to local water resources.
Alternatives to Traditional Solar Energy: Minimizing Water Usage
While solar energy itself is relatively water-efficient, there are alternative technologies and approaches that further minimize water usage. These innovations aim to address the potential water impact of solar energy and enhance its sustainability. Let’s explore some of these alternatives:
- Solar PV with Water-Saving Measures: Integrating water-saving measures in the manufacturing process of solar PV panels can reduce the water requirements even further. For example, the adoption of advanced recycling systems and water-efficient manufacturing processes can minimize water usage.
- Dry Cooling Technologies: As mentioned earlier, the use of dry cooling technologies instead of water-based cooling systems in CSP plants significantly reduces water consumption. By utilizing air or alternative coolants, these technologies eliminate or greatly reduce the need for water in the cooling process.
- Floating Solar Farms: Floatovoltaics, a concept where solar panels are installed on water bodies, can be an innovative solution to reduce land usage and minimize water requirements. These floating solar farms also help in reducing evaporation from reservoirs or lakes, further conserving water resources.
By implementing these alternatives and technologies, the water footprint of solar energy can be further reduced, making it an even more sustainable option for power generation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, solar energy itself requires minimal amounts of water for electricity generation. The water usage primarily lies in the manufacturing of solar panels and cooling processes, but it is significantly lower compared to traditional energy sources. While there are potential impacts on water resources, proper water management practices and the adoption of water-saving measures can mitigate these effects. Additionally, alternative technologies like dry cooling and floating solar farms offer innovative solutions to minimize water usage in solar energy systems. Overall, solar energy stands out as a water-efficient and sustainable option for power generation.
Key Takeaways: Does Solar Energy Require Water?
- Solar energy does not require water to generate electricity.
- Solar panels use sunlight to convert it into electricity without the need for water.
- This makes solar energy a sustainable and eco-friendly source of power.
- Unlike fossil fuel power plants, solar power does not produce harmful emissions or consume large amounts of water.
- Although solar panels require regular cleaning to maintain efficiency, they do not need water for their operation.
Frequently Asked Questions
As we explore the topic of solar energy, many questions may arise. Here are some common inquiries related to solar energy and its water requirements.
Why is solar energy considered a water-friendly alternative?
Solar energy is often hailed as a water-friendly alternative because it doesn’t require large quantities of water to generate electricity. Unlike other power sources, like coal or natural gas, solar panels harness energy from the sun without needing water to generate heat or cool down machinery. This means that solar power plants minimize water usage and reduce strain on our water resources.
With the increasing scarcity of water in many regions around the world, it becomes crucial to adopt solutions that conserve water. Solar energy provides a sustainable and environmentally friendly option that alleviates the burden on water supplies.
Does the manufacturing of solar panels use a lot of water?
The manufacture of solar panels does involve some water usage, but it is significantly lower compared to other forms of energy generation. The water footprint of solar panel manufacturing is relatively small, primarily due to the fact that the production process relies on clean and dry manufacturing techniques. These techniques eliminate the need for water-intensive cooling processes or the extraction of water-intensive raw materials.
Furthermore, technological advancements in solar panel manufacturing have led to a reduction in water usage. Companies are continuously finding ways to optimize manufacturing processes, reducing their water footprint even further. As a result, the overall water consumption associated with solar panel production is relatively minimal when compared to the benefits of renewable energy.
Is water used for cleaning solar panels?
Water is occasionally used to clean solar panels, but the frequency and amount required are relatively low. Solar panels are designed to be self-cleaning to some extent, as they are usually angled to allow dirt and debris to slide off when it rains. However, in areas with limited rainfall or heavy pollution levels, occasional cleaning may be necessary to ensure optimal efficiency.
When cleaning is required, there are water-efficient methods available to minimize water usage. Some cleaning techniques involve the use of specialized brushes or robotic systems that require only small amounts of water. These methods help conserve water while maintaining the effectiveness of the solar panels.
Can solar panels be used in arid regions with water scarcity?
Solar panels are indeed a viable energy solution for arid regions with water scarcity. In fact, solar energy can play a crucial role in helping these regions address their water challenges. Solar-powered pumps, for example, can be used to extract groundwater for irrigation or to power desalination plants that convert seawater into freshwater.
Additionally, since solar energy does not require water for its operation, it can alleviate the strain on already stretched water supplies in arid regions. By adopting solar power, these areas can reduce the dependency on traditional water-intensive power sources, enhancing water conservation efforts and promoting water sustainability.
Are there any water-related environmental concerns associated with solar energy?
While solar energy itself has minimal water-related environmental concerns, there are some indirect considerations to keep in mind. The manufacturing process of solar panels involves the usage of certain chemicals and materials that can be harmful if not handled properly. It is essential to handle and dispose of these materials responsibly to prevent contamination of water sources.
Moreover, when large-scale solar projects are located in sensitive ecosystems, such as desert areas or near bodies of water, there can be potential impacts on local flora and fauna. Proper planning and environmental assessments should be conducted to mitigate any adverse effects and ensure minimal disturbance to the surrounding water ecosystems.
Summary
Solar energy is a great renewable source that doesn’t need water to generate electricity. It uses sunlight to produce power, which means it’s good for the environment and doesn’t put a strain on water resources. Solar panels, the devices that capture sunlight, can be installed in many places and can provide electricity for homes and businesses. So, solar energy is a water-friendly option for clean and sustainable power.
However, it’s important to keep in mind that solar panels do need water for cleaning and maintenance. Regular cleaning helps them work efficiently, and some cleaning methods use water. But overall, solar energy is a smart choice because it doesn’t require any significant amount of water for its operation.